A lathe machine is designed primarily for rotating workpieces to perform operations such as cutting, sanding, and drilling along the axis, making it ideal for creating cylindrical shapes. In contrast, a milling machine moves the cutting tool against a stationary workpiece, enabling you to create complex shapes, slots, and holes with precise control over multiple axes.
Table of Comparison
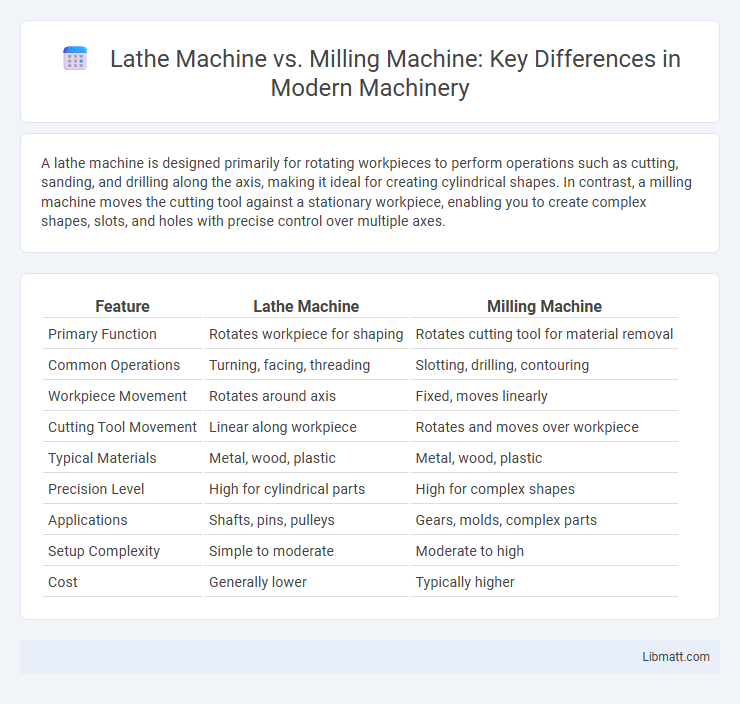
| Feature | Lathe Machine | Milling Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Rotates workpiece for shaping | Rotates cutting tool for material removal |
| Common Operations | Turning, facing, threading | Slotting, drilling, contouring |
| Workpiece Movement | Rotates around axis | Fixed, moves linearly |
| Cutting Tool Movement | Linear along workpiece | Rotates and moves over workpiece |
| Typical Materials | Metal, wood, plastic | Metal, wood, plastic |
| Precision Level | High for cylindrical parts | High for complex shapes |
| Applications | Shafts, pins, pulleys | Gears, molds, complex parts |
| Setup Complexity | Simple to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher |
Introduction to Lathe and Milling Machines
Lathe machines are primarily used for cutting, shaping, and drilling materials by rotating the workpiece against a stationary cutting tool, making them ideal for cylindrical or symmetrical parts. Milling machines operate by moving a rotating cutting tool along multiple axes to remove material from a stationary workpiece, allowing complex shapes and surfaces to be created. Both are essential in manufacturing, with lathes excelling in turning operations and milling machines offering versatile machining capabilities.
Key Differences Between Lathe and Milling Machines
Lathe machines rotate the workpiece against a cutting tool primarily for shaping cylindrical parts, while milling machines use rotary cutters to remove material from a stationary workpiece, ideal for complex shapes and surfaces. Key differences include the motion type--lathe offers rotational movement of the workpiece, and milling provides multi-axis tool movement--and the typical applications, with lathes excelling in turning operations and milling machines in slotting, drilling, and contouring. Your choice depends on the specific machining task, material, and precision required for the finished product.
Construction and Design Comparison
Lathe machines feature a rotating workpiece with stationary cutting tools, characterized by a robust bed, headstock, and tailstock that ensure precision in cylindrical shaping tasks. Milling machines incorporate a movable table and a rotating cutting tool, offering versatility in handling complex geometries and multi-axis operations due to their spindle and column design. Your choice depends on the desired machining process, where lathe machines excel in turning and milling machines dominate in cutting flat or irregular surfaces.
Working Principles Explained
A lathe machine operates by rotating the workpiece around a fixed axis while a cutting tool moves linearly to shape the material, primarily used for cylindrical parts. In contrast, a milling machine holds the workpiece stationary while the rotating cutting tool moves along multiple axes to remove material, suitable for complex shapes and surface contours. Both machines rely on precise control of cutting speed and feed rate to achieve accurate dimensions and surface finishes.
Types of Operations Performed
Lathe machines primarily perform turning operations, where the workpiece rotates against a cutting tool to shape cylindrical parts, including drilling, threading, and facing. Milling machines execute a variety of cutting tasks by moving the workpiece against a rotating multi-tooth cutter, capable of operations like slotting, contouring, drilling, and gear cutting. Your choice depends on whether you need rotary shaping with precision or complex surfaces and profiles created through multi-directional cutting.
Advantages of Lathe Machines
Lathe machines offer precise cylindrical shaping by rotating the workpiece against a cutting tool, making them ideal for creating symmetrical objects like shafts and bolts. Their simplicity, affordability, and ease of setup provide cost-effective solutions for turning tasks compared to milling machines. You benefit from faster production times and superior surface finish when working with lathe machines in metalworking projects.
Benefits of Milling Machines
Milling machines offer precise material removal and complex shaping capabilities, making them ideal for creating intricate parts with tight tolerances. Your projects benefit from versatile tooling options and adaptability to various materials such as metals, plastics, and composites. Enhanced efficiency in rapid prototyping and production environments makes milling machines a valuable asset in modern manufacturing.
Applications in Various Industries
Lathe machines excel in industries requiring precise cylindrical shaping, such as automotive, aerospace, and metalworking, for tasks like turning, threading, and drilling cylindrical parts. Milling machines are vital in electronics, aerospace, and manufacturing sectors for cutting complex shapes, slots, and gears on flat or irregular surfaces with high accuracy. Both machines serve critical roles in tooling and prototyping but differ significantly in their machining capabilities and applications across industrial processes.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Lathe and Milling Machines
When choosing between lathe and milling machines, consider the type of workpiece and desired operations: lathes excel at cylindrical shaping and turning, while milling machines are ideal for complex surface contours and slot cutting. Evaluate precision requirements, as milling machines often offer higher versatility in creating detailed features, whereas lathes provide efficient rotational symmetry. Your decision should also factor in production volume, machine size, and tooling costs to optimize efficiency and budget.
Conclusion: Which is Best for Your Needs?
Choosing between a lathe machine and a milling machine depends on the specific machining tasks and material requirements. Lathe machines excel in cylindrical and rotational parts, offering precision for turning, facing, and threading operations, while milling machines provide versatile capabilities for complex shapes, slots, and surface contouring with multiple axes. Evaluating project complexity, desired finish, and production volume helps determine whether a lathe's specialization or a milling machine's multifaceted use best suits your manufacturing needs.
Lathe machine vs milling machine Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com