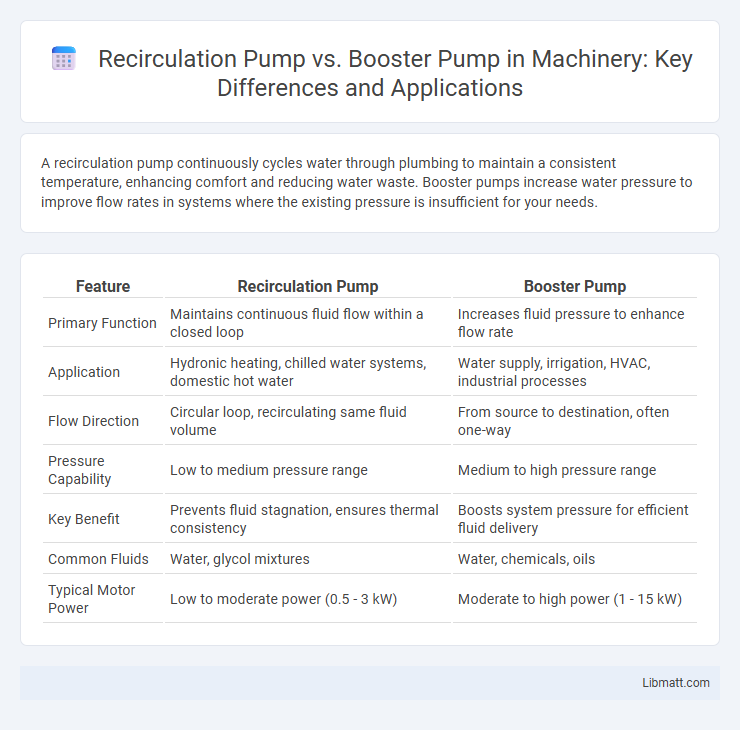
A recirculation pump continuously cycles water through plumbing to maintain a consistent temperature, enhancing comfort and reducing water waste. Booster pumps increase water pressure to improve flow rates in systems where the existing pressure is insufficient for your needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recirculation Pump | Booster Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Maintains continuous fluid flow within a closed loop | Increases fluid pressure to enhance flow rate |
| Application | Hydronic heating, chilled water systems, domestic hot water | Water supply, irrigation, HVAC, industrial processes |
| Flow Direction | Circular loop, recirculating same fluid volume | From source to destination, often one-way |
| Pressure Capability | Low to medium pressure range | Medium to high pressure range |
| Key Benefit | Prevents fluid stagnation, ensures thermal consistency | Boosts system pressure for efficient fluid delivery |
| Common Fluids | Water, glycol mixtures | Water, chemicals, oils |
| Typical Motor Power | Low to moderate power (0.5 - 3 kW) | Moderate to high power (1 - 15 kW) |
Introduction to Recirculation and Booster Pumps
Recirculation pumps maintain continuous water movement within plumbing systems to provide instant hot water, improving energy efficiency and user comfort. Booster pumps increase water pressure in systems where supply is inadequate, ensuring consistent flow for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Both pumps serve distinct roles in optimizing water distribution based on pressure control and circulation needs.
What is a Recirculation Pump?
A recirculation pump is a specialized device designed to continuously circulate hot water through plumbing systems to ensure instant hot water availability at fixtures, reducing water waste and wait times. Unlike booster pumps, which primarily increase water pressure for improved flow, recirculation pumps maintain a consistent temperature by looping water back to the heater. Understanding how your recirculation pump operates can significantly enhance your home's water efficiency and comfort.
What is a Booster Pump?
A booster pump is a mechanical device designed to increase water pressure in plumbing systems, ensuring efficient flow in residential, commercial, and industrial applications. It draws water from a source and boosts its pressure to overcome resistance in pipes and fixtures, enhancing performance in high-demand areas. Commonly used in buildings with low municipal water pressure or complex piping networks, booster pumps maintain consistent water delivery and improve system reliability.
Key Differences Between Recirculation and Booster Pumps
Recirculation pumps are designed to maintain a consistent flow of heated water within a plumbing system, ensuring immediate hot water availability at fixtures, while booster pumps primarily increase water pressure in low-pressure systems to improve flow rates. You benefit from a recirculation pump when aiming to reduce water waste and wait times for hot water, whereas booster pumps enhance pressure for irrigation, high-rise buildings, or industrial processes. Key differences include their primary function--temperature maintenance versus pressure enhancement--and typical installation points within the water system.
Main Applications of Recirculation Pumps
Recirculation pumps are primarily used in residential and commercial hot water systems to maintain a constant flow, ensuring instant hot water availability and reducing water waste. These pumps circulate hot water through the plumbing system, preventing the need to wait for hot water at taps and showers. Common applications include hydronic heating systems, solar water heating setups, and domestic hot water recirculation loops.
Main Applications of Booster Pumps
Booster pumps are primarily used in buildings and water supply systems to increase water pressure for reliable distribution across multiple floors or distant outlets. They are essential in irrigation systems, firefighting setups, and industrial processes requiring consistent high pressure. Your water system benefits significantly from a booster pump when main supply pressure is insufficient for optimal performance.
Pros and Cons of Recirculation Pumps
Recirculation pumps improve energy efficiency by continuously circulating hot water, reducing wait time and water waste at taps. However, they consume electricity even when hot water use is low, potentially increasing energy costs if not properly managed. Your choice depends on balancing comfort benefits against operational expenses and the specific needs of your plumbing system.
Pros and Cons of Booster Pumps
Booster pumps increase water pressure and flow rate, making them ideal for high-rise buildings and irrigation systems, but they can consume more energy and require regular maintenance. They effectively address low-pressure issues in plumbing systems, ensuring consistent water delivery, though noise and initial cost may be higher compared to other solutions. Your choice depends on balancing efficiency, cost, and specific system needs when opting for a booster pump.
Choosing the Right Pump for Your Needs
Choosing the right pump depends on the specific application: recirculation pumps are ideal for maintaining consistent water temperature in plumbing systems by continuously circulating hot water, reducing wait times and water waste. Booster pumps are designed to increase water pressure in systems with low flow, ensuring adequate delivery to higher floors or distant fixtures. Assessing factors such as required flow rate, pressure needs, and system layout will guide the selection between recirculation and booster pumps for optimal performance.
Conclusion: Recirculation Pump vs Booster Pump
Recirculation pumps are essential for maintaining consistent hot water flow by continuously circulating water through pipes, preventing delays and wastage. Booster pumps, however, are designed to increase water pressure in plumbing systems where the existing pressure is inadequate for delivering optimal flow. Choosing between recirculation and booster pumps depends on the need for either continuous hot water availability or enhanced water pressure in the system.
Recirculation pump vs booster pump Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com