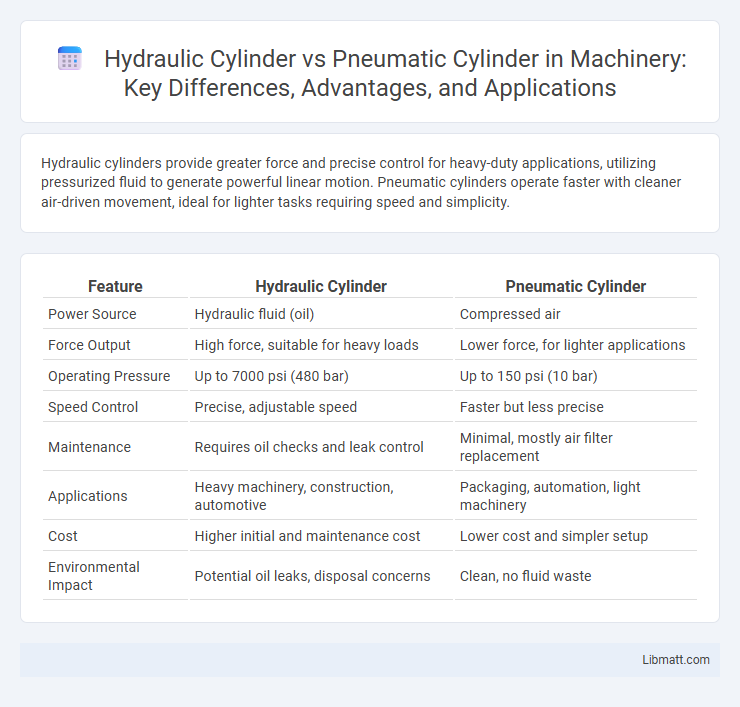
Hydraulic cylinders provide greater force and precise control for heavy-duty applications, utilizing pressurized fluid to generate powerful linear motion. Pneumatic cylinders operate faster with cleaner air-driven movement, ideal for lighter tasks requiring speed and simplicity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hydraulic Cylinder | Pneumatic Cylinder |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Hydraulic fluid (oil) | Compressed air |
| Force Output | High force, suitable for heavy loads | Lower force, for lighter applications |
| Operating Pressure | Up to 7000 psi (480 bar) | Up to 150 psi (10 bar) |
| Speed Control | Precise, adjustable speed | Faster but less precise |
| Maintenance | Requires oil checks and leak control | Minimal, mostly air filter replacement |
| Applications | Heavy machinery, construction, automotive | Packaging, automation, light machinery |
| Cost | Higher initial and maintenance cost | Lower cost and simpler setup |
| Environmental Impact | Potential oil leaks, disposal concerns | Clean, no fluid waste |
Introduction to Hydraulic and Pneumatic Cylinders
Hydraulic cylinders use pressurized fluid to generate powerful linear motion and force, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications requiring high load capacities. Pneumatic cylinders rely on compressed air to create motion, offering faster response times and cleaner operation suited for lighter tasks and environments where fluid leaks must be avoided. Understanding the differences between hydraulic and pneumatic cylinders helps you select the right actuator based on power, speed, and application requirements.
How Hydraulic Cylinders Work
Hydraulic cylinders operate by converting hydraulic energy into mechanical force through the movement of fluid under pressure within a sealed chamber. A piston inside the cylinder moves back and forth as pressurized hydraulic fluid enters and exits, creating linear motion ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring high force. Understanding how hydraulic cylinders work can help you select the right actuator for tasks demanding precise control and durability.
How Pneumatic Cylinders Work
Pneumatic cylinders operate by using compressed air to create linear motion, where air pressure pushes a piston inside the cylinder to extend or retract the rod. These cylinders are known for their speed, cleanliness, and ability to function in environments where hydraulic fluids might pose contamination risks. Understanding how pneumatic cylinders work allows you to select the right actuator for applications requiring rapid, lightweight, and low-force movement compared to hydraulic cylinders.
Key Differences Between Hydraulic and Pneumatic Cylinders
Hydraulic cylinders use incompressible fluids like oil to generate high force with precise control, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications requiring strong, consistent power. Pneumatic cylinders utilize compressed air, offering faster movement and simpler design but with lower force output and less precise control due to air compressibility. Key differences include hydraulic cylinders' higher force capacity, better load holding, and slower speed, compared to pneumatic cylinders' quicker operation, cleaner setup, and easier maintenance.
Advantages of Hydraulic Cylinders
Hydraulic cylinders provide significantly higher force output compared to pneumatic cylinders due to the incompressibility of hydraulic fluid, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications. They offer precise control and smooth movement under high loads, which enhances performance in manufacturing, construction, and automotive machinery. The robust design of hydraulic cylinders ensures durability and reliability in demanding environments, outperforming pneumatic alternatives in terms of power density and operational lifespan.
Benefits of Pneumatic Cylinders
Pneumatic cylinders offer fast response times and smooth operation, making them ideal for repetitive motion applications with moderate force requirements. They provide a clean, reliable power source powered by compressed air, reducing maintenance costs and increasing system longevity. Your equipment benefits from lightweight design and safer operation in hazardous environments due to lower pressure levels compared to hydraulic systems.
Common Applications for Hydraulic Cylinders
Hydraulic cylinders are commonly used in heavy machinery such as construction equipment, industrial presses, and agricultural machinery due to their ability to generate high force and precise control. They are ideal for applications requiring heavy lifting, pushing, or pulling, including excavators, forklifts, and hydraulic presses. These cylinders excel in environments demanding powerful and consistent motion under high pressure.
Typical Uses for Pneumatic Cylinders
Pneumatic cylinders are commonly used in automation systems, packaging machinery, and material handling due to their fast operation and clean energy source. They are ideal for applications requiring lightweight force and repeated motion, such as conveyor systems and robotics in food processing plants. Your choice of pneumatic cylinders supports efficient, low-maintenance performance in environments where compressed air is readily available.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Hydraulic and Pneumatic Cylinders
When selecting between hydraulic and pneumatic cylinders, consider factors such as force requirements, with hydraulic cylinders providing higher force and pneumatic cylinders suited for lighter loads. The operating environment plays a crucial role, as hydraulic systems handle high-pressure and harsh conditions better, while pneumatic systems excel in clean and fast applications. Maintenance complexity and cost should also be evaluated, since hydraulic cylinders demand more upkeep and fluid management compared to the simpler pneumatic counterparts.
Summary: Which Cylinder is Right for Your Application?
Hydraulic cylinders deliver high force and precise control, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring powerful lifting or pushing. Pneumatic cylinders offer faster speeds and cleaner operation, well-suited for lighter loads and repetitive motions in automation tasks. Your choice depends on factors like required force, speed, environmental conditions, and system complexity.
Hydraulic cylinder vs pneumatic cylinder Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com