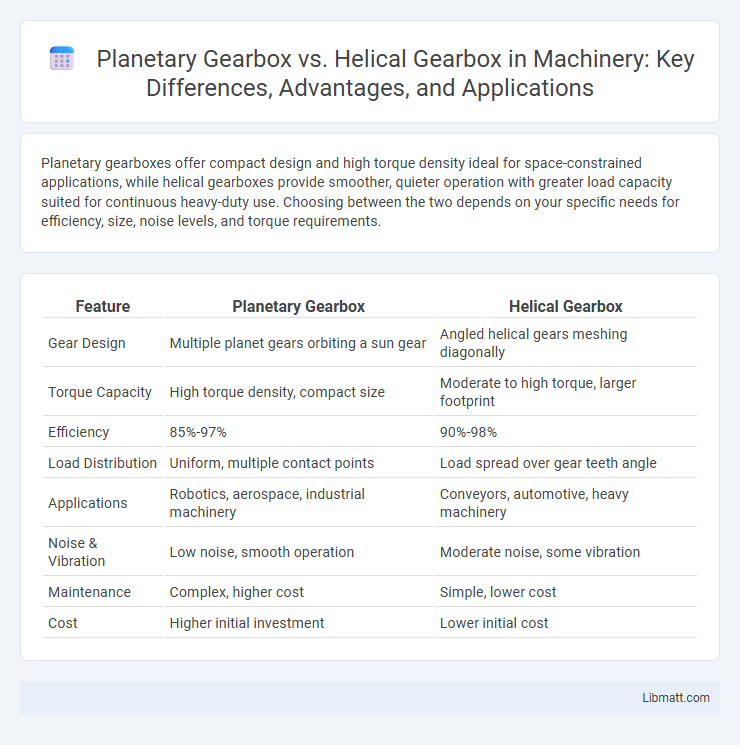
Planetary gearboxes offer compact design and high torque density ideal for space-constrained applications, while helical gearboxes provide smoother, quieter operation with greater load capacity suited for continuous heavy-duty use. Choosing between the two depends on your specific needs for efficiency, size, noise levels, and torque requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Planetary Gearbox | Helical Gearbox |
|---|---|---|
| Gear Design | Multiple planet gears orbiting a sun gear | Angled helical gears meshing diagonally |
| Torque Capacity | High torque density, compact size | Moderate to high torque, larger footprint |
| Efficiency | 85%-97% | 90%-98% |
| Load Distribution | Uniform, multiple contact points | Load spread over gear teeth angle |
| Applications | Robotics, aerospace, industrial machinery | Conveyors, automotive, heavy machinery |
| Noise & Vibration | Low noise, smooth operation | Moderate noise, some vibration |
| Maintenance | Complex, higher cost | Simple, lower cost |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower initial cost |
Overview of Planetary and Helical Gearboxes
Planetary gearboxes feature a central sun gear, multiple planet gears, and an outer ring gear, offering high torque density, compact design, and excellent load distribution ideal for applications requiring precision and durability. Helical gearboxes utilize helical gears with angled teeth that provide smooth and quiet operation, efficient power transmission, and high-speed capabilities, making them suitable for conveyors, compressors, and automotive drives. Both gearboxes serve distinct industrial needs, with planetary gearboxes excelling in high torque and space-constrained environments, while helical gearboxes perform well in high-speed, low-to-medium torque applications.
Key Differences in Design and Structure
Planetary gearboxes feature a central sun gear surrounded by multiple planet gears that rotate around it, providing high torque density and compact design ideal for space-limited applications. Helical gearboxes consist of parallel or crossed helical gears with angled teeth, offering smoother operation, higher load capacity, and quieter performance. Your choice depends on the need for torque efficiency and structural compactness in planetary gearboxes versus the balanced speed, load handling, and noise reduction of helical gearboxes.
Efficiency Comparison: Planetary vs Helical Gearboxes
Planetary gearboxes typically offer higher efficiency, often reaching up to 97%, due to their compact design and load distribution across multiple planet gears, reducing friction and wear. Helical gearboxes, while efficient in the range of 94-96%, generate more axial load and friction because of the angled teeth, which can slightly reduce their overall efficiency. The choice between planetary and helical gearboxes depends on the specific application's torque requirements, space constraints, and the desired balance between efficiency and durability.
Torque Transmission Capabilities
Planetary gearboxes provide superior torque transmission capabilities due to their multiple gear contact points, distributing loads evenly and enabling higher torque density within a compact design. Helical gearboxes, while efficient and capable of handling moderate torque, typically offer less torque capacity compared to planetary systems because of their single gear mesh arrangement. Your selection should consider the torque requirements of your application, as planetary gearboxes excel in high-torque scenarios requiring durability and precise load sharing.
Space and Weight Considerations
Planetary gearboxes offer a compact design and higher torque density, making them ideal for applications with strict space and weight constraints, such as aerospace and robotics. Helical gearboxes, while efficient and capable of handling high loads, typically require more installation space and have a heavier build due to their parallel shaft configuration. The planetary system's coaxial arrangement leads to better power-to-weight ratios compared to the bulkier helical gear mechanisms.
Applications in Various Industries
Planetary gearboxes are widely used in robotics, aerospace, and heavy machinery due to their compact size, high torque density, and efficiency in transmitting power under varying load conditions. Helical gearboxes dominate automotive, conveyors, and industrial equipment applications, offering smooth and quiet operation along with high load-carrying capacity and durability. Both gear types enhance precision and reliability in manufacturing, but planetary gearboxes excel in applications requiring compactness and torque, while helical gearboxes suit continuous, high-speed operations.
Maintenance and Durability Factors
Planetary gearboxes offer enhanced durability due to their load distribution across multiple gears, reducing wear and extending maintenance intervals compared to helical gearboxes. Helical gearboxes, while providing smoother operation and higher efficiency, typically require more frequent alignment checks and lubricant changes to maintain optimal performance. Both gearbox types benefit from proper lubrication and periodic inspection, but planetary gearboxes generally demand less maintenance due to their robust design and balanced load handling.
Cost Comparison and Investment Value
Planetary gearboxes typically offer higher initial costs due to their complex design and superior torque density, but they provide excellent investment value through enhanced efficiency and longer service life. Helical gearboxes generally have lower upfront costs and simpler maintenance, appealing to budget-conscious operations with less demanding torque requirements. Your choice should weigh upfront expenses against long-term performance benefits to maximize return on investment.
Noise and Vibration Levels
Planetary gearboxes typically produce lower noise and vibration levels due to their load distribution across multiple gears, resulting in smoother operation. Helical gearboxes generate moderate noise and vibration as their angled teeth mesh gradually but focus stress on fewer gear pairs. Optimizing gear design and materials in both gearbox types can further reduce acoustic emissions and enhance vibration control.
Choosing the Right Gearbox for Your Application
Selecting the right gearbox depends on torque requirements, space constraints, and load distribution. Planetary gearboxes offer high torque density, compact design, and better load sharing, making them ideal for precision applications with limited space. Helical gearboxes provide smoother operation and higher efficiency at lower speeds, suitable for applications needing quiet performance and consistent power transmission.
Planetary gearbox vs helical gearbox Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com