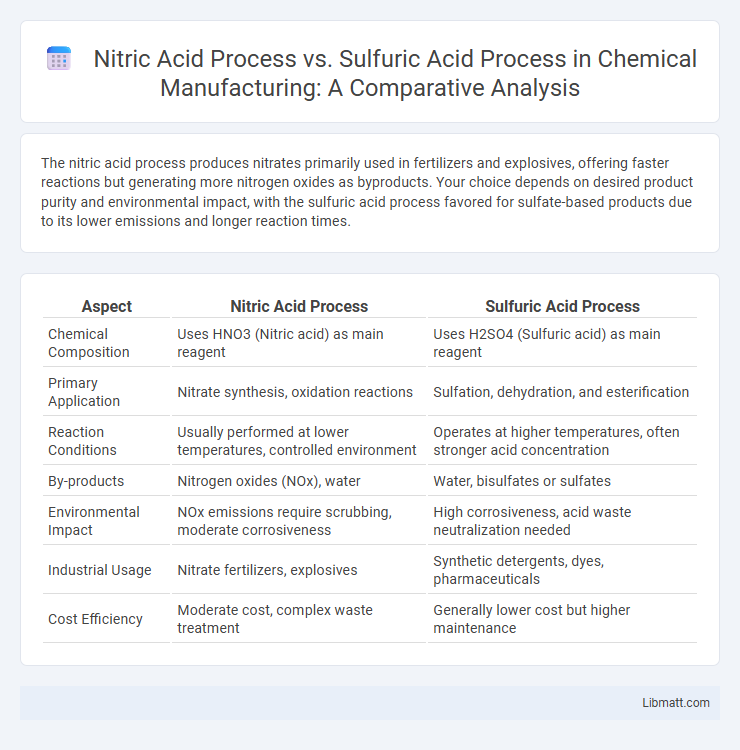
The nitric acid process produces nitrates primarily used in fertilizers and explosives, offering faster reactions but generating more nitrogen oxides as byproducts. Your choice depends on desired product purity and environmental impact, with the sulfuric acid process favored for sulfate-based products due to its lower emissions and longer reaction times.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Nitric Acid Process | Sulfuric Acid Process |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Uses HNO3 (Nitric acid) as main reagent | Uses H2SO4 (Sulfuric acid) as main reagent |
| Primary Application | Nitrate synthesis, oxidation reactions | Sulfation, dehydration, and esterification |
| Reaction Conditions | Usually performed at lower temperatures, controlled environment | Operates at higher temperatures, often stronger acid concentration |
| By-products | Nitrogen oxides (NOx), water | Water, bisulfates or sulfates |
| Environmental Impact | NOx emissions require scrubbing, moderate corrosiveness | High corrosiveness, acid waste neutralization needed |
| Industrial Usage | Nitrate fertilizers, explosives | Synthetic detergents, dyes, pharmaceuticals |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate cost, complex waste treatment | Generally lower cost but higher maintenance |
Overview of Nitric Acid and Sulfuric Acid Processes
The nitric acid process involves synthesizing nitric acid primarily through the Ostwald process, where ammonia is oxidized to produce nitrogen dioxide, which then reacts with water, emphasizing high-temperature catalytic oxidation. The sulfuric acid process centers on producing sulfuric acid by burning sulfur to sulfur dioxide, followed by catalytic oxidation to sulfur trioxide, then absorption in water or concentrated sulfuric acid. Your choice between these processes depends on the desired acid's end-use in fertilizers, explosives, or chemical manufacturing, highlighting their distinct industrial applications and production methods.
Chemical Reactions Involved in Each Process
The Nitric acid process primarily involves the reaction of ammonia with nitric acid to produce ammonium nitrate through an exothermic neutralization reaction. The Sulfuric acid process, on the other hand, involves the reaction of ammonia with sulfuric acid to form ammonium sulfate, followed by a secondary reaction to produce fertilizers. Your choice between these methods depends on factors such as desired fertilizer type and process efficiency based on these distinct chemical reactions.
Raw Materials and Feedstocks Comparison
The Nitric acid process primarily utilizes ammonia as its raw material, whereas the Sulfuric acid process relies on sulfur and phosphate rock. Ammonia feedstock in the Nitric acid process leads to the production of nitric acid used in fertilizers, while the Sulfuric acid process produces sulfuric acid crucial for phosphate fertilizer production. Your choice between these processes depends on the availability and cost of ammonia versus sulfur and phosphate rock in your feedstock supply chain.
Process Flow Diagrams: Key Differences
Nitric acid and sulfuric acid processes have distinct process flow diagrams reflecting their chemical reactions and industrial applications. The nitric acid process primarily involves catalytic oxidation of ammonia to produce nitrogen oxides, followed by absorption in water to form nitric acid, whereas the sulfuric acid process oxidizes sulfur dioxide to sulfur trioxide before absorbing it into water or concentrated sulfuric acid. Understanding these key differences in flow diagrams helps optimize Your production setup for efficiency and environmental compliance.
Efficiency and Yield Analysis
The Nitric acid process typically achieves higher efficiency in nitration reactions, with yields often exceeding 90% due to better selectivity and faster reaction rates. In contrast, the Sulfuric acid process, while cost-effective, usually results in lower yields around 70-80% because of side reactions and byproduct formation. Advanced control of temperature and reactant ratios in the Nitric acid process further optimizes product purity and throughput, enhancing overall industrial efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Emissions
The Nitric acid process typically generates higher nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions, contributing to air pollution and acid rain, whereas the Sulfuric acid process produces sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions, posing risks of respiratory problems and environmental acidification. Advanced scrubbing and catalytic reduction systems are essential in both processes to mitigate harmful emissions and comply with environmental regulations. Overall, the Sulfuric acid process often requires more stringent controls due to the persistent nature of sulfur compounds in the atmosphere.
Safety Considerations and Hazards
The Nitric acid process involves handling highly corrosive and toxic nitrogen oxides, requiring stringent ventilation and protective equipment to prevent inhalation and chemical burns. The Sulfuric acid process presents significant risks of acid spills, exothermic reactions, and the release of sulfur dioxide gas, necessitating robust containment systems and emergency neutralization protocols. Both processes demand rigorous safety training and continuous monitoring to mitigate exposure hazards and environmental impact.
Industrial Applications and Product Quality
The Nitric acid process is primarily used in the production of ammonium nitrate fertilizers, offering high purity and efficient nitrogen content ideal for agricultural applications. The Sulfuric acid process dominates phosphate fertilizer manufacturing, producing superphosphate and triple superphosphate with consistent calcium phosphate content and better handling of impurities. Your choice between these processes impacts product quality, with the Nitric acid process providing faster reaction times and higher-grade end products suitable for specific industrial needs.
Economic Comparison: Costs and Scalability
The sulfuric acid process generally offers lower operational costs and higher scalability for large-scale industrial applications due to its established infrastructure and availability of raw materials. The nitric acid process incurs higher expenses in raw materials and energy consumption, limiting its economic feasibility primarily to niche or smaller-scale productions. Your choice between these processes should consider long-term cost-efficiency and production volume requirements to optimize economic returns.
Future Trends and Innovations in Acid Production
Emerging trends in acid production emphasize sustainable technologies and zero-emission processes to reduce environmental impact in both nitric acid and sulfuric acid manufacturing. Innovations include membrane-based electrochemical cells for low-energy nitric acid synthesis and advanced catalytic converters improving sulfuric acid yield and purity. Integration of digital monitoring systems and AI-driven process optimization enhances efficiency and reduces operational costs across acid production plants.
Nitric acid process vs sulfuric acid process Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com