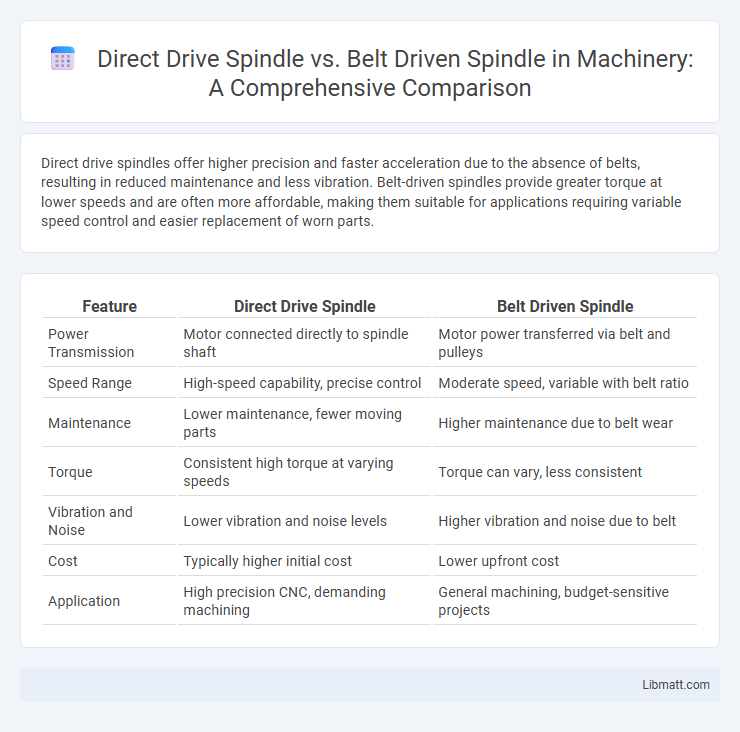
Direct drive spindles offer higher precision and faster acceleration due to the absence of belts, resulting in reduced maintenance and less vibration. Belt-driven spindles provide greater torque at lower speeds and are often more affordable, making them suitable for applications requiring variable speed control and easier replacement of worn parts.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Direct Drive Spindle | Belt Driven Spindle |
|---|---|---|
| Power Transmission | Motor connected directly to spindle shaft | Motor power transferred via belt and pulleys |
| Speed Range | High-speed capability, precise control | Moderate speed, variable with belt ratio |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance, fewer moving parts | Higher maintenance due to belt wear |
| Torque | Consistent high torque at varying speeds | Torque can vary, less consistent |
| Vibration and Noise | Lower vibration and noise levels | Higher vibration and noise due to belt |
| Cost | Typically higher initial cost | Lower upfront cost |
| Application | High precision CNC, demanding machining | General machining, budget-sensitive projects |
Introduction to Direct Drive and Belt Driven Spindles
Direct drive spindles deliver power directly from the motor to the spindle shaft, offering higher precision, faster acceleration, and reduced maintenance compared to belt driven spindles. Belt driven spindles use a belt to transfer motor power, allowing for easier speed adjustments and absorbing shock loads but may experience wear and vibration over time. Your choice between direct drive and belt driven spindles depends on the desired balance of speed, accuracy, maintenance, and cost.
How Direct Drive Spindles Work
Direct drive spindles operate by coupling the motor directly to the spindle shaft, eliminating belts and pulleys to provide precise rotational speed and torque control. This direct connection reduces mechanical losses, vibration, and maintenance needs, resulting in higher efficiency and smoother performance. Your CNC machine benefits from faster acceleration, improved accuracy, and quieter operation compared to belt-driven spindles.
How Belt Driven Spindles Operate
Belt driven spindles operate by transferring power from the motor to the spindle shaft through a flexible belt, allowing for adjustable speed and torque. This system reduces motor vibration and noise, enhancing machining precision and tool life. When selecting your spindle, consider that belt driven models offer greater flexibility in speed tuning compared to direct drive designs.
Key Performance Differences
Direct drive spindles offer higher torque and faster acceleration due to the absence of belts, resulting in superior precision and reduced maintenance compared to belt-driven spindles. Belt-driven spindles provide more flexibility in speed variation and cost-effective replacement parts but often suffer from vibration, belt wear, and efficiency losses. Understanding these key performance differences helps you select the optimal spindle type for applications requiring high accuracy and durability versus budget-sensitive projects with varying speed demands.
Efficiency and Power Transmission Comparison
Direct drive spindles deliver higher efficiency by eliminating power losses associated with belt slippage and stretch, ensuring consistent torque and speed. Belt-driven spindles experience reduced efficiency due to friction and potential belt degradation, which can cause power transmission losses up to 10-15%. The direct connection in direct drive systems enables precise power transfer, enhancing machining accuracy and energy savings.
Speed and Torque Characteristics
Direct drive spindles deliver higher torque at low speeds due to the direct coupling between the motor and spindle, providing precise control and rapid acceleration without torque loss. Belt-driven spindles rely on pulley ratios that can limit torque output and introduce slip, reducing torque consistency especially under heavy load conditions. Speed stability in direct drive systems surpasses belt-driven counterparts, making them ideal for applications requiring high torque at variable speeds and superior precision.
Maintenance and Longevity
Direct drive spindles require less maintenance due to fewer moving parts, reducing wear and tear, which significantly extends their longevity compared to belt-driven spindles. Belt-driven spindles need regular belt inspections and replacements, increasing downtime and ongoing maintenance costs. Choosing a direct drive spindle can enhance your machine's reliability and lifespan by minimizing mechanical failures commonly associated with belt wear.
Noise and Vibration Considerations
Direct drive spindles produce significantly lower noise and vibration levels due to the elimination of belts and pulleys, resulting in smoother operation and higher precision. In contrast, belt driven spindles generate more noise and vibration because of belt tension variations and slippage during high-speed rotation, affecting machining accuracy. For applications requiring minimal acoustic disturbance and enhanced surface finish quality, direct drive spindles are the preferred choice.
Application Suitability and Industry Use-Cases
Direct drive spindles excel in high-precision applications such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing due to their superior accuracy, higher torque at low speeds, and reduced maintenance requirements. Belt-driven spindles are better suited for woodworking, metal fabrication, and general-purpose machining where cost efficiency and ease of spindle replacement are priorities. Your choice between these spindle types should align with the specific demands of your industry and application precision needs.
Cost Analysis and ROI
Direct drive spindles typically have a higher upfront cost compared to belt-driven spindles but offer lower maintenance expenses and longer lifespan, enhancing overall ROI. Belt-driven spindles are generally less expensive initially but incur higher long-term costs due to belt replacements and reduced efficiency. Evaluating total cost of ownership alongside production demands is crucial to determining the most cost-effective spindle choice for maximizing return on investment.
Direct drive spindle vs belt driven spindle Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com