A box furnace offers a spacious chamber ideal for uniform heating of larger or irregularly shaped samples, while a tube furnace provides precise temperature control within a confined cylindrical space, making it perfect for controlled atmosphere experiments and smaller samples. Your choice depends on the sample size, application requirements, and the need for controlled gas environments during heating processes.
Table of Comparison
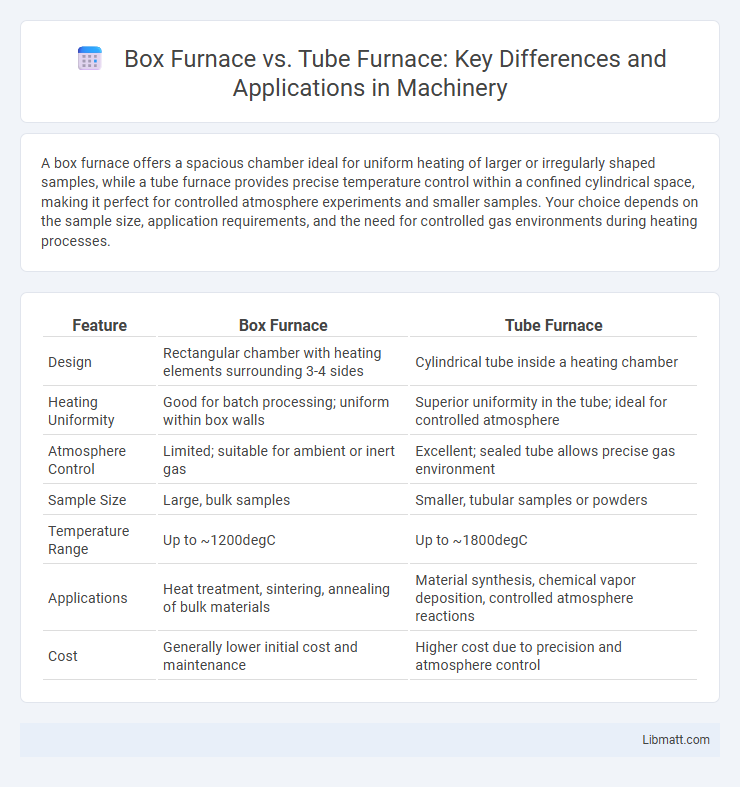
| Feature | Box Furnace | Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Rectangular chamber with heating elements surrounding 3-4 sides | Cylindrical tube inside a heating chamber |
| Heating Uniformity | Good for batch processing; uniform within box walls | Superior uniformity in the tube; ideal for controlled atmosphere |
| Atmosphere Control | Limited; suitable for ambient or inert gas | Excellent; sealed tube allows precise gas environment |
| Sample Size | Large, bulk samples | Smaller, tubular samples or powders |
| Temperature Range | Up to ~1200degC | Up to ~1800degC |
| Applications | Heat treatment, sintering, annealing of bulk materials | Material synthesis, chemical vapor deposition, controlled atmosphere reactions |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost and maintenance | Higher cost due to precision and atmosphere control |
Introduction to Box and Tube Furnaces
Box furnaces provide uniform heating in a spacious chamber ideal for large or multiple samples, while tube furnaces offer precise temperature control within a narrow cylindrical tube suited for controlled atmosphere processes. Your choice depends on the sample size and the need for specific environmental control during heating. Tube furnaces excel in applications requiring gas flow and vacuum conditions, whereas box furnaces are preferred for batch processing and general heat treatment.
Key Differences Between Box and Tube Furnaces
Box furnaces offer a spacious chamber ideal for uniform heat treatment of bulk materials, while tube furnaces provide a narrow, cylindrical design suited for precise temperature control and small-sample processing. Key differences include heating uniformity, sample size capacity, and operational temperature range; box furnaces typically handle larger volumes with even heat distribution, whereas tube furnaces excel in controlled atmospheres and smaller experimental setups. This distinction impacts applications in industries such as ceramics, metallurgy, and chemical research.
Design and Construction Features
Box furnaces feature a rectangular chamber with easily accessible front or top-loading doors, designed for uniform heat distribution and versatility in processing larger or irregularly shaped materials. Tube furnaces consist of a cylindrical heating chamber enclosed within a protective outer shell, ideal for controlled atmosphere experiments and treatments requiring consistent temperature along the length of the tube. The construction of tube furnaces enables precise thermal gradients and gas flow control, while box furnaces prioritize spacious interiors and modular shelving for varied sample arrangements.
Heating Efficiency and Temperature Uniformity
Box furnaces provide superior heating efficiency through their insulated chamber design, minimizing heat loss and allowing rapid temperature ramp-up. Tube furnaces excel in temperature uniformity along the length of the heating zone, ensuring consistent thermal processing for elongated samples or materials requiring precise thermal gradients. Selection between the two depends on application needs for either quick heating or highly uniform temperature distribution.
Applications and Use Cases
Box furnaces are widely used for batch processing in industries requiring uniform heating, such as metal annealing, ceramic sintering, and glass tempering, due to their spacious chamber and precise temperature control. Tube furnaces excel in continuous processing and controlled atmosphere applications, including material synthesis, chemical vapor deposition, and heat treatment of small components inside quartz or ceramic tubes. Their design facilitates gas flow and rapid temperature changes, making them ideal for research labs and advanced material development.
Size, Capacity, and Volume Considerations
Box furnaces typically offer larger internal volumes and greater capacity, making them ideal for processing bulky materials and batch treatments, while tube furnaces feature smaller, cylindrical chambers designed for precise heating of sample tubes or rods. Box furnaces provide a larger heating area and uniform temperature distribution across a broad space, whereas tube furnaces concentrate heat along the length of the tube, allowing for controlled environments and specialized gas flow. Size-wise, box furnaces are bulkier and require more lab space, whereas tube furnaces are compact and suited for limited spaces with smaller sample sizes.
Energy Consumption and Cost Comparison
Box furnaces typically consume more energy due to larger heating volumes and lower insulation efficiency, resulting in higher operational costs. Tube furnaces, with their compact design and improved insulation, offer better energy efficiency, reducing power consumption and ongoing expenses. Selecting a tube furnace can lead to significant cost savings in energy over long-term industrial or laboratory use.
Temperature Control and Precision
Tube furnaces offer superior temperature control and precision due to their cylindrical design, which allows for more uniform heating and faster ramp rates, making them ideal for processes requiring accurate and consistent thermal conditions. Box furnaces typically have a larger workspace but may experience slight temperature gradients, resulting in less precise control compared to tube furnaces. Your choice should consider the specific temperature uniformity and control requirements of your application to achieve optimal results.
Maintenance and Durability
Box furnaces often require more frequent maintenance due to their larger chamber size and multiple heating elements, which can wear unevenly over time. Tube furnaces offer enhanced durability with their streamlined design and uniform heating, reducing the risk of hot spots and minimizing wear on internal components. Regular calibration and cleaning extend the lifespan of both types, but tube furnaces generally provide lower maintenance costs and longer operational life in demanding industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Furnace for Your Needs
Box furnaces offer spacious interiors suitable for heating larger samples or multiple items simultaneously, making them ideal for bulk processing applications. Tube furnaces provide precise temperature control and a controlled atmosphere environment, perfect for delicate materials or research requiring uniform heat distribution. Choosing the right furnace depends on your sample size, temperature requirements, and process atmosphere to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
Box furnace vs tube furnace Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com