Digital calipers provide precise, easy-to-read measurements with a digital display, enhancing accuracy and reducing reading errors compared to dial calipers. Your choice depends on preference for instant digital readings versus the traditional, mechanical dial mechanism favored for durability and simplicity.
Table of Comparison
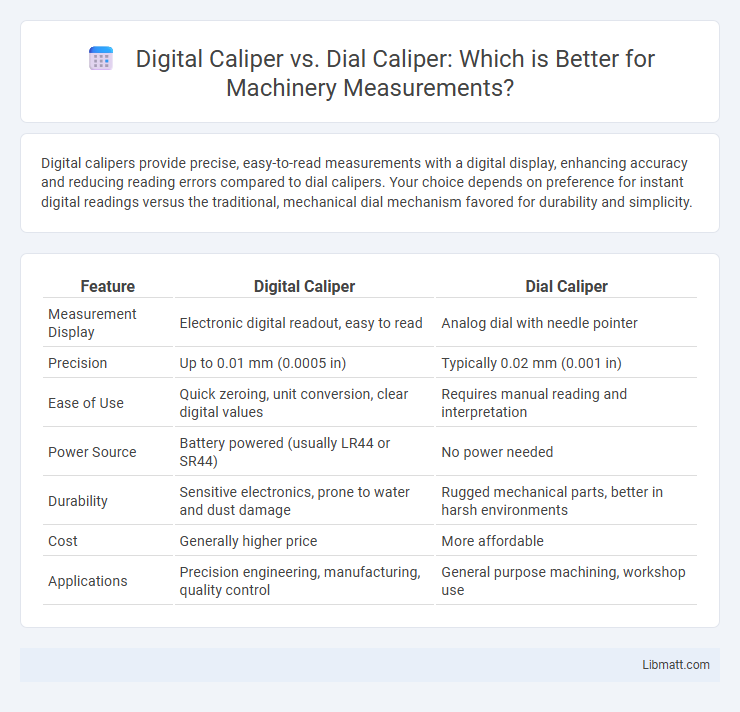
| Feature | Digital Caliper | Dial Caliper |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Display | Electronic digital readout, easy to read | Analog dial with needle pointer |
| Precision | Up to 0.01 mm (0.0005 in) | Typically 0.02 mm (0.001 in) |
| Ease of Use | Quick zeroing, unit conversion, clear digital values | Requires manual reading and interpretation |
| Power Source | Battery powered (usually LR44 or SR44) | No power needed |
| Durability | Sensitive electronics, prone to water and dust damage | Rugged mechanical parts, better in harsh environments |
| Cost | Generally higher price | More affordable |
| Applications | Precision engineering, manufacturing, quality control | General purpose machining, workshop use |
Introduction to Digital and Dial Calipers
Digital calipers provide precise measurements displayed on an electronic screen, enhancing readability and reducing human error. Dial calipers use a mechanical dial with a needle indicator to show measurements, relying on manual interpretation and offering a reliable, analog alternative. Both tools measure internal, external, depth, and step dimensions with varying ease of use and accuracy depending on the application.
How Digital Calipers Work
Digital calipers use electronic sensors to measure the distance between their jaws, converting mechanical movement into digital readings displayed on an LCD screen. Your measurements are instantly precise due to the high-resolution linear encoder technology, which eliminates manual reading errors common in dial calipers. This efficiency makes digital calipers ideal for tasks requiring quick, accurate, and easy-to-read measurements.
How Dial Calipers Work
Dial calipers operate using a rack and pinion mechanism that translates linear movement into rotational motion, moving a needle around a dial to display measurements with precision. The dial, usually marked in increments down to 0.001 inches or 0.02 millimeters, provides a direct visual reading of dimensions such as internal, external, and depth measurements. Unlike digital calipers, dial calipers require manual zeroing and interpretation of the dial face, making them reliable tools that do not depend on batteries or electronic components.
Accuracy and Precision Comparison
Digital calipers offer higher accuracy and precision compared to dial calipers, typically providing measurements with a resolution of 0.01 mm or 0.0005 inches. Dial calipers generally have a resolution of 0.02 mm or 0.001 inches, which may lead to less precise readings for detailed measurements. Your choice between these tools impacts the consistency and reliability of measurement results, with digital calipers favored in applications requiring fine accuracy.
Ease of Use and Readability
Digital calipers offer superior ease of use with an electronic display that provides quick and clear measurement readings, reducing the risk of human error. Dial calipers require interpreting the position of the needle against the scale, which can be less intuitive and slower for precise measurements. Your efficiency improves with digital calipers due to their straightforward, instantly readable results.
Durability and Maintenance
Digital calipers typically feature robust construction with stainless steel bodies and sealed electronic components that offer good durability and require minimal maintenance compared to dial calipers. Dial calipers, while durable with metal parts, may require regular cleaning and occasional dial mechanism adjustment or lubrication to maintain accuracy. Both types benefit from careful handling and storage to extend their lifespan and performance reliability.
Battery Dependency vs Mechanical Reliability
Digital calipers rely on batteries for their display and measurement functions, which can lead to interruptions if the battery is depleted, requiring regular battery replacements to maintain accuracy. Dial calipers operate entirely mechanically, ensuring consistent reliability without dependence on power sources, making them ideal for environments where battery failure is a concern. The trade-off between digital ease of reading and mechanical durability influences the choice based on specific application needs.
Cost and Affordability
Digital calipers generally offer higher precision and ease of reading but come at a higher cost, making them less affordable for budget-conscious users. Dial calipers, while less expensive and more durable due to their mechanical design, may require more skill to read accurately. Your choice depends on balancing the initial investment with long-term usability and accuracy needs.
Typical Applications and Best Use Cases
Digital calipers excel in applications requiring quick, precise measurements and easy data transfer, making them ideal for quality control in manufacturing and engineering tasks. Dial calipers are preferred for environments where battery dependency is a concern, providing reliable measurements in workshops and field inspections with less electronic interference. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize advanced functionality and data accuracy or simplicity and durability in typical use cases.
Choosing the Right Caliper for Your Needs
Digital calipers offer precise, easy-to-read measurements with instant metric and imperial conversions, making them ideal for users seeking speed and accuracy in diverse applications. Dial calipers provide durable, mechanical reliability without batteries, preferred for environments requiring robust tools and straightforward operation. Selecting the right caliper depends on your specific measurement requirements, work environment, and preference for either digital display convenience or traditional dial mechanics.
Digital caliper vs dial caliper Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com