Soft sensors use mathematical models and algorithms to estimate process variables that are difficult or expensive to measure directly, while hard sensors are physical devices that provide direct, real-time measurements. Your choice between soft and hard sensors depends on factors like cost, accuracy, and the specific application needs in industrial or environmental monitoring.
Table of Comparison
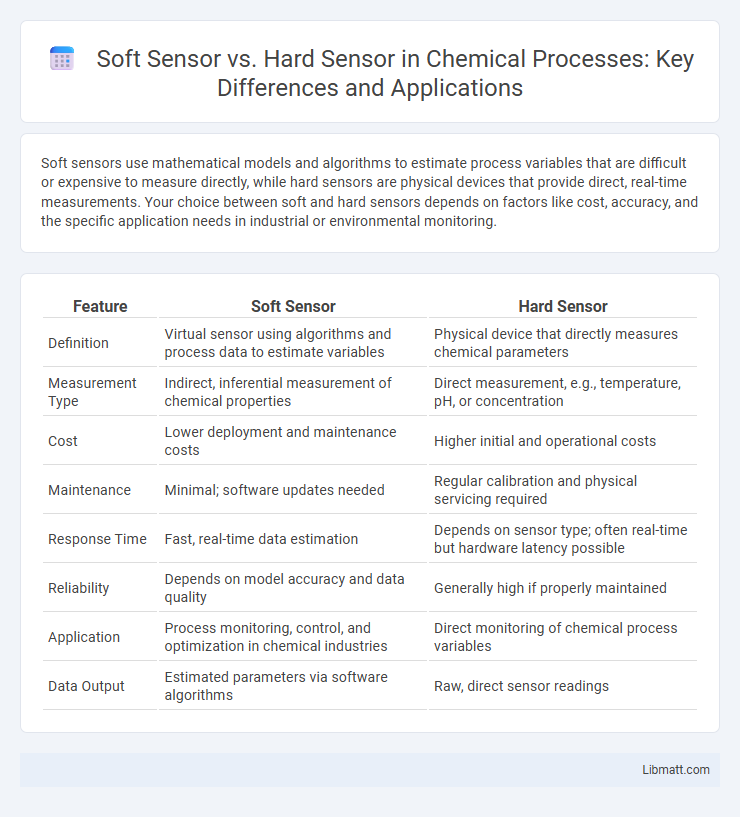
| Feature | Soft Sensor | Hard Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual sensor using algorithms and process data to estimate variables | Physical device that directly measures chemical parameters |
| Measurement Type | Indirect, inferential measurement of chemical properties | Direct measurement, e.g., temperature, pH, or concentration |
| Cost | Lower deployment and maintenance costs | Higher initial and operational costs |
| Maintenance | Minimal; software updates needed | Regular calibration and physical servicing required |
| Response Time | Fast, real-time data estimation | Depends on sensor type; often real-time but hardware latency possible |
| Reliability | Depends on model accuracy and data quality | Generally high if properly maintained |
| Application | Process monitoring, control, and optimization in chemical industries | Direct monitoring of chemical process variables |
| Data Output | Estimated parameters via software algorithms | Raw, direct sensor readings |
Introduction to Soft Sensors and Hard Sensors
Soft sensors use data algorithms and models to estimate variables that are difficult or expensive to measure directly, while hard sensors rely on physical devices to detect and measure environmental or mechanical parameters. By integrating data from multiple sources, soft sensors provide real-time insights without additional hardware, enhancing your system's predictive capabilities. Hard sensors deliver precise, direct measurements essential for immediate control and monitoring in various industrial applications.
Defining Soft Sensors: Key Characteristics
Soft sensors utilize algorithms and data-driven models to estimate process variables that physical hard sensors cannot directly measure. They leverage real-time data from multiple hard sensors, applying machine learning or statistical methods to generate accurate, continuous estimates. Your system benefits from soft sensors by enhancing monitoring capabilities without additional hardware costs, enabling improved control and predictive maintenance.
What are Hard Sensors? An Overview
Hard sensors are physical devices designed to directly measure specific environmental or system variables such as temperature, pressure, or humidity. These sensors rely on hardware components like thermocouples, strain gauges, and accelerometers to provide accurate, real-time data essential for industrial automation and control systems. Their precision and reliability enable critical monitoring in applications ranging from manufacturing processes to environmental tracking.
Core Differences: Soft Sensor vs Hard Sensor
Soft sensors estimate process variables using algorithms and data from existing hard sensors, enabling real-time predictions without direct physical measurement. Hard sensors rely on physical devices to measure tangible parameters like temperature, pressure, or flow with direct contact or environmental interaction. The core difference lies in data acquisition: hard sensors provide raw measured data, while soft sensors deliver inferred values through computational models based on that data.
Advantages of Soft Sensors
Soft sensors offer significant advantages by providing real-time estimation of variables that are difficult or costly to measure directly through physical sensors. They enhance predictive maintenance and process control in industrial applications by utilizing data-driven models and historical sensor data to infer unmeasured parameters. These virtual sensors reduce hardware costs and increase system flexibility, enabling more adaptive and intelligent monitoring solutions.
Benefits and Limitations of Hard Sensors
Hard sensors provide direct and accurate physical measurements, essential for real-time monitoring in industrial processes and critical systems. Their benefits include high reliability, robustness in harsh environments, and straightforward calibration. However, hard sensors can be costly, require regular maintenance, and may be limited by physical constraints or sensor placement challenges in complex systems.
Common Applications of Soft Sensors
Soft sensors are widely used in industrial process control, where they estimate unmeasured variables such as chemical concentrations, temperature, or pressure by analyzing accessible data from hard sensors. They enhance performance in sectors like manufacturing, energy production, and environmental monitoring by providing real-time insights and predictive analytics that improve decision-making and system efficiency. Your operations benefit from soft sensors' ability to reduce costs and maintenance efforts compared to traditional hard sensor installations.
Typical Use Cases for Hard Sensors
Hard sensors are typically used in industrial automation for real-time monitoring of physical parameters such as temperature, pressure, and flow rate. They play a crucial role in safety-critical systems like chemical processing plants, aerospace, and manufacturing lines where precise and reliable data acquisition is essential. Hard sensors provide direct measurement, ensuring high accuracy and immediate response, which is vital for process control and equipment protection.
Integration and Implementation Challenges
Soft sensors leverage algorithms and data fusion to estimate measurements from hard sensors, enabling integration without extensive physical hardware modifications. However, their implementation requires robust calibration, real-time data processing capabilities, and reliable communication networks to ensure accurate and timely outputs. Your system's success depends on addressing these challenges to harmonize soft sensor models with existing hard sensor infrastructures effectively.
Future Trends in Sensor Technology
Future trends in sensor technology emphasize the integration of soft sensors with advanced artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms, enabling real-time data estimation and predictive analytics in complex industrial processes. Development in soft sensor technology targets enhanced accuracy, robustness, and adaptability by leveraging big data from hard sensors and IoT devices. Innovations in hybrid sensing systems combine the reliability of hard sensors with the flexibility of soft sensors, driving advancements in automation, smart manufacturing, and digital twin technologies.
soft sensor vs hard sensor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com