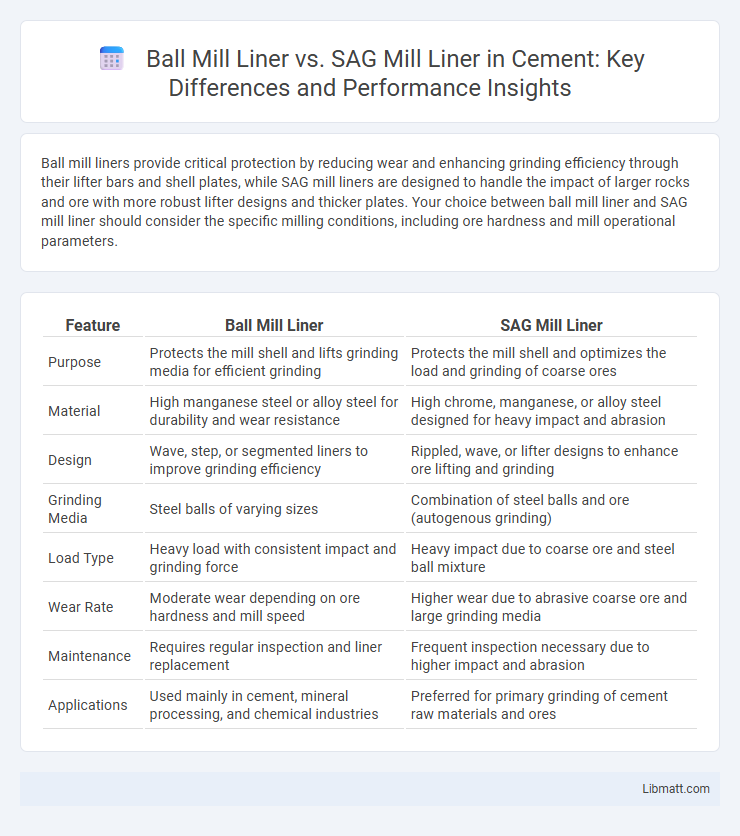
Ball mill liners provide critical protection by reducing wear and enhancing grinding efficiency through their lifter bars and shell plates, while SAG mill liners are designed to handle the impact of larger rocks and ore with more robust lifter designs and thicker plates. Your choice between ball mill liner and SAG mill liner should consider the specific milling conditions, including ore hardness and mill operational parameters.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ball Mill Liner | SAG Mill Liner |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protects the mill shell and lifts grinding media for efficient grinding | Protects the mill shell and optimizes the load and grinding of coarse ores |
| Material | High manganese steel or alloy steel for durability and wear resistance | High chrome, manganese, or alloy steel designed for heavy impact and abrasion |
| Design | Wave, step, or segmented liners to improve grinding efficiency | Rippled, wave, or lifter designs to enhance ore lifting and grinding |
| Grinding Media | Steel balls of varying sizes | Combination of steel balls and ore (autogenous grinding) |
| Load Type | Heavy load with consistent impact and grinding force | Heavy impact due to coarse ore and steel ball mixture |
| Wear Rate | Moderate wear depending on ore hardness and mill speed | Higher wear due to abrasive coarse ore and large grinding media |
| Maintenance | Requires regular inspection and liner replacement | Frequent inspection necessary due to higher impact and abrasion |
| Applications | Used mainly in cement, mineral processing, and chemical industries | Preferred for primary grinding of cement raw materials and ores |
Introduction: Understanding Ball Mill and SAG Mill Liners
Ball mill liners and SAG mill liners serve crucial roles in protecting the mill shell and enhancing grinding efficiency by extending the lifespan of the grinding equipment. Ball mill liners typically feature lifter bars or wave plating designed to lift and cascade grinding media, optimizing the grinding process in the ball mills. SAG mill liners, often composed of higher-chrome alloy materials, focus on withstanding impact and abrasion by large ore chunks, thus providing durability in semi-autogenous grinding operations.
Key Functions of Mill Liners
Ball mill liners protect the mill shell from wear and impact while enhancing grinding efficiency by lifting and cascading the charge for better material interaction. SAG mill liners are designed to withstand more severe impact and abrasion, providing critical protection and optimizing grinding through strategic lifter design that handles both rock and ore particles. Both liners play essential roles in prolonging equipment life, improving grinding performance, and reducing maintenance downtime in mineral processing.
Material Composition: Ball Mill vs SAG Mill Liners
Ball mill liners are typically made from high-chrome white iron, manganese steel, or rubber composites, designed to withstand heavy impact and abrasive wear during grinding. SAG mill liners are commonly fabricated from high-manganese steel or alloyed steels with added chromium, providing enhanced resistance to impact and abrasion caused by larger ore chunks and grinding media. The material composition of SAG mill liners prioritizes toughness and wear resistance to accommodate the higher stress and larger feed size compared to ball mill liners.
Design Differences Between Ball and SAG Mill Liners
Ball mill liners are designed with deep grooves and thicker profiles to protect the shell from heavy impact and abrasion, ensuring optimal grinding efficiency by lifting and cascading the grinding media. SAG mill liners feature a more complex design with lifter bars and embossed plates that enhance the ore lifting process, promoting effective fragmentation and reducing wear from coarse ore handling. Your choice between ball mill liners and SAG mill liners depends on the specific grinding process demands and material characteristics, as their structural differences directly influence performance and liner longevity.
Wear Life and Durability Comparison
Ball mill liners generally offer longer wear life due to their robust design and thick manganese steel construction, which resists abrasion and impact during continuous grinding. SAG mill liners, while engineered for durability under variable load conditions, typically exhibit faster wear because of the larger feed size and more aggressive tumbling action. Optimizing liner material composition and design tailored to specific mill conditions significantly enhances durability and reduces downtime in both mill types.
Impact on Grinding Efficiency
Ball mill liners and SAG mill liners play a crucial role in grinding efficiency by influencing the motion and impact of the charge inside the mills. Ball mill liners typically provide a higher impact force that enhances fine grinding, leading to better particle size reduction and energy utilization. Your choice between these liners can significantly affect the throughput and overall performance of the grinding circuit by optimizing the grinding media interaction and wear resistance.
Maintenance Requirements and Downtime
Ball mill liners typically require more frequent maintenance due to higher wear rates from continuous impact and abrasion, leading to increased downtime for inspection and replacement compared to SAG mill liners. SAG mill liners, designed for a combination of impact and abrasion, generally have longer service life and lower maintenance frequency but necessitate careful monitoring to prevent unexpected failures during grinding operations. Optimizing liner material selection and implementing predictive maintenance strategies can significantly reduce downtime and improve overall mill efficiency for both ball and SAG mills.
Cost Considerations: Ball Mill vs SAG Mill Liners
Ball mill liners generally have a lower initial cost compared to SAG mill liners due to simpler design and smaller size. SAG mill liners require more robust materials and complex engineering to handle larger impacts and abrasive forces, leading to higher expenses. The lifecycle cost of SAG mill liners can be justified by increased durability and reduced maintenance frequency in heavy-duty grinding applications.
Performance in Various Mining Applications
Ball mill liners and SAG mill liners differ significantly in performance across mining applications due to their design and material composition; ball mill liners excel in grinding fine particles with consistent wear resistance, while SAG mill liners are optimized for handling larger rocks and higher impact forces, offering superior durability and adaptability in abrasive conditions. The choice between these liners directly impacts grinding efficiency, with SAG liners providing better performance in primary crushing and coarse grinding, whereas ball mill liners are preferred for secondary grinding stages where finer particle reduction is needed. Understanding these distinctions helps you select the appropriate liner to maximize equipment lifespan, reduce downtime, and improve overall ore processing efficiency.
Choosing the Right Liner for Your Mill
Selecting the right liner between a ball mill liner and a SAG mill liner depends on factors such as mill type, ore hardness, and grinding process. Ball mill liners typically offer higher abrasion resistance and are suited for fine grinding, while SAG mill liners are designed for impact resistance in coarse grinding applications. Optimizing liner material and design enhances mill performance, reduces maintenance costs, and extends liner lifespan.
Ball Mill Liner vs SAG Mill Liner Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com