Raw meal proportioning ensures precise measurement of each ingredient to maintain consistent chemical composition, while blending homogenizes the mixture to achieve uniformity and optimize kiln performance. Your control over both processes is crucial for producing high-quality clinker and improving overall cement production efficiency.
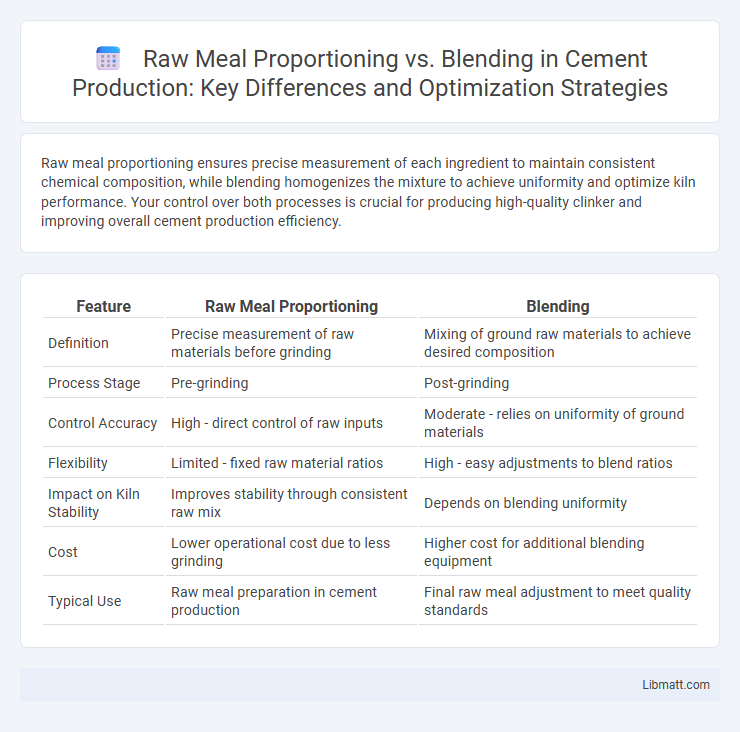
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Raw Meal Proportioning | Blending |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Precise measurement of raw materials before grinding | Mixing of ground raw materials to achieve desired composition |
| Process Stage | Pre-grinding | Post-grinding |
| Control Accuracy | High - direct control of raw inputs | Moderate - relies on uniformity of ground materials |
| Flexibility | Limited - fixed raw material ratios | High - easy adjustments to blend ratios |
| Impact on Kiln Stability | Improves stability through consistent raw mix | Depends on blending uniformity |
| Cost | Lower operational cost due to less grinding | Higher cost for additional blending equipment |
| Typical Use | Raw meal preparation in cement production | Final raw meal adjustment to meet quality standards |
Introduction to Raw Meal Proportioning and Blending
Raw meal proportioning involves accurately measuring and combining raw materials to ensure the appropriate chemical composition before the kiln process, optimizing cement quality and energy efficiency. Blending focuses on homogenizing these materials to create a consistent mixture, reducing variability and improving the stability of the raw meal. Your control over both processes directly impacts the performance and cost-effectiveness of cement production.
Fundamentals of Raw Material Proportioning
Raw meal proportioning is the precise measurement and control of raw materials like limestone, clay, and silica to ensure consistent chemical composition in cement production. Accurate proportioning relies on real-time data from sampling and chemical analysis to maintain the desired balance of oxides such as CaO, SiO2, and Al2O3. This process minimizes variability before blending, optimizing kiln performance and clinker quality by reducing energy consumption and emissions.
Principles of Raw Meal Blending in Cement Manufacturing
Raw meal blending in cement manufacturing ensures consistent chemical composition by combining different raw materials to achieve the desired mix of calcium, silica, alumina, and iron oxides. Precision in raw meal proportioning controls the homogeneity and reactivity of the mixture, directly impacting clinker quality and kiln performance. Advanced blending techniques use real-time chemical analysis and automated control systems to optimize raw mix uniformity, reduce fuel consumption, and enhance overall cement production efficiency.
Key Differences Between Proportioning and Blending
Raw meal proportioning controls the precise quantity of each raw material entering the kiln to maintain chemical consistency, using weigh feeders for accurate measurement. Blending involves mixing these raw materials homogeneously to achieve uniform composition, often using mechanical mixers or blending beds. The key difference is proportioning targets exact feed rates to control composition, while blending ensures thorough mixing to prevent chemical variability in the final raw meal.
Equipment Used for Proportioning and Blending
Raw meal proportioning utilizes weigh feeders and belt scales to precisely measure individual raw materials based on preset recipes, ensuring consistent chemical composition before mixing. Blending equipment typically involves rotary drum blenders, pug mills, or ribbon blenders, designed to homogenize the combined raw meal to achieve uniformity in particle size and chemical distribution. Advanced automated control systems integrate both proportioning and blending equipment to optimize material flow and maintain stringent quality standards in cement production.
Impact on Product Quality and Consistency
Raw meal proportioning ensures accurate measurement of each component, directly influencing the uniformity of chemical composition and enhancing product quality. Blending homogenizes the mixed materials, reducing variability and ensuring consistent raw meal characteristics, which leads to stable kiln operation and improved final product performance. Combining precise proportioning with effective blending minimizes fluctuations, resulting in superior clinker quality and consistent cement properties.
Process Control and Automation Technologies
Raw meal proportioning involves precise measurement of individual raw materials for cement production, using automated weighing systems and real-time sensors to ensure consistent chemical composition. Blending combines these measured materials into a uniform mixture, utilizing advanced programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and computerized process control systems for optimized homogenization. Integration of automation technologies in both stages enhances process control, reduces human error, and improves overall production efficiency and quality consistency.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
Raw meal proportioning optimizes the precise ratio of raw materials, reducing unnecessary grinding and improving kiln feed consistency, which directly enhances energy efficiency. Blending, while ensuring homogeneity, can mask variations that lead to overgrinding and higher thermal consumption. Prioritizing proportioning minimizes energy use by stabilizing raw meal chemistry, reducing fuel consumption in the clinker production process.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Raw meal proportioning faces challenges such as inconsistent feedstock moisture and variable chemical composition, leading to imbalanced kiln feed and production inefficiencies. Blending techniques address these issues by homogenizing raw materials, stabilizing chemical properties like lime saturation factor (LSF) and silica ratio, which improves clinker quality and reduces fuel consumption. Implementing real-time monitoring and automated control systems enhances precision in both proportioning and blending processes, minimizing operational disruptions and optimizing cement manufacturing.
Future Trends in Raw Meal Preparation
Future trends in raw meal preparation emphasize advanced sensor technology and AI-driven controls to optimize raw meal proportioning and blending for cement production. Innovations in real-time chemical composition analysis enable precise adjustments, reducing waste and improving clinker quality. Your operations can benefit from these technologies through enhanced process efficiency, sustainability, and cost savings.
Raw Meal Proportioning vs Blending Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com