Direct filtration removes particles by passing a fluid directly through a filter medium, effectively capturing contaminants on the filter surface, while crossflow filtration involves fluid flowing tangentially across the filter, reducing clogging and allowing continuous separation of solids from liquids. You benefit from choosing crossflow filtration when handling fluids with high solid content, ensuring longer filter life and higher efficiency.
Table of Comparison
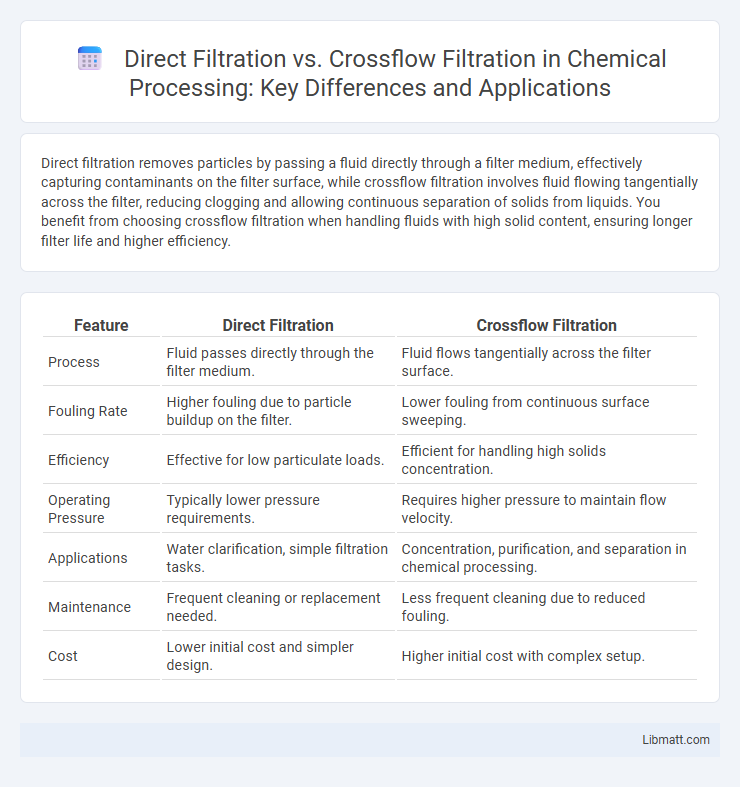
| Feature | Direct Filtration | Crossflow Filtration |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Fluid passes directly through the filter medium. | Fluid flows tangentially across the filter surface. |
| Fouling Rate | Higher fouling due to particle buildup on the filter. | Lower fouling from continuous surface sweeping. |
| Efficiency | Effective for low particulate loads. | Efficient for handling high solids concentration. |
| Operating Pressure | Typically lower pressure requirements. | Requires higher pressure to maintain flow velocity. |
| Applications | Water clarification, simple filtration tasks. | Concentration, purification, and separation in chemical processing. |
| Maintenance | Frequent cleaning or replacement needed. | Less frequent cleaning due to reduced fouling. |
| Cost | Lower initial cost and simpler design. | Higher initial cost with complex setup. |
Introduction to Filtration Methods
Direct filtration involves passing a fluid through a filter medium where particles are trapped on the surface, enabling rapid separation with relatively low energy consumption. Crossflow filtration, also known as tangential flow filtration, subjects the feed stream to flow parallel to the membrane surface, minimizing clogging and allowing continuous operation with higher filtration efficiency. These fundamental filtration methods are widely applied in industries like water treatment, food processing, and biotechnology for efficient particle and solute separation.
What is Direct Filtration?
Direct filtration is a water treatment process where raw water passes through a filter medium without prior sedimentation or coagulation, removing suspended solids and particles directly. It is commonly used for water with low turbidity and stable quality, enabling efficient filtration with reduced operational complexity and cost. This method is advantageous in settings requiring quick water clarification but may not be suitable for highly contaminated or variable water sources.
What is Crossflow Filtration?
Crossflow filtration, also known as tangential flow filtration, involves the continuous movement of feed solution parallel to the membrane surface, allowing smaller molecules and solvents to pass through while retaining larger particles and solutes. This method reduces membrane fouling and increases filtration efficiency compared to direct filtration, which pushes feed perpendicular to the membrane, causing faster clogging. Crossflow filtration is widely used in bioprocessing, water treatment, and food industries for its ability to handle high solids content and maintain consistent permeate flux.
Key Differences Between Direct and Crossflow Filtration
Direct filtration involves passing the feed solution directly through the filter media, where suspended solids are retained on the surface, leading to rapid clogging and requiring frequent cleaning. Crossflow filtration circulates the feed tangentially across the membrane surface, minimizing buildup by continuously sweeping away retained particles, resulting in higher efficiency and longer membrane life. Your choice between these methods depends on factors like feed suspension concentration, desired filtration rate, and maintenance capabilities.
Efficiency and Performance Comparison
Direct filtration offers higher initial filtration rates due to straightforward particle retention but tends to clog quickly, reducing long-term efficiency. Crossflow filtration maintains consistent performance by continuously sweeping the membrane surface, minimizing fouling and extending operational lifespan. Your choice depends on balancing immediate throughput with sustained filtration efficiency for optimal process outcomes.
Applications of Direct Filtration
Direct filtration is widely utilized in water treatment processes such as surface water purification, where suspended solids are removed efficiently without prior sedimentation. It is commonly applied in municipal water plants to treat relatively low-turbidity waters, enabling rapid processing with simpler equipment. Industries like food and beverage and pharmaceuticals also employ direct filtration for clarifying liquids and removing particulates while maintaining product quality.
Applications of Crossflow Filtration
Crossflow filtration is widely applied in biopharmaceutical production for separating cells from fermentation broths and concentrating proteins with high purity. It is essential in wastewater treatment to remove suspended solids and organic matter while maintaining high membrane flux. Additionally, crossflow filtration enables efficient clarification and concentration in the food and beverage industry, particularly for dairy processing and fruit juice purification.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Method
Direct filtration offers simplicity and lower energy consumption, making it cost-effective for applications with low particulate loads, but it is limited by rapid filter clogging and reduced efficiency with high solids content. Crossflow filtration provides continuous removal of particles through tangential flow, enhancing filter lifespan and suitability for high solids or viscous fluids, yet it demands higher energy input and complex system design. Each method balances operational costs and filtration performance depending on the specific process requirements and feed characteristics.
Choosing the Right Filtration Method
Choosing the right filtration method depends on your application's specific requirements such as feed composition, desired purity, and operational efficiency. Direct filtration excels in processing clear fluids with low particle loads, providing a straightforward, cost-effective solution for simple separations. Crossflow filtration offers enhanced performance for complex mixtures by continuously sweeping the membrane surface, reducing fouling, and enabling higher recovery rates and longer membrane lifespan.
Future Trends in Filtration Technologies
Emerging filtration technologies are shifting towards enhanced efficiency with crossflow filtration becoming a dominant method due to its ability to minimize membrane fouling and extend filter lifespan. Direct filtration remains valuable for simpler applications, but future trends emphasize integrating smart sensors and AI-driven controls in crossflow systems to optimize performance and reduce operational costs. You can expect these advancements to revolutionize filtration processes across industries, enabling more sustainable and precise separation techniques.
direct filtration vs crossflow filtration Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com