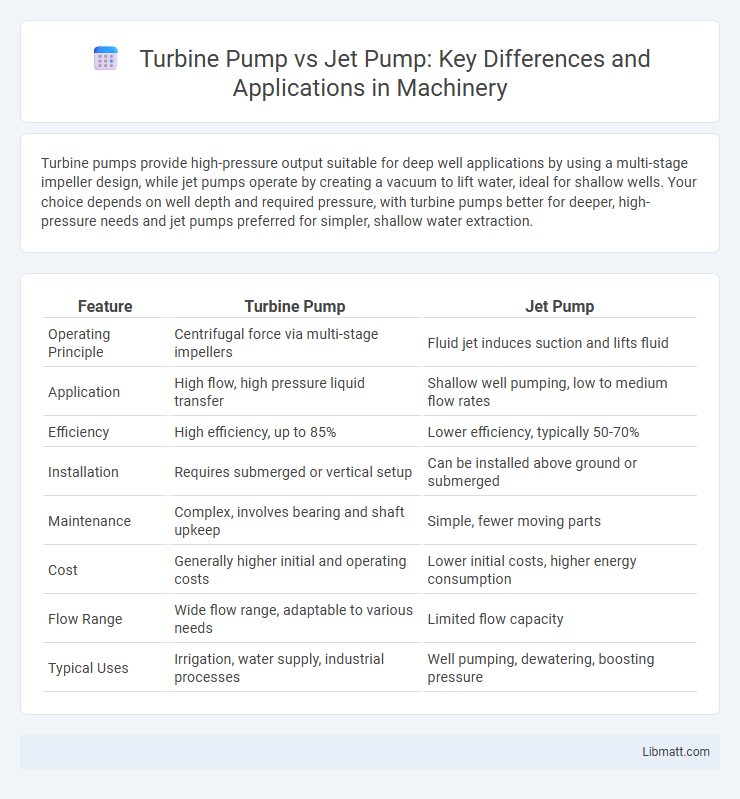
Turbine pumps provide high-pressure output suitable for deep well applications by using a multi-stage impeller design, while jet pumps operate by creating a vacuum to lift water, ideal for shallow wells. Your choice depends on well depth and required pressure, with turbine pumps better for deeper, high-pressure needs and jet pumps preferred for simpler, shallow water extraction.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Turbine Pump | Jet Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Principle | Centrifugal force via multi-stage impellers | Fluid jet induces suction and lifts fluid |
| Application | High flow, high pressure liquid transfer | Shallow well pumping, low to medium flow rates |
| Efficiency | High efficiency, up to 85% | Lower efficiency, typically 50-70% |
| Installation | Requires submerged or vertical setup | Can be installed above ground or submerged |
| Maintenance | Complex, involves bearing and shaft upkeep | Simple, fewer moving parts |
| Cost | Generally higher initial and operating costs | Lower initial costs, higher energy consumption |
| Flow Range | Wide flow range, adaptable to various needs | Limited flow capacity |
| Typical Uses | Irrigation, water supply, industrial processes | Well pumping, dewatering, boosting pressure |
Introduction to Turbine Pumps and Jet Pumps
Turbine pumps utilize multiple impellers mounted on a shaft to generate high pressure and flow in applications such as water supply and industrial processes. Jet pumps operate by creating a vacuum through a high-velocity jet of fluid, drawing water from wells or reservoirs without moving parts submerged in the fluid. Both pumps serve critical roles in fluid transfer, with turbine pumps excelling in consistent high-pressure output and jet pumps known for simplicity and reliable suction capabilities.
How Turbine Pumps Work
Turbine pumps operate by using a rotating impeller to draw fluid into the pump and accelerate it through multiple stages, creating high pressure for efficient fluid movement. These pumps are ideal for deep well applications where high volumes and consistent pressure are required, efficiently handling fluids with minimal cavitation risk. Your choice of turbine pumps ensures reliable performance in demanding water supply and industrial systems due to their robust design and ability to maintain steady flow rates at various depths.
How Jet Pumps Operate
Jet pumps operate by utilizing a high-velocity jet of fluid to create a pressure differential that draws fluid from a source, enabling efficient water lifting from deep wells or difficult-to-reach areas. The pump consists of a nozzle and venturi, where fluid accelerates through the nozzle, decreasing pressure in the venturi section and causing suction that pulls additional fluid. Your system's performance depends on correctly matching the jet pump design to the required lift and flow rate for optimal efficiency.
Key Differences Between Turbine and Jet Pumps
Turbine pumps use a rotating impeller to move fluid efficiently at high pressures, making them ideal for deep well applications and continuous flow requirements. Jet pumps operate based on fluid dynamics principles, using a high-velocity jet of water to create suction and lift water, suited for shallow wells and variable flow conditions. Understanding these key differences helps you select the right pump for your specific depth and performance needs.
Efficiency Comparison: Turbine vs Jet Pumps
Turbine pumps typically offer higher efficiency than jet pumps due to their design, which minimizes energy loss during fluid transfer and is optimized for high flow rates and high pressure applications. Jet pumps rely on fluid dynamics involving a motive fluid to lift or move another fluid, resulting in lower overall efficiency because of energy conversion losses and mixed flow turbulence. In applications demanding consistent high efficiency and energy savings, turbine pumps are preferred over jet pumps, especially in industrial and agricultural water systems.
Applications of Turbine Pumps
Turbine pumps are widely used in applications requiring high flow rates and moderate to high pressure, such as water supply systems, irrigation, and industrial processes. Their vertical design makes them ideal for deep well pumping, cooling tower circulation, and boiler feedwater delivery. You can rely on turbine pumps for reliable performance in municipal water treatment, fire protection systems, and agricultural water distribution.
Applications of Jet Pumps
Jet pumps are widely used in applications requiring fluid transfer from deep wells or locations with limited space, such as agricultural irrigation, municipal water supply, and oil extraction. Their ability to operate efficiently without moving parts in the submerged section makes them ideal for pumping fluids with solids or corrosive properties. You can rely on jet pumps for cost-effective, low-maintenance solutions in demanding environments where conventional turbine pumps might face operational challenges.
Cost Analysis: Turbine Pumps vs Jet Pumps
Turbine pumps generally exhibit higher initial capital costs compared to jet pumps due to their complex design and enhanced efficiency for high-flow applications. Jet pumps offer a cost-effective solution with lower upfront expenses, but incur higher operational costs because of reduced energy efficiency and increased maintenance needs. For long-term investments, turbine pumps provide superior cost benefits through energy savings and durability, offsetting their greater initial expenditure.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Pump Type
Turbine pumps offer high efficiency and can handle large volumes of water at high pressures, making them ideal for deep well applications but they require significant maintenance due to their complex components. Jet pumps are simpler, less expensive, and versatile for shallow wells, yet they provide lower efficiency and limited lift capabilities compared to turbine pumps. Understanding your specific pumping needs will help you determine if the high performance of a turbine pump or the cost-effectiveness of a jet pump suits your project best.
Choosing the Right Pump for Your Needs
Turbine pumps excel in applications requiring high flow rates and consistent pressure, making them ideal for irrigation, municipal water supply, and industrial processes. Jet pumps are better suited for shallow wells and situations where the pump must create suction to lift water from below the pump level, often used in residential water systems. Evaluating factors like water source depth, required pressure, and flow rate ensures selecting the right pump type for efficient and reliable performance.
Turbine pump vs jet pump Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com