Vertical mills offer better space efficiency and are ideal for grinding materials with high moisture content, while horizontal mills provide greater capacity and are more suitable for dry materials requiring finer grinding. Your choice depends on the specific processing requirements, including material type, desired output size, and available installation space.
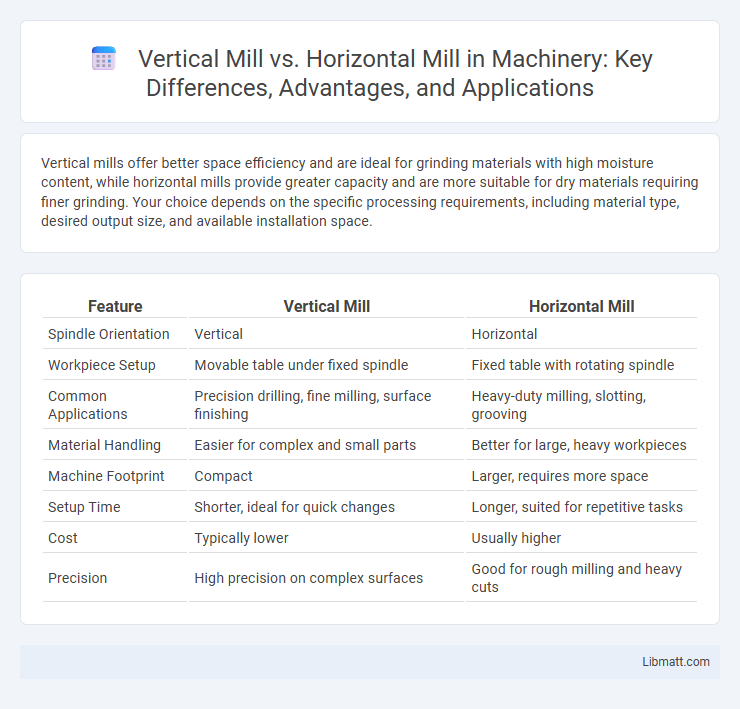
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vertical Mill | Horizontal Mill |
|---|---|---|
| Spindle Orientation | Vertical | Horizontal |
| Workpiece Setup | Movable table under fixed spindle | Fixed table with rotating spindle |
| Common Applications | Precision drilling, fine milling, surface finishing | Heavy-duty milling, slotting, grooving |
| Material Handling | Easier for complex and small parts | Better for large, heavy workpieces |
| Machine Footprint | Compact | Larger, requires more space |
| Setup Time | Shorter, ideal for quick changes | Longer, suited for repetitive tasks |
| Cost | Typically lower | Usually higher |
| Precision | High precision on complex surfaces | Good for rough milling and heavy cuts |
Overview of Vertical and Horizontal Mills
Vertical mills feature a spindle oriented vertically, allowing for efficient grinding of large materials with a smaller footprint, making them ideal for high-precision tasks in industries like mining and cement production. Horizontal mills have a horizontally oriented spindle and are designed for heavy-duty grinding of bulk materials, commonly used in metal processing and chemical manufacturing due to their ability to handle larger workloads. The choice between vertical and horizontal mills depends on factors such as material type, desired particle size, production capacity, and space constraints.
Core Design Differences
Vertical mills feature a spindle oriented vertically, allowing the cutting tool to move up and down, enabling efficient machining of deep and complex profiles. In contrast, horizontal mills have a horizontally positioned spindle, making them ideal for heavy-duty tasks and the removal of large amounts of material with better stability. The core design difference lies in the spindle orientation and movement, which directly impacts the tool accessibility and types of operations each mill can perform effectively.
Space and Footprint Considerations
Vertical mills typically require less floor space due to their compact, upright design, making them ideal for facilities with limited footprint availability. Horizontal mills occupy more horizontal area because of the length of their bed and worktable, which can impact workflow and space optimization in smaller workshops. Choosing between vertical and horizontal mill configurations depends on balancing space constraints with the specific machining requirements of the operation.
Efficiency and Output Capabilities
Vertical mills typically offer higher efficiency due to their ability to handle gravity-assisted material flow, reducing energy consumption during milling operations. Horizontal mills provide robust output capabilities, especially for processing larger volumes of heavy or coarse materials with consistent particle size distribution. Your choice between vertical and horizontal mills should consider the trade-off between energy efficiency and the scale of production needed for optimal performance.
Material Versatility and Application Scope
Vertical mills excel in material versatility, efficiently handling a wide range of materials including minerals, ores, and chemicals due to their adaptable grinding mechanics and compact design. Horizontal mills are favored in heavy-duty applications like cement and steel production, providing consistent performance with coarse and abrasive materials through their longer, horizontal grinding length. Both mill types serve diverse industrial sectors, but vertical mills offer greater flexibility for fine to medium grinding, while horizontal mills dominate large-scale, high-capacity operations.
Maintenance and Operational Costs
Vertical mills typically have lower maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts and easier access to components, which reduces downtime and labor expenses. Horizontal mills may incur higher operational costs because their design often requires more frequent lubrication, alignment, and part replacements to maintain precision. Efficient vertical mill operation can lead to reduced energy consumption, while horizontal mills might require more power, impacting overall operational expenses.
Precision and Accuracy Factors
Vertical mills offer superior precision and accuracy due to their rigid column structure, which minimizes tool deflection and vibration during machining. Horizontal mills provide better accuracy in heavy-duty cutting by maintaining consistent spindle load and chip removal efficiency, which reduces thermal distortion. Both types require proper tooling and calibration to achieve optimal machining tolerances in manufacturing processes.
Energy Consumption Comparison
Vertical mills generally consume 20-30% less energy compared to horizontal mills due to their efficient grinding mechanisms and improved material flow. The vertical design allows for lower power requirements by utilizing gravity to aid in the milling process, reducing the load on the motor. Industrial case studies show energy savings of up to 25% when switching from horizontal to vertical mills in cement and mineral processing applications.
Industry-Specific Use Cases
Vertical mills are commonly used in industries such as cement production and mineral processing due to their ability to handle large, abrasive materials with efficient grinding and drying capabilities. Horizontal mills are preferred in metalworking and manufacturing sectors for precise machining tasks, offering superior control for shaping complex parts. Your choice between vertical and horizontal mills should align with specific industry requirements, including the nature of materials and desired outcomes.
Choosing the Right Mill for Your Needs
Selecting the right mill depends on your material type, processing capacity, and desired product fineness. Vertical mills offer space-saving design and energy efficiency, making them ideal for fine grinding and handling sticky or abrasive materials. Horizontal mills provide greater flexibility for larger feed sizes and higher throughput, suitable for coarse grinding and bulk material processing.
Vertical mill vs horizontal mill Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com