Oil-lubricated compressors provide superior durability and quieter operation by minimizing internal friction, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications. Oil-free compressors offer low maintenance and cleaner air output, perfect for environments where contamination must be avoided, ensuring your equipment runs efficiently without oil-related concerns.
Table of Comparison
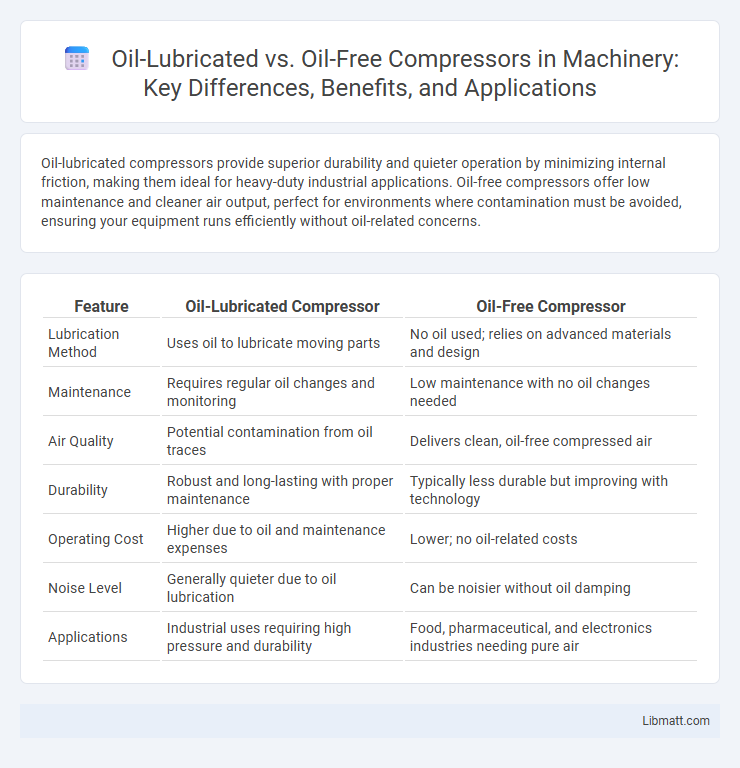
| Feature | Oil-Lubricated Compressor | Oil-Free Compressor |
|---|---|---|
| Lubrication Method | Uses oil to lubricate moving parts | No oil used; relies on advanced materials and design |
| Maintenance | Requires regular oil changes and monitoring | Low maintenance with no oil changes needed |
| Air Quality | Potential contamination from oil traces | Delivers clean, oil-free compressed air |
| Durability | Robust and long-lasting with proper maintenance | Typically less durable but improving with technology |
| Operating Cost | Higher due to oil and maintenance expenses | Lower; no oil-related costs |
| Noise Level | Generally quieter due to oil lubrication | Can be noisier without oil damping |
| Applications | Industrial uses requiring high pressure and durability | Food, pharmaceutical, and electronics industries needing pure air |
Introduction to Air Compressors
Air compressors, essential for converting power into pressurized air, come in two main types: oil-lubricated and oil-free. Oil-lubricated compressors offer enhanced durability and quieter operation due to their self-lubricating components, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial use. Your choice between these compressors depends on maintenance preferences, application requirements, and the need for clean air output.
Understanding Oil-Lubricated Compressors
Oil-lubricated compressors utilize a continuous oil film to reduce friction between moving parts, enhancing durability and performance in heavy-duty industrial applications. Their design allows for higher pressure output and quieter operation compared to oil-free models, making them ideal for demanding tasks requiring consistent efficiency. Understanding these features helps you select the best compressor type for applications where longevity and reliability are critical.
What Are Oil-Free Compressors?
Oil-free compressors use advanced materials like Teflon-coated pistons or composites to eliminate the need for oil lubrication, ensuring cleaner, contamination-free air. These compressors are ideal for applications requiring high air purity, such as medical, food processing, and electronics industries. Understanding your needs helps determine if an oil-free compressor offers the best balance of maintenance ease and air quality for your operation.
Key Differences Between Oil-Lubricated and Oil-Free Compressors
Oil-lubricated compressors use oil to reduce friction and wear, offering higher durability and quieter operation, ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications. Oil-free compressors rely on alternative materials and designs to prevent contamination, making them suitable for environments requiring clean air, such as medical and food industries. Key differences include maintenance frequency, operational lifespan, noise levels, and air purity, with oil-lubricated models requiring regular oil changes and oil-free units offering lower maintenance but typically higher noise.
Performance and Efficiency Comparison
Oil-lubricated compressors typically offer higher performance and efficiency due to superior lubrication, which reduces friction and wear on moving parts, extending the equipment's lifespan. In contrast, oil-free compressors require less maintenance and produce cleaner air but may experience faster wear and slightly lower energy efficiency. Your choice depends on balancing the need for high durability and efficiency against the desire for low maintenance and contamination-free operation.
Maintenance Requirements and Costs
Oil-lubricated compressors require regular oil changes and filter replacements to maintain optimal performance, which increases maintenance time and costs compared to oil-free compressors. Oil-free compressors eliminate the need for oil maintenance, reducing downtime and expenses associated with oil disposal and contamination risks. The higher initial investment for oil-free models can be offset by lower long-term maintenance costs and enhanced reliability in sensitive applications.
Applications and Industry Uses
Oil-lubricated compressors are widely used in heavy-duty industrial applications such as manufacturing, automotive repair, and large-scale HVAC systems due to their durability and ability to handle continuous, high-pressure operation. Oil-free compressors are preferred in industries requiring clean, contaminant-free air, including pharmaceuticals, food and beverage production, and electronics manufacturing where air purity is critical. Both types serve distinct roles, with oil-lubricated models excelling in power-intensive tasks and oil-free units ensuring compliance with stringent hygiene and safety standards.
Noise Levels and Work Environment Impact
Oil-lubricated compressors generally produce lower noise levels due to the lubricating oil's ability to dampen mechanical vibrations, making them suitable for indoor or noise-sensitive work environments. Oil-free compressors tend to generate higher noise levels because they lack the dampening effect of oil, which can impact worker comfort in enclosed or quiet settings. Selecting between the two depends on balancing noise sensitivity requirements and maintenance preferences within the specific work environment.
Longevity and Reliability Factors
Oil-lubricated compressors offer superior longevity and reliability due to continuous lubrication that reduces internal wear and prevents overheating, making them ideal for heavy-duty and industrial applications. Oil-free compressors eliminate contamination risks and require less maintenance but may experience shorter lifespans and increased wear under high-stress or continuous-use conditions. Your choice between these compressor types should consider the balance between maintenance demands, operational environment, and desired equipment lifespan.
Choosing the Right Compressor for Your Needs
Oil-lubricated compressors offer superior durability and quieter operation, making them ideal for heavy-duty tasks and continuous use in industrial settings. Oil-free compressors require less maintenance and are preferred for applications needing clean, oil-free air, such as in food processing or medical environments. Evaluating your usage frequency, maintenance capability, and air quality requirements helps you choose the right compressor that balances performance and operational costs.
Oil-lubricated vs oil-free compressor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com