Hydration heat influences the setting time of cement by accelerating chemical reactions, causing quicker hardening and strength gain. Understanding the balance between hydration heat and setting time helps you optimize concrete performance for your specific construction needs.
Table of Comparison
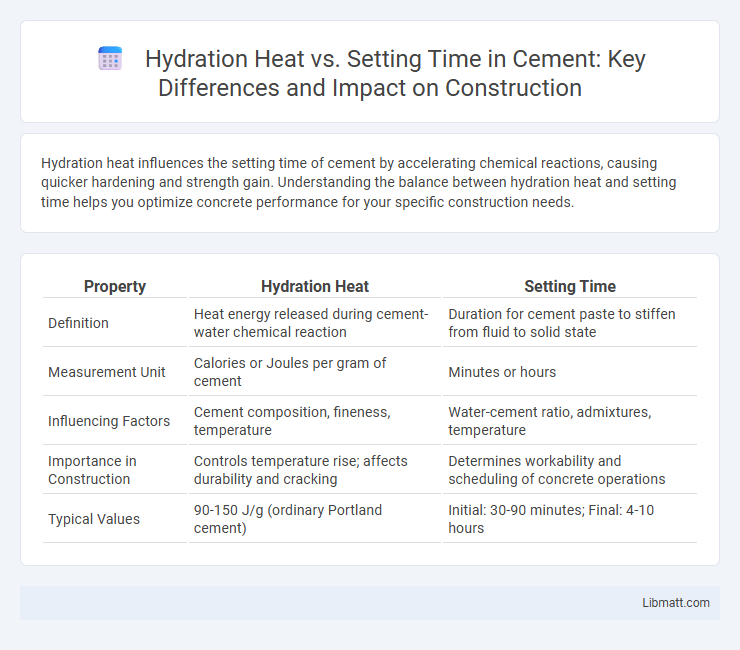
| Property | Hydration Heat | Setting Time |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Heat energy released during cement-water chemical reaction | Duration for cement paste to stiffen from fluid to solid state |
| Measurement Unit | Calories or Joules per gram of cement | Minutes or hours |
| Influencing Factors | Cement composition, fineness, temperature | Water-cement ratio, admixtures, temperature |
| Importance in Construction | Controls temperature rise; affects durability and cracking | Determines workability and scheduling of concrete operations |
| Typical Values | 90-150 J/g (ordinary Portland cement) | Initial: 30-90 minutes; Final: 4-10 hours |
Understanding Hydration Heat in Cement
Hydration heat in cement refers to the exothermic reaction when water combines with cement compounds, releasing thermal energy that influences the rate of setting and hardening. High hydration heat accelerates the setting time, potentially causing early cracking due to thermal stresses in large concrete pours. Controlling hydration heat through cement composition and additives optimizes setting time and ensures structural integrity.
Defining Setting Time in Concrete
Setting time in concrete defines the duration required for the mix to transition from a fluid to a solid state, marking the initial phase when it gains sufficient stiffness to resist deformation. This period directly influences hydration heat, as the chemical reactions between cement and water release heat, accelerating or delaying the setting process. Understanding your concrete's setting time is crucial for scheduling construction activities and ensuring optimal strength development.
Factors Influencing Hydration Heat
Hydration heat is influenced by factors such as cement composition, particle size, temperature, and water-to-cement ratio, which directly affect the rate of chemical reactions during curing. Higher temperatures and finer particles increase hydration heat, accelerating setting time and potentially impacting concrete strength. Understanding these variables helps you control the balance between hydration heat and setting time for optimal concrete performance.
Variables Affecting Setting Time
Variables affecting setting time include temperature, water-cement ratio, and admixture type, all influencing hydration heat evolution. Higher temperatures accelerate hydration heat, thus shortening the setting time, while lower temperatures slow the reaction, extending it. Your control over these factors can help optimize concrete performance for specific construction needs.
Relationship Between Hydration Heat and Setting Time
The relationship between hydration heat and setting time is crucial in concrete curing processes, as higher hydration heat typically signals faster chemical reactions that reduce setting time. Excessive heat generation during hydration can lead to rapid hardening, impacting workability and potentially causing thermal cracking. Understanding this interaction helps you optimize mix design for desired setting times while controlling temperature to ensure structural integrity and durability.
Impact on Concrete Strength and Durability
Hydration heat influences concrete strength by accelerating the chemical reactions, increasing early-age strength but potentially causing thermal cracking that compromises durability. Setting time impacts the workability and finishing processes, where faster setting can lead to reduced strength development, and slower setting may improve long-term durability by enhancing microstructure formation. Balancing hydration heat and setting time is essential for optimizing concrete strength and ensuring long-term durability in construction applications.
Measurement Methods for Hydration Heat
Hydration heat measurement employs calorimetry techniques such as isothermal and semi-adiabatic calorimeters to monitor the heat evolution during cement hydration. These methods provide precise data on heat flow and cumulative heat, essential for understanding the hydration kinetics and setting time influences. Accurate thermal profiling helps optimize concrete mix designs for improved performance and durability.
Techniques to Control Setting Time
Controlling the setting time of concrete involves techniques such as adjusting the water-to-cement ratio, using chemical admixtures like retarders or accelerators, and regulating curing temperature to influence hydration heat. Low heat cement formulations and supplementary cementitious materials like fly ash or slag reduce peak hydration temperatures, thereby extending setting time. Precise manipulation of these factors optimizes structural performance and durability by aligning hydration heat evolution with project timing requirements.
Practical Implications in Construction
Hydration heat directly influences setting time by accelerating or decelerating the cement curing process, impacting formwork removal and construction scheduling. High hydration heat can lead to thermal cracking risks in large concrete structures, necessitating careful temperature control to ensure durability. Optimizing the balance between hydration heat and setting time is critical for structural integrity and efficient project timelines in concrete construction.
Innovations in Managing Hydration Heat and Setting Time
Innovations in managing hydration heat and setting time focus on advanced admixtures like superplasticizers and retarders that optimize curing processes for concrete. Utilizing nanomaterials and phase change materials helps control internal temperature fluctuations, reducing thermal cracking risks during hydration. Your construction projects benefit from improved durability and faster strength development through these cutting-edge technologies.
Hydration heat vs Setting time Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com