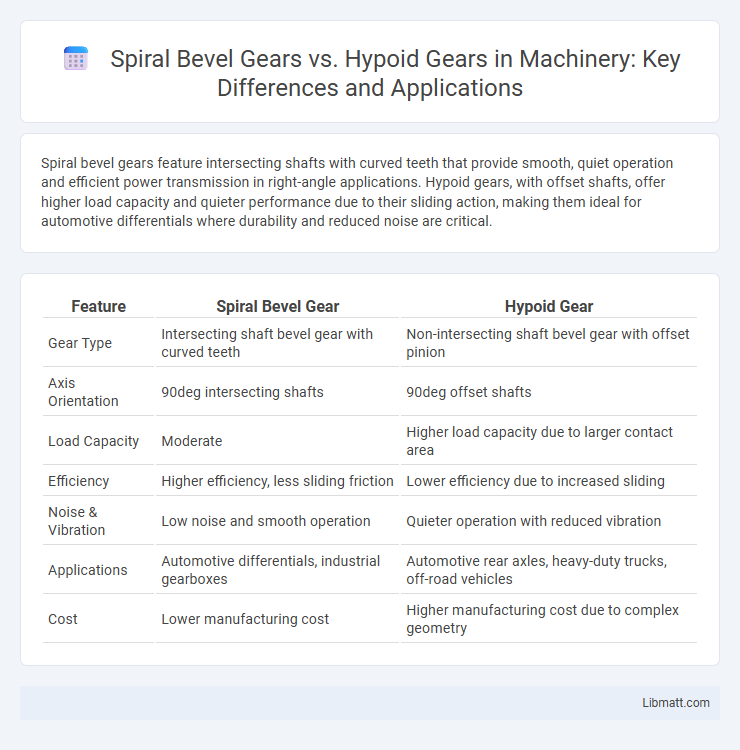
Spiral bevel gears feature intersecting shafts with curved teeth that provide smooth, quiet operation and efficient power transmission in right-angle applications. Hypoid gears, with offset shafts, offer higher load capacity and quieter performance due to their sliding action, making them ideal for automotive differentials where durability and reduced noise are critical.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Spiral Bevel Gear | Hypoid Gear |
|---|---|---|
| Gear Type | Intersecting shaft bevel gear with curved teeth | Non-intersecting shaft bevel gear with offset pinion |
| Axis Orientation | 90deg intersecting shafts | 90deg offset shafts |
| Load Capacity | Moderate | Higher load capacity due to larger contact area |
| Efficiency | Higher efficiency, less sliding friction | Lower efficiency due to increased sliding |
| Noise & Vibration | Low noise and smooth operation | Quieter operation with reduced vibration |
| Applications | Automotive differentials, industrial gearboxes | Automotive rear axles, heavy-duty trucks, off-road vehicles |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing cost | Higher manufacturing cost due to complex geometry |
Introduction to Spiral Bevel and Hypoid Gears
Spiral bevel gears feature curved teeth that engage smoothly, providing efficient power transmission in right-angle drives. Hypoid gears are an advanced type of bevel gear with an offset axis, enabling higher torque capacity and reduced noise in automotive differentials. Your choice between these gears hinges on application requirements like load, speed, and spatial constraints.
Design and Geometry Differences
Spiral bevel gears feature intersecting shafts with curved teeth that spiral along the gear face, allowing smooth and efficient torque transmission at right angles. Hypoid gears differ by having non-intersecting shafts with offset axes, enabling larger pinion diameter and higher torque capacity while reducing noise and vibration. The hypoid gear's unique geometry includes an offset between the pinion and gear shafts, resulting in sliding action on the tooth surfaces, unlike the pure rolling contact in spiral bevel gears.
How Each Gear Type Works
Spiral bevel gears transmit torque between perpendicular shafts using curved teeth cut on the cone-shaped gear body, ensuring smooth and efficient power transfer with minimal noise. Hypoid gears operate similarly but have shafts that do not intersect, featuring an offset axis that allows for larger pinion size and increased contact area, enhancing load capacity and durability. Understanding the differences in tooth geometry and shaft alignment helps you select the right gear type for your specific mechanical application.
Load Distribution and Strength Comparison
Spiral bevel gears provide smooth load distribution across the tooth surface due to their curved teeth, resulting in moderate strength suitable for lighter to medium-duty applications. Hypoid gears, featuring offset axes and larger contact surfaces, deliver superior load distribution and higher strength, making them ideal for heavy-duty, high-torque applications with enhanced durability. Your choice between the two should consider the load requirements and desired gear strength for optimal performance.
Efficiency and Power Transmission
Spiral bevel gears generally offer higher mechanical efficiency due to their simpler meshing action, resulting in less friction and heat generation during power transmission. Hypoid gears, with their offset axes, provide smoother operation and greater load capacity but experience slightly lower efficiency because of increased sliding contact between the gear teeth. In high-torque applications like automotive differentials, hypoid gears transmit more power effectively despite marginally reduced efficiency compared to spiral bevel gears.
Noise, Vibration, and Smoothness of Operation
Spiral bevel gears generate moderate noise and vibration levels due to their curved tooth design, offering relatively smooth operation in automotive applications. Hypoid gears, with their offset axes and sliding action, typically produce lower noise and vibration, resulting in quieter and smoother performance, especially under high-load conditions. The hypoid gear's enhanced meshing characteristics improve operational smoothness, making it a preferred choice for rear axle drives where noise reduction is critical.
Lubrication and Maintenance Requirements
Spiral bevel gears require high-quality, synthetic gear oils with proper additives to ensure effective lubrication under moderate sliding and rolling contact. Hypoid gears experience more sliding action and heat generation, necessitating specialized hypoid gear oils with extreme pressure (EP) additives for optimal wear protection and thermal stability. Regular maintenance for hypoid gears involves monitoring oil condition and timely changes to prevent pitting and scoring, while spiral bevel gears demand less frequent oil changes but consistent checks for gear alignment and lubricant contamination.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Spiral bevel gears typically have lower manufacturing costs due to simpler machining processes and less stringent tolerances compared to hypoid gears, which require more complex cutting techniques and precise alignment. Hypoid gears involve specialized tooling and harder materials, increasing production expenses but offering improved strength and smoother operation. Cost efficiency depends on the application requirements, with spiral bevel gears favored for budget-conscious projects and hypoid gears chosen for high-performance, durability-focused designs.
Best Applications for Spiral Bevel and Hypoid Gears
Spiral bevel gears excel in applications requiring precise torque transfer between intersecting shafts at right angles, commonly found in automotive differentials and aerospace mechanisms due to their smooth operation and high efficiency. Hypoid gears are ideal for use in automotive rear axles and heavy machinery, where their ability to handle higher torque loads and offset shaft design improve durability and load capacity. Both gear types are essential in power transmission systems but are selected based on specific requirements such as load, speed, and spatial constraints.
Choosing the Right Gear for Your Application
Selecting the right gear for your application depends on load capacity, efficiency, and noise considerations. Spiral bevel gears offer high efficiency and smooth operation, making them ideal for moderate load applications requiring precision. Hypoid gears provide greater torque capacity and quieter performance, suited for heavy-duty automotive differentials and high-load machinery.
Spiral bevel gear vs hypoid gear Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com