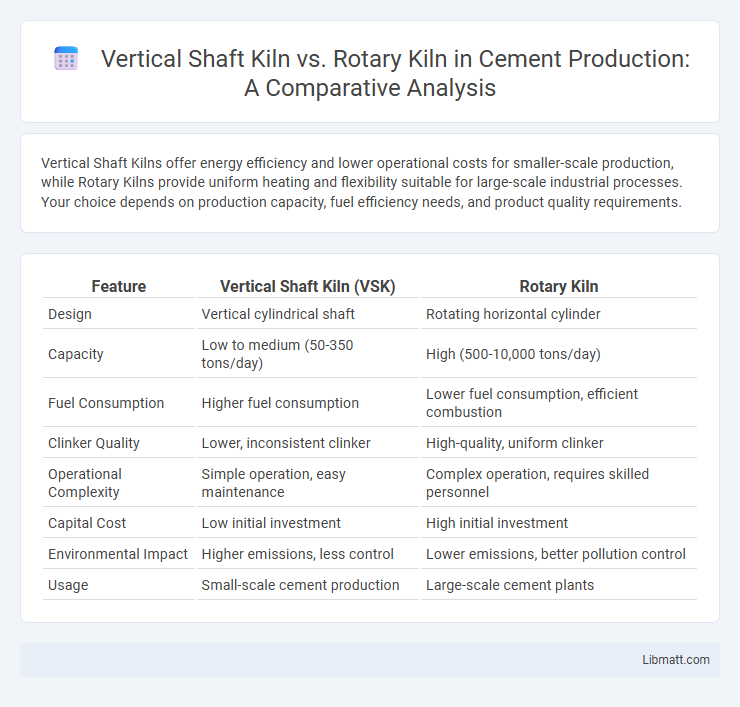
Vertical Shaft Kilns offer energy efficiency and lower operational costs for smaller-scale production, while Rotary Kilns provide uniform heating and flexibility suitable for large-scale industrial processes. Your choice depends on production capacity, fuel efficiency needs, and product quality requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vertical Shaft Kiln (VSK) | Rotary Kiln |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Vertical cylindrical shaft | Rotating horizontal cylinder |
| Capacity | Low to medium (50-350 tons/day) | High (500-10,000 tons/day) |
| Fuel Consumption | Higher fuel consumption | Lower fuel consumption, efficient combustion |
| Clinker Quality | Lower, inconsistent clinker | High-quality, uniform clinker |
| Operational Complexity | Simple operation, easy maintenance | Complex operation, requires skilled personnel |
| Capital Cost | Low initial investment | High initial investment |
| Environmental Impact | Higher emissions, less control | Lower emissions, better pollution control |
| Usage | Small-scale cement production | Large-scale cement plants |
Overview of Vertical Shaft Kiln and Rotary Kiln Technologies
Vertical Shaft Kiln (VSK) technology features a vertical design where raw materials move downward by gravity through a stationary combustion zone, enabling energy-efficient cement production with lower heat consumption and reduced emissions. Rotary Kiln technology employs a rotating cylindrical vessel that ensures thorough mixing and uniform heating of raw materials, supporting high-capacity output and versatile processing of various materials in cement and other industries. Understanding these differences helps you select the technology that aligns with your production goals, operational efficiency, and environmental considerations.
Key Differences in Kiln Design and Construction
Vertical shaft kilns feature a compact, vertical design with raw materials fed from the top and clinker discharged from the bottom, promoting gravity-assisted material flow, while rotary kilns have a long, cylindrical, inclined rotating structure that transports materials through continuous rotation. Construction of vertical shaft kilns involves simpler brick lining and lower refractory requirements due to lower operating temperatures, contrasting with rotary kilns which require heavy-duty refractory lining capable of withstanding high temperatures and mechanical stress. The rotary kiln's design supports higher production capacity and better control over heating zones, whereas vertical shaft kilns operate at lower throughput with limited thermal uniformity.
Operating Principles of Vertical Shaft Kilns
Vertical Shaft Kilns operate by feeding raw material at the top, which descends through the combustion zone heated by burners surrounding the shaft, facilitating efficient heat transfer and calcination. The vertical design allows continuous counter-current flow of fuel and air, enhancing thermal efficiency and consistent product quality. This process contrasts with Rotary Kilns, where material moves horizontally in a rotating drum, making Vertical Shaft Kilns more energy-efficient for smaller-scale cement production.
Rotary Kiln Working Mechanisms Explained
Rotary kilns operate by rotating a cylindrical shell on a slight incline, allowing materials to gradually move from the feed end to the discharge end while exposed to high temperatures for calcination or sintering. The kiln's continuous rotation ensures uniform heat distribution and efficient chemical reactions during processes such as cement manufacturing or mineral processing. Understanding your rotary kiln's working mechanisms helps optimize fuel consumption, temperature control, and product quality.
Energy Efficiency Comparison: Vertical Shaft Kiln vs Rotary Kiln
Vertical Shaft Kilns typically offer higher energy efficiency compared to Rotary Kilns due to their lower fuel consumption and better heat retention, achieving energy savings of up to 30%. Rotary Kilns require continuous fuel input to maintain rotation and heat distribution, resulting in higher fuel costs and emissions. Optimizing your cement production process with a Vertical Shaft Kiln can significantly reduce energy expenditure and improve operational sustainability.
Product Quality and Output Variations
Vertical Shaft Kilns (VSK) generally produce cement with lower consistency in particle size distribution, leading to variable product quality, while Rotary Kilns deliver more uniform and higher-quality output due to continuous rotation ensuring better clinker formation. The output of VSKs is typically lower, ranging from 10 to 50 tons per day, compared to Rotary Kilns, which can handle several thousand tons per day, making them more suitable for large-scale production. Your choice between the two will impact both the consistency of the cement quality and the overall production capacity of your plant.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Vertical Shaft Kilns (VSK) typically exhibit lower energy consumption and reduced CO2 emissions compared to Rotary Kilns, making them more environmentally friendly for small to medium-scale cement production. Rotary Kilns, while versatile and suited for large-scale operations, generally have higher fuel usage and greater greenhouse gas output due to continuous rotary motion and higher thermal inertia. Your choice between VSK and Rotary Kiln significantly influences emission levels and resource efficiency, critical factors in environmental impact assessment.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Operational Expenses
Vertical Shaft Kilns (VSK) typically have lower installation costs due to their simpler structure and smaller footprint compared to Rotary Kilns, which require extensive foundations and support systems. Operational expenses for VSKs tend to be reduced because of lower fuel consumption and minimized maintenance requirements, whereas Rotary Kilns incur higher energy costs and more frequent maintenance due to their complex rotating mechanism. The overall cost-effectiveness of VSKs makes them suitable for small to medium-scale cement production, while Rotary Kilns are preferred for large-scale operations despite their higher installation and operational costs.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifespan
Vertical Shaft Kilns have lower maintenance requirements due to their simpler design and fewer moving parts, enabling cost-effective operation over time. Rotary Kilns demand more frequent and intensive maintenance because of their complex mechanical components and continuous rotation, which can lead to higher wear and tear. Your choice between these kiln types should consider the trade-off between maintenance intensity and expected lifespan, with Rotary Kilns generally offering longer operational life under proper upkeep.
Choosing the Right Kiln: Application Suitability
Vertical shaft kilns excel in small to medium-scale production requiring consistent thermal efficiency and lower fuel consumption, making them ideal for industries like lime or refractory manufacturing. Rotary kilns provide greater versatility and capacity, handling larger volumes and more diverse materials such as cement, minerals, and chemicals with precise temperature control. Your choice depends on production scale, material type, and energy considerations to ensure optimal application suitability.
Vertical Shaft Kiln vs Rotary Kiln Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com