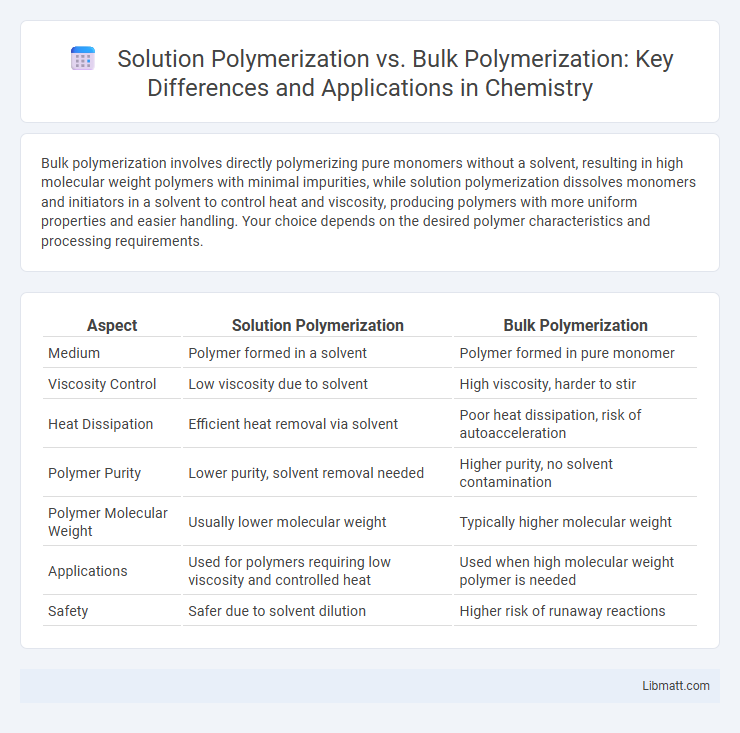
Bulk polymerization involves directly polymerizing pure monomers without a solvent, resulting in high molecular weight polymers with minimal impurities, while solution polymerization dissolves monomers and initiators in a solvent to control heat and viscosity, producing polymers with more uniform properties and easier handling. Your choice depends on the desired polymer characteristics and processing requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Solution Polymerization | Bulk Polymerization |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Polymer formed in a solvent | Polymer formed in pure monomer |
| Viscosity Control | Low viscosity due to solvent | High viscosity, harder to stir |
| Heat Dissipation | Efficient heat removal via solvent | Poor heat dissipation, risk of autoacceleration |
| Polymer Purity | Lower purity, solvent removal needed | Higher purity, no solvent contamination |
| Polymer Molecular Weight | Usually lower molecular weight | Typically higher molecular weight |
| Applications | Used for polymers requiring low viscosity and controlled heat | Used when high molecular weight polymer is needed |
| Safety | Safer due to solvent dilution | Higher risk of runaway reactions |
Introduction to Polymerization Methods
Solution polymerization involves dissolving monomers and initiators in a solvent, enabling better heat control and ease of handling viscous materials, making it suitable for producing polymers with controlled molecular weights. Bulk polymerization occurs without a solvent, where pure monomers polymerize directly, offering high purity polymers and simpler processing but with challenges in heat dissipation and viscosity management. Both methods are essential in industry, with solution polymerization favored for coatings and adhesives, while bulk polymerization is common in manufacturing polymers such as polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA).
Overview of Solution Polymerization
Solution polymerization involves dissolving both the monomer and initiator in a solvent, which helps control the reaction temperature and viscosity. This method provides better heat dissipation and ease of handling compared to bulk polymerization, reducing the risk of runaway reactions. Your choice of solvent and monomer concentration directly influences polymer molecular weight and product uniformity in solution polymerization.
Overview of Bulk Polymerization
Bulk polymerization is a method where monomers polymerize without solvents, resulting in high-purity polymers with minimal contamination. This technique offers excellent control over molecular weight and polymer structure but requires efficient heat management due to the exothermic reaction. Your choice of bulk polymerization can optimize product properties for applications demanding pristine polymer quality.
Key Differences Between Solution and Bulk Polymerization
Solution polymerization involves dissolving monomers in a solvent, which helps control reaction temperature and viscosity, leading to better heat dissipation and easier molecular weight regulation. Bulk polymerization occurs without a solvent, resulting in higher monomer concentration, faster polymerization rates, but poses challenges in heat removal and viscosity management. The choice between these methods depends on desired polymer properties, process control, and application-specific requirements.
Advantages of Solution Polymerization
Solution polymerization offers advantages such as improved heat dissipation due to the solvent's thermal conductivity, which prevents overheating and uncontrolled reactions. The resulting polymer solution allows for easier viscosity control and better mixing, enhancing reaction uniformity and molecular weight distribution. Furthermore, solution polymerization facilitates the production of polymers with high molecular weights and allows for easier handling of exothermic reactions compared to bulk polymerization.
Advantages of Bulk Polymerization
Bulk polymerization offers advantages such as high purity of the final polymer due to minimal use of solvents and additives, resulting in fewer contamination issues. It provides better control over molecular weight distribution and produces polymers with superior mechanical properties. Your projects benefit from simpler processing and reduced environmental concerns, making bulk polymerization an efficient and cost-effective method.
Limitations of Solution Polymerization
Solution polymerization faces limitations such as the need for large amounts of solvents that can lead to environmental concerns and increased costs for solvent recovery and disposal. The presence of solvents often results in lower polymerization rates and may dilute the monomer concentration, ultimately affecting the molecular weight and polymer properties. Heat removal challenges during exothermic reactions and potential solvent-polymer interactions can also hinder product purity and process efficiency.
Limitations of Bulk Polymerization
Bulk polymerization is limited by poor heat dissipation, which can lead to uncontrolled exothermic reactions and polymer degradation. The high viscosity of the reaction mixture hinders effective mixing, causing uneven polymerization and lower molecular weight control. Your ability to produce high-quality polymers is constrained by these thermal and mixing challenges compared to solution polymerization.
Applications of Solution and Bulk Polymerization
Solution polymerization is commonly used in producing coatings, adhesives, and flexible packaging due to its excellent control over molecular weight and heat dissipation. Bulk polymerization is preferred in manufacturing high-purity polymers like polystyrene and polyethylene for rigid plastic products, where minimal solvent removal is crucial. Your choice depends on whether you need precise polymer properties or cost-effective, solvent-free production.
Choosing the Right Polymerization Method
Choosing the right polymerization method depends on factors such as monomer solubility, heat management, and desired polymer properties. Solution polymerization offers better temperature control and easier viscosity management due to the presence of solvent, making it suitable for high molecular weight polymers or heat-sensitive monomers. Bulk polymerization provides higher purity and simpler processing but requires effective heat dissipation to prevent runaway reactions, ideal for applications demanding minimal solvent residue.
Solution polymerization vs bulk polymerization Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com