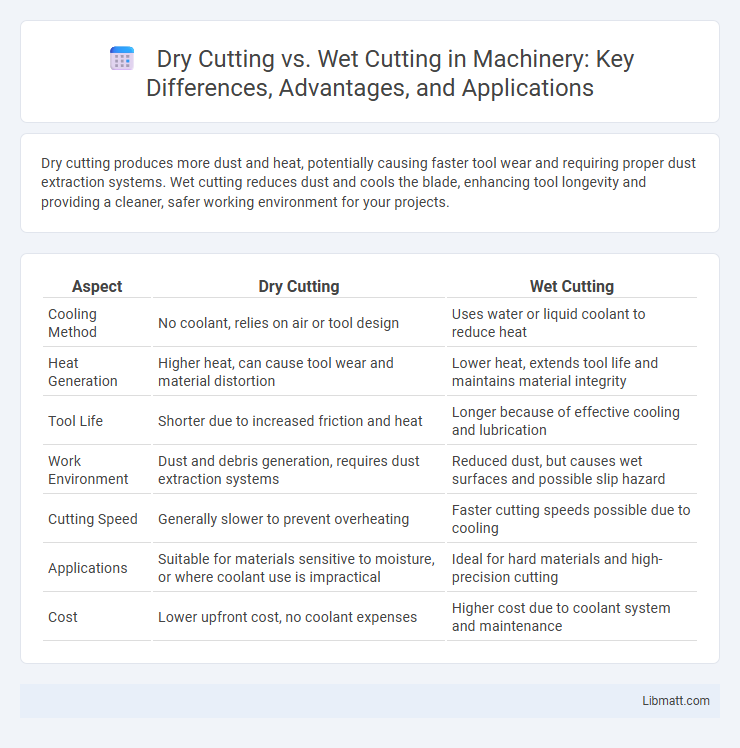
Dry cutting produces more dust and heat, potentially causing faster tool wear and requiring proper dust extraction systems. Wet cutting reduces dust and cools the blade, enhancing tool longevity and providing a cleaner, safer working environment for your projects.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Dry Cutting | Wet Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Method | No coolant, relies on air or tool design | Uses water or liquid coolant to reduce heat |
| Heat Generation | Higher heat, can cause tool wear and material distortion | Lower heat, extends tool life and maintains material integrity |
| Tool Life | Shorter due to increased friction and heat | Longer because of effective cooling and lubrication |
| Work Environment | Dust and debris generation, requires dust extraction systems | Reduced dust, but causes wet surfaces and possible slip hazard |
| Cutting Speed | Generally slower to prevent overheating | Faster cutting speeds possible due to cooling |
| Applications | Suitable for materials sensitive to moisture, or where coolant use is impractical | Ideal for hard materials and high-precision cutting |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost, no coolant expenses | Higher cost due to coolant system and maintenance |
Introduction to Dry Cutting and Wet Cutting
Dry cutting uses high-speed blades without water, generating significant heat and dust, making it suitable for quick, precise cuts on materials like metal or concrete where dust control isn't critical. Wet cutting employs water to cool the blade and suppress dust, enhancing blade longevity and reducing airborne particles, which is essential for health and safety in confined or indoor environments. Your choice between dry and wet cutting depends on material properties, job site conditions, and dust management requirements.
Key Differences Between Dry Cutting and Wet Cutting
Dry cutting generates higher dust levels and heat, requiring effective dust extraction systems and cooling methods to prevent tool damage and improve safety. Wet cutting uses water or other fluids to suppress dust and cool the blade, enhancing cutting precision and extending tool life while reducing airborne particles. Choosing between the two depends on material type, environmental conditions, and specific safety regulations in construction or manufacturing settings.
Advantages of Dry Cutting
Dry cutting eliminates the need for water or coolant, reducing mess and cleanup time on job sites. It allows for greater portability and ease of use in environments lacking water sources, making it ideal for outdoor or remote projects. Additionally, dry cutting often results in faster cutting speeds and improved visibility of the cutting line, enhancing precision and productivity.
Advantages of Wet Cutting
Wet cutting offers superior dust suppression, significantly reducing airborne particulates and enhancing worker safety in construction and fabrication environments. The use of water during wet cutting minimizes blade overheating, extending tool life and maintaining cutting precision. This method also improves visibility by clearing debris from the cutting area, leading to cleaner and more accurate cuts.
Disadvantages of Dry Cutting
Dry cutting generates significant heat and dust, increasing the risk of blade damage and equipment wear. The absence of coolant can lead to faster tool deterioration and lower precision due to thermal expansion. Dust inhalation poses health hazards, making dry cutting less suitable for indoor or poorly ventilated environments.
Disadvantages of Wet Cutting
Wet cutting involves using water to suppress dust and cool the blade, but it presents several disadvantages such as increased water consumption, potential water runoff contamination, and the need for effective water management systems to prevent environmental damage. It can also create a slippery work surface, raising the risk of accidents and reducing operational efficiency. Furthermore, the use of water may cause corrosion in some cutting equipment, increasing maintenance requirements and costs.
Safety Considerations for Both Methods
Dry cutting generates significant dust and airborne particles, posing inhalation risks that necessitate proper respiratory protection and adequate ventilation to ensure your safety. Wet cutting reduces dust exposure by using water to suppress particles, lowering the risk of respiratory issues but requiring caution to prevent electrical hazards and slips from wet surfaces. Both methods demand appropriate personal protective equipment and adherence to safety protocols to mitigate risks associated with dust, debris, and tool handling.
Tools and Equipment Used in Each Technique
Dry cutting utilizes abrasives like diamond blades or carbide-tipped tools designed to operate without coolant, often paired with dust extraction systems to manage airborne particles. Wet cutting employs similar diamond or carbide blades but requires water delivery systems such as pumps, hoses, and spray nozzles to cool the blade and suppress dust during operation. Both techniques depend on specialized saws or grinders optimized for their specific cooling and dust control methods to enhance tool longevity and worker safety.
Best Applications for Dry and Wet Cutting
Dry cutting is best suited for applications involving softer materials, light-duty tasks, and situations where water is unavailable, such as cutting wood, plastics, or drywall. Wet cutting is ideal for heavy-duty jobs requiring dust suppression and cooling, particularly when working with concrete, stone, masonry, and metal. Your choice between dry and wet cutting depends on the material hardness, dust control needs, and the cutting environment.
Choosing the Right Cutting Method for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate cutting method depends on your project's material, precision requirements, and safety considerations. Dry cutting is ideal for smaller, quick jobs with materials that produce minimal dust, while wet cutting uses water to reduce dust and heat, making it suitable for thicker, denser materials like concrete or stone. Consider your project's environment and equipment capabilities to optimize efficiency and ensure the best results.
Dry cutting vs wet cutting Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com