Direct current (DC) drives provide precise speed control and high starting torque, making them ideal for applications requiring smooth acceleration and variable speed. Alternating current (AC) drives offer improved efficiency, lower maintenance, and better suitability for industrial use, with many modern AC drives using variable frequency technology to closely match the performance of DC drives while reducing operational costs.
Table of Comparison
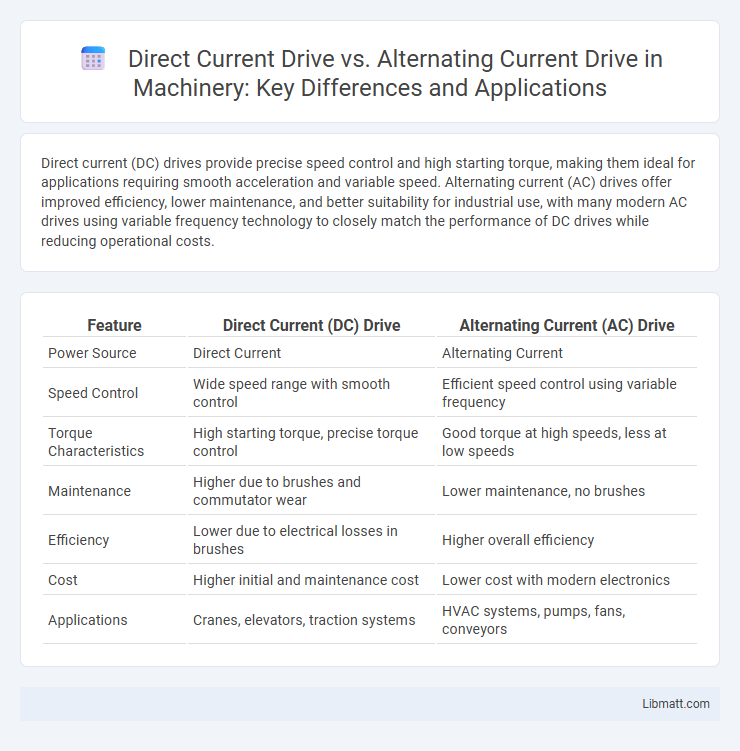
| Feature | Direct Current (DC) Drive | Alternating Current (AC) Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Direct Current | Alternating Current |
| Speed Control | Wide speed range with smooth control | Efficient speed control using variable frequency |
| Torque Characteristics | High starting torque, precise torque control | Good torque at high speeds, less at low speeds |
| Maintenance | Higher due to brushes and commutator wear | Lower maintenance, no brushes |
| Efficiency | Lower due to electrical losses in brushes | Higher overall efficiency |
| Cost | Higher initial and maintenance cost | Lower cost with modern electronics |
| Applications | Cranes, elevators, traction systems | HVAC systems, pumps, fans, conveyors |
Introduction to Electric Drives
Electric drives convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, utilizing either direct current (DC) or alternating current (AC) motors for precise speed and torque control. DC drives offer excellent speed regulation and high starting torque, ideal for applications requiring fine control such as elevators and cranes. AC drives, leveraging advanced inverter technology, provide energy efficiency, reduced maintenance, and versatility, becoming prevalent in industrial automation and HVAC systems.
Overview of Direct Current (DC) Drives
Direct Current (DC) drives control the speed and torque of DC motors by adjusting the armature voltage or field current, offering precise and smooth performance ideal for applications requiring variable speed control. Your choice of a DC drive provides high starting torque and excellent speed regulation, especially in industrial machinery and traction systems. These drives convert AC power to regulated DC voltage, ensuring efficient motor operation while facilitating fine-tuned control for complex processes.
Overview of Alternating Current (AC) Drives
Alternating Current (AC) drives control motor speed and torque by adjusting the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor using sophisticated variable frequency drive (VFD) technology. AC drives offer energy efficiency, precise speed control, and reduced mechanical stress, making them ideal for industrial applications such as conveyors, pumps, and HVAC systems. Their use of induction or synchronous motors enables low maintenance requirements compared to direct current (DC) drives, which rely on brushes and commutators.
Key Differences Between DC and AC Drives
DC drives use direct current to control motor speed with precise torque and smooth acceleration, ideal for applications requiring variable speed and high starting torque. AC drives employ alternating current and variable frequency control, offering lower maintenance and higher efficiency in industrial environments with induction motors. The key differences lie in their motor types, control methods, maintenance requirements, and efficiency levels, with DC drives providing finer speed control and AC drives favoring robustness and energy savings.
Efficiency Comparison: DC vs AC Drives
DC drives generally offer higher efficiency at low speeds due to precise torque control and reduced power loss, making them ideal for applications requiring fine speed regulation. AC drives, especially those with modern vector control technology, provide improved efficiency over a wide speed range and lower maintenance costs since they lack brushes and commutators. The overall efficiency advantage depends on the specific application, motor design, and control strategy, with AC drives often favored for industrial environments due to better performance at varying speeds and reduced mechanical wear.
Applications of DC Drives
DC drives are widely used in applications requiring precise speed control and high starting torque, such as electric vehicles, cranes, and elevators. They are essential in industries where smooth acceleration and deceleration are critical, including robotics and conveyor systems. DC drives excel in variable-speed applications that demand accurate control over motor performance.
Applications of AC Drives
AC drives are widely used in industrial applications such as conveyor systems, pumps, and HVAC systems due to their energy efficiency and precise speed control. They are ideal for variable torque loads and provide seamless integration with modern automation systems through advanced motor control techniques. Industries leveraging AC drives benefit from reduced maintenance costs, improved system reliability, and enhanced operational flexibility.
Cost Analysis: DC vs AC Drives
Direct current (DC) drives generally have higher initial costs due to their complex components and maintenance requirements, while alternating current (AC) drives offer lower upfront expenses and greater energy efficiency. AC drives benefit from reduced operational costs over time, leveraging simpler design, fewer maintenance needs, and advanced inverter technology. Your choice between DC and AC drives should weigh initial investment against long-term savings and application-specific performance.
Maintenance and Reliability Factors
Direct current (DC) drives require more frequent maintenance due to the presence of brushes and commutators, which are prone to wear and need regular inspection or replacement, impacting overall reliability. Alternating current (AC) drives feature rugged construction with fewer moving parts and no brushes, resulting in lower maintenance demands and higher operational reliability. Modern AC drives also benefit from advanced thermal protection and diagnostics, further enhancing system uptime and reducing maintenance costs compared to traditional DC drives.
Choosing the Right Drive for Your Application
Direct current (DC) drives offer precise speed control and high starting torque, making them ideal for applications requiring fine adjustments and variable speeds, such as conveyor belts and hoists. Alternating current (AC) drives provide robust performance, lower maintenance costs, and better efficiency in high-power applications like pumps, fans, and compressors. Choosing the right drive for your application depends on factors such as required torque, control precision, energy efficiency, and maintenance budgets.
Direct current drive vs alternating current drive Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com