White cement offers a bright, clean finish ideal for decorative projects and can be easily tinted to achieve various colors, while colored cement is pre-mixed with pigments for consistent, uniform hues directly in the material. You can choose white cement for flexibility in color customization or colored cement for time-saving, vibrant applications in architectural designs.
Table of Comparison
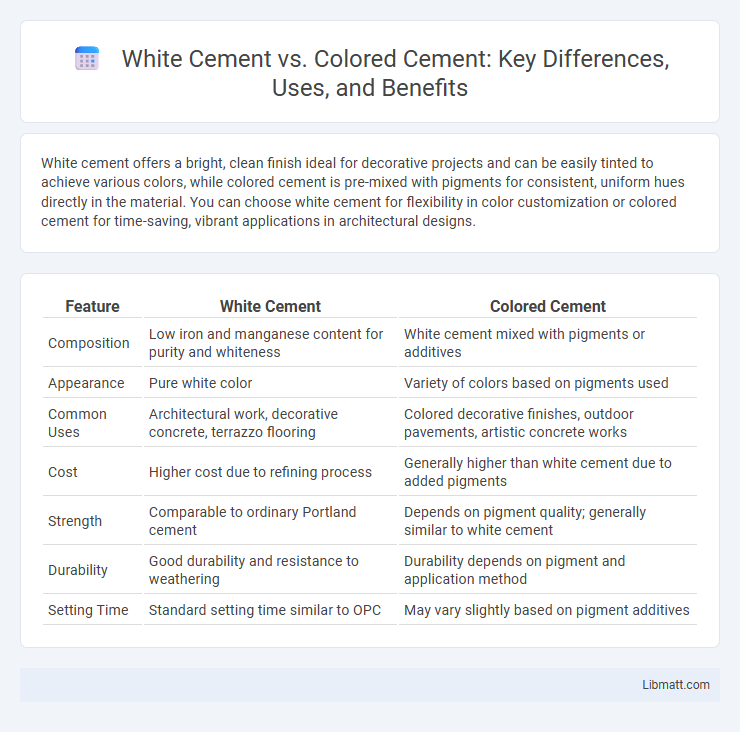
| Feature | White Cement | Colored Cement |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Low iron and manganese content for purity and whiteness | White cement mixed with pigments or additives |
| Appearance | Pure white color | Variety of colors based on pigments used |
| Common Uses | Architectural work, decorative concrete, terrazzo flooring | Colored decorative finishes, outdoor pavements, artistic concrete works |
| Cost | Higher cost due to refining process | Generally higher than white cement due to added pigments |
| Strength | Comparable to ordinary Portland cement | Depends on pigment quality; generally similar to white cement |
| Durability | Good durability and resistance to weathering | Durability depends on pigment and application method |
| Setting Time | Standard setting time similar to OPC | May vary slightly based on pigment additives |
Introduction to White and Colored Cement
White cement offers a bright, pure white color ideal for decorative and architectural projects requiring a clean finish. Colored cement incorporates pigments to produce a wide range of hues, allowing customization for landscaping, flooring, and artistic applications. Your choice between white and colored cement depends on the desired aesthetic effect and project requirements, balancing color intensity with structural performance.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
White cement is produced using raw materials with low iron and manganese content, such as kaolin and limestone, and undergoes a precise calcination process at controlled kiln temperatures to maintain its color integrity. Colored cement incorporates pigments like iron oxide or chromium oxide into the white cement base or grey cement, carefully balancing pigment concentration to achieve consistent hues without compromising strength. Manufacturing colored cement requires meticulous pigment dispersion and additional grinding stages to ensure uniform color distribution and optimal bonding properties.
Key Properties and Characteristics
White cement features a pure white color due to low iron and manganese content, offering high aesthetic value and superior brightness for architectural finishes. Colored cement is produced by adding mineral pigments to white or gray cement, providing a range of vibrant colors while maintaining similar mechanical strength and durability. Both types exhibit good workability and impermeability, but colored cement allows for customized visual effects without compromising structural integrity.
Aesthetic Applications and Visual Impact
White cement offers a clean, bright base ideal for aesthetic applications requiring vivid, true color reproduction and a smooth, refined finish. Colored cement, created by adding pigments to white or gray cement, provides versatile color options that enhance visual impact and allow you to customize surfaces for decorative architectural projects. Choosing between white and colored cement depends on the desired hue intensity, brightness, and the specific visual appeal of your construction or design work.
Durability and Performance Comparison
White cement offers superior durability in environments exposed to UV radiation and weathering due to its higher resistance to chemical attacks and lower thermal conductivity. Colored cement, while aesthetically versatile, may exhibit slightly reduced performance under extreme conditions because pigments can affect the cement matrix's strength and long-term resistance. Both types provide adequate structural integrity, but white cement generally excels in maintaining color stability and surface hardness over extended periods.
Common Uses in Construction and Design
White cement is commonly used in architectural applications, decorative facades, terrazzo flooring, and precast panels where aesthetics and brightness are crucial. Colored cement, often pigmented, is preferred for outdoor pavements, driveways, garden paths, and landscaping projects to achieve vibrant and durable color effects. Both types offer versatility, but white cement serves as a base for producing a wide range of light, pastel, and pure colors, while colored cement provides ready-made, rich hues for creative design elements in construction.
Cost and Availability Factors
White cement generally costs 20-30% more than colored cement due to the higher purity raw materials and specialized manufacturing processes involved. Colored cement availability depends on the specific pigments and regional demand, often leading to limited stock compared to the more widely produced white cement. Construction projects requiring aesthetic finishes should consider both the cost premium of white cement and potential delays due to colored cement supply constraints.
Environmental Considerations
White cement typically has higher energy consumption and CO2 emissions during production compared to colored cement due to its raw material processing and higher kiln temperatures. Colored cement often incorporates pigments and additives that can include environmentally harmful substances, though advances in eco-friendly pigments are reducing this impact. You can minimize environmental impact by selecting products certified for sustainability and low emissions in both white and colored cement options.
Maintenance and Longevity
White cement offers superior resistance to weathering and fading, ensuring vibrant colors persist longer, which reduces the need for frequent maintenance. Colored cement, depending on the pigments used, may require periodic sealing or touch-ups to maintain its appearance and protect against surface degradation. Your choice between white and colored cement should consider the specific environmental exposure and desired upkeep effort for optimal longevity.
Choosing the Right Cement for Your Project
White cement offers a bright, uniform finish ideal for architectural and decorative projects requiring aesthetic appeal, while colored cement provides a wide range of hues for creative design and customization. Selecting the right cement depends on factors like desired color retention, UV resistance, and project environment, with white cement often preferred for precision and brightness, and colored cement suited for vibrant, durable surfaces in landscaping or exterior applications. Consider material cost, mixing compatibility, and long-term performance to ensure the cement aligns with your project's structural and visual goals.
White cement vs Colored cement Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com