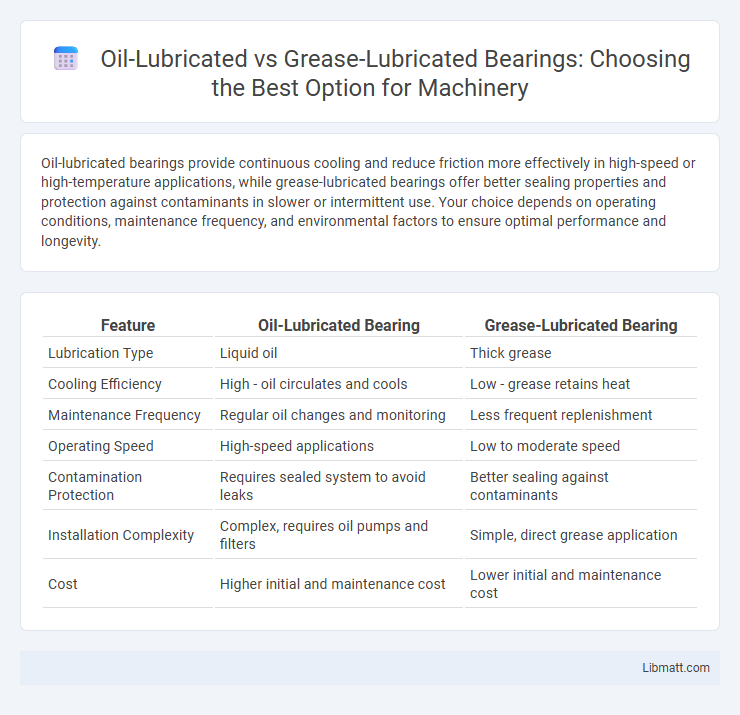
Oil-lubricated bearings provide continuous cooling and reduce friction more effectively in high-speed or high-temperature applications, while grease-lubricated bearings offer better sealing properties and protection against contaminants in slower or intermittent use. Your choice depends on operating conditions, maintenance frequency, and environmental factors to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Oil-Lubricated Bearing | Grease-Lubricated Bearing |
|---|---|---|
| Lubrication Type | Liquid oil | Thick grease |
| Cooling Efficiency | High - oil circulates and cools | Low - grease retains heat |
| Maintenance Frequency | Regular oil changes and monitoring | Less frequent replenishment |
| Operating Speed | High-speed applications | Low to moderate speed |
| Contamination Protection | Requires sealed system to avoid leaks | Better sealing against contaminants |
| Installation Complexity | Complex, requires oil pumps and filters | Simple, direct grease application |
| Cost | Higher initial and maintenance cost | Lower initial and maintenance cost |
Introduction to Bearing Lubrication Methods
Oil-lubricated bearings utilize a continuous oil film to reduce friction and dissipate heat, making them ideal for high-speed or heavy-load applications due to their superior cooling and contamination removal properties. Grease-lubricated bearings rely on a thicker, semi-solid lubricant that provides long-lasting protection and is suitable for low-speed or sealed environments where maintenance access is limited. Both methods significantly influence bearing lifespan, performance, and maintenance schedules by addressing different operational requirements and environmental conditions.
Overview of Oil-Lubricated Bearings
Oil-lubricated bearings use a continuous supply of oil to reduce friction, prevent wear, and maintain optimal operating temperatures, making them ideal for high-speed and heavy-load applications. They typically offer better heat dissipation and cleaner operation compared to grease-lubricated bearings, which rely on a thicker lubricant that stays in place but may generate more heat over time. Your machinery can achieve longer service life and improved performance with oil-lubricated bearings, especially in environments requiring precise lubrication management.
Overview of Grease-Lubricated Bearings
Grease-lubricated bearings provide effective sealing against contaminants and superior corrosion protection by using a semi-solid lubricant that adheres well to bearing surfaces. These bearings require less frequent maintenance compared to oil-lubricated types, making them ideal for applications where re-lubrication is challenging. Your machinery benefits from enhanced durability and reduced risk of lubricant leakage with grease-lubricated bearings.
Performance Comparison: Oil vs Grease Lubrication
Oil-lubricated bearings provide superior cooling and contaminant removal due to continuous oil circulation, resulting in better performance under high-speed and heavy-load conditions. Grease-lubricated bearings offer longer maintenance intervals and excellent sealing properties, making them suitable for low to moderate speeds and environments where re-lubrication is challenging. Your choice between oil and grease lubrication should consider the specific operating conditions, load, speed, and maintenance capabilities for optimal bearing performance.
Maintenance Requirements and Intervals
Oil-lubricated bearings require regular monitoring and timely oil changes, typically every 3 to 6 months depending on operating conditions, to prevent contamination and ensure optimal performance. Grease-lubricated bearings demand less frequent maintenance, often needing re-greasing only every 6 to 12 months, reducing downtime in applications with limited access. Your choice between the two should consider the ease of inspection and the intended maintenance intervals to maximize bearing lifespan and reliability.
Operating Temperature Considerations
Oil-lubricated bearings excel in high-temperature environments due to oil's superior thermal conductivity and heat dissipation properties, maintaining stable lubrication under extreme conditions. Grease-lubricated bearings are more suitable for moderate temperatures, as grease retains its consistency but may degrade or harden at elevated temperatures, reducing effectiveness. Selecting the appropriate lubrication depends on the bearing's operating temperature range, ensuring optimal performance and extended service life.
Contamination Protection and Cleanliness
Oil-lubricated bearings offer superior contamination protection by continuously flushing out debris and contaminants, maintaining a cleaner operating environment compared to grease-lubricated bearings. Grease-lubricated bearings, while providing a sealed barrier against outside contaminants, can trap dirt within the grease, potentially accelerating wear and reducing performance over time. Selecting the right lubrication type for your application is crucial to ensure optimal cleanliness and extend the bearing's service life.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-Term
Oil-lubricated bearings typically have higher initial costs due to complex sealing systems and oil circulation equipment but offer lower long-term maintenance expenses because oil's continuous lubrication reduces wear and extends bearing life. Grease-lubricated bearings generally incur lower upfront costs with simpler installation and minimal additional components; however, they often require more frequent relubrication and higher maintenance efforts, increasing total lifecycle costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership, oil-lubricated bearings may provide better economic value in high-load, high-speed applications, while grease-lubricated types suit low-speed, intermittent-use environments.
Application Suitability and Industry Use Cases
Oil-lubricated bearings provide superior cooling and are ideal for high-speed, heavy-load applications commonly found in automotive engines and industrial turbines. Grease-lubricated bearings offer better sealing and protection against contaminants, making them suitable for environments like agriculture machinery and construction equipment. Your choice depends on operational conditions, with oil lubrication preferred for continuous, high-temperature use and grease lubrication favored for intermittent or dusty settings.
Key Factors in Choosing Between Oil and Grease Lubrication
Oil-lubricated bearings offer superior cooling and continuous lubrication, making them ideal for high-speed or high-temperature applications, while grease-lubricated bearings provide better sealing and protection against contaminants in slower, lower-temperature environments. Key factors in choosing between oil and grease lubrication include operating speed, temperature range, exposure to contaminants, and maintenance intervals. Understanding these variables ensures your machinery performs optimally with the right lubrication type.
Oil-lubricated bearing vs grease-lubricated bearing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com