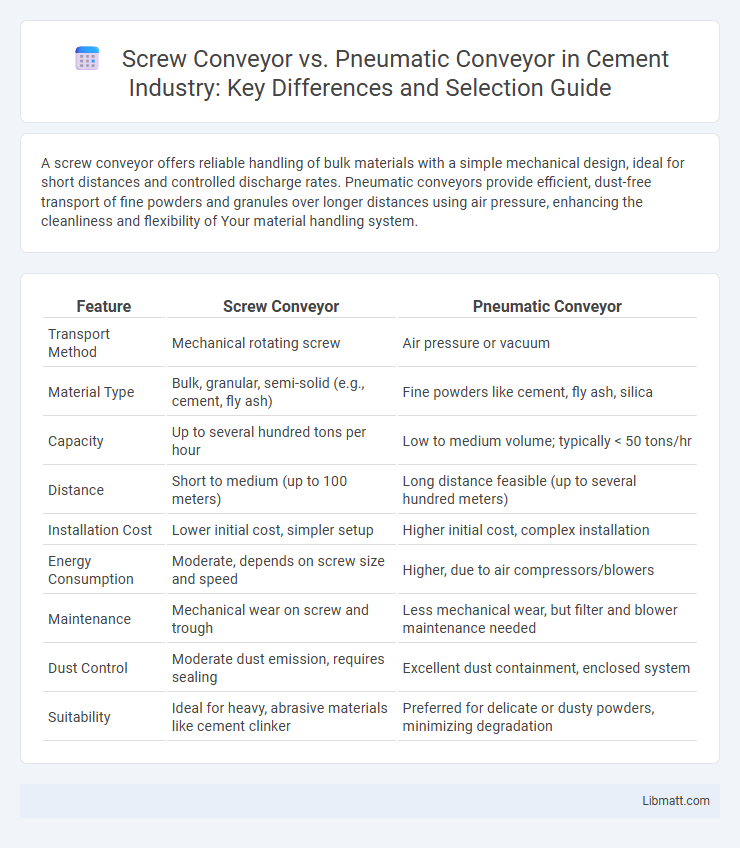
A screw conveyor offers reliable handling of bulk materials with a simple mechanical design, ideal for short distances and controlled discharge rates. Pneumatic conveyors provide efficient, dust-free transport of fine powders and granules over longer distances using air pressure, enhancing the cleanliness and flexibility of Your material handling system.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Screw Conveyor | Pneumatic Conveyor |
|---|---|---|
| Transport Method | Mechanical rotating screw | Air pressure or vacuum |
| Material Type | Bulk, granular, semi-solid (e.g., cement, fly ash) | Fine powders like cement, fly ash, silica |
| Capacity | Up to several hundred tons per hour | Low to medium volume; typically < 50 tons/hr |
| Distance | Short to medium (up to 100 meters) | Long distance feasible (up to several hundred meters) |
| Installation Cost | Lower initial cost, simpler setup | Higher initial cost, complex installation |
| Energy Consumption | Moderate, depends on screw size and speed | Higher, due to air compressors/blowers |
| Maintenance | Mechanical wear on screw and trough | Less mechanical wear, but filter and blower maintenance needed |
| Dust Control | Moderate dust emission, requires sealing | Excellent dust containment, enclosed system |
| Suitability | Ideal for heavy, abrasive materials like cement clinker | Preferred for delicate or dusty powders, minimizing degradation |
Introduction to Bulk Material Handling Solutions
Screw conveyors and pneumatic conveyors are essential bulk material handling solutions designed to transport powders, granules, and other bulk solids efficiently in various industries. Screw conveyors use a rotating helical screw blade within a tube to move materials, offering precise control and suitability for short-distance, heavy, or abrasive materials. Pneumatic conveyors rely on air pressure or vacuum to propel materials through pipelines, providing flexibility in routing and minimizing contamination risks, making them ideal for fragile or hazardous substances.
Overview of Screw Conveyors
Screw conveyors consist of a helical screw blade rotating inside a tube or trough to transport bulk materials efficiently. They are highly effective for moving semi-solid materials such as grains, food waste, and aggregates over short distances with consistent flow rates. Their robust design allows operation in harsh environments and easy customization for varying material densities and conveyor lengths.
Overview of Pneumatic Conveyors
Pneumatic conveyors use air pressure or vacuum to transport bulk materials through pipelines efficiently and with minimal dust emission, making them ideal for handling delicate or abrasive powders in industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals. These systems offer high-speed material transfer and flexible routing options, reducing contamination risk and maintenance compared to traditional mechanical conveyors. You can optimize your material handling process by selecting pneumatic conveyors for precise, enclosed transport solutions that maintain product integrity.
Key Differences Between Screw and Pneumatic Conveyors
Screw conveyors use a rotating helical screw blade to move bulk materials along a trough, making them ideal for short distances and controlled material flow. Pneumatic conveyors rely on air pressure or vacuum to transport materials through pipelines at high speeds, suitable for long distances and complex routing. Key differences include energy efficiency, with screw conveyors consuming less power, and material handling versatility, where pneumatic systems excel in moving fine, powdery, or abrasive materials without contamination.
Material Compatibility and Handling Capabilities
Screw conveyors excel in handling abrasive, granular, and semi-solid materials such as grains, powders, and sludge, offering precise control and minimal material degradation during transport. Pneumatic conveyors are ideal for fine, dusty, or lightweight materials like flour, plastic pellets, and chemicals, using air pressure to move materials through enclosed pipelines, which reduces contamination risks. Your choice depends on material characteristics and handling requirements, with screw conveyors suited for dense, coarse materials and pneumatic systems optimal for delicate, dust-prone substances.
Energy Efficiency and Operating Costs Comparison
Screw conveyors typically consume less energy for short-distance, moderate-capacity material handling due to mechanical power delivery, resulting in lower operating costs. Pneumatic conveyors require higher energy input to generate compressed air or vacuum pressure, increasing electricity consumption and maintenance expenses for air filtration systems. Efficiency advantages of screw conveyors diminish over long transport distances or complex routing, where pneumatic systems can reduce material degradation and labor costs despite higher energy usage.
Installation, Maintenance, and Space Requirements
Screw conveyors require straightforward installation with fixed structures and moderate space, making them ideal for compact setups, while pneumatic conveyors need complex ductwork and more vertical or horizontal space to operate efficiently. Maintenance of screw conveyors involves routine inspection of screw flights and bearings, which is generally simpler compared to pneumatic systems that demand careful monitoring of air pressure, filters, and blowers. Your choice depends on available space and ease of upkeep, with screw conveyors favoring simplicity and pneumatic conveyors offering flexible routing but higher maintenance demands.
Safety Considerations for Both Systems
Screw conveyors reduce dust exposure and minimize spillage, lowering the risk of fire and respiratory hazards, while their enclosed design safeguards workers from moving parts. Pneumatic conveyors require careful management of pressure levels and static electricity to prevent explosions, with proper filtration systems essential to avoid airborne particle hazards. Your choice should factor in these safety considerations, including maintenance protocols and system enclosure, to ensure a secure working environment.
Application Scenarios: When to Choose Each Conveyor
Screw conveyors excel in transporting granular or semi-solid materials such as grains, cement, and food products over short to medium distances within controlled environments, making them ideal for industries like agriculture, construction, and food processing. Pneumatic conveyors are preferred for moving powdered, fine, or fragile materials like flour, plastic pellets, and pharmaceuticals over longer distances or complex pathways, especially when maintaining material cleanliness and minimizing contamination is critical. Choosing between the two depends on factors like material characteristics, required conveyance distance, system complexity, and the need for dust control or energy efficiency.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Conveyor for Your Needs
Choosing between a screw conveyor and a pneumatic conveyor depends on your material type, handling environment, and system maintenance preferences. Screw conveyors are ideal for handling abrasive or semi-solid materials, offering a cost-effective, low-maintenance solution for short-distance transport. Pneumatic conveyors provide flexibility in conveying fine, dry powders over longer distances with enclosed systems that reduce contamination and dust.
Screw Conveyor vs Pneumatic Conveyor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com