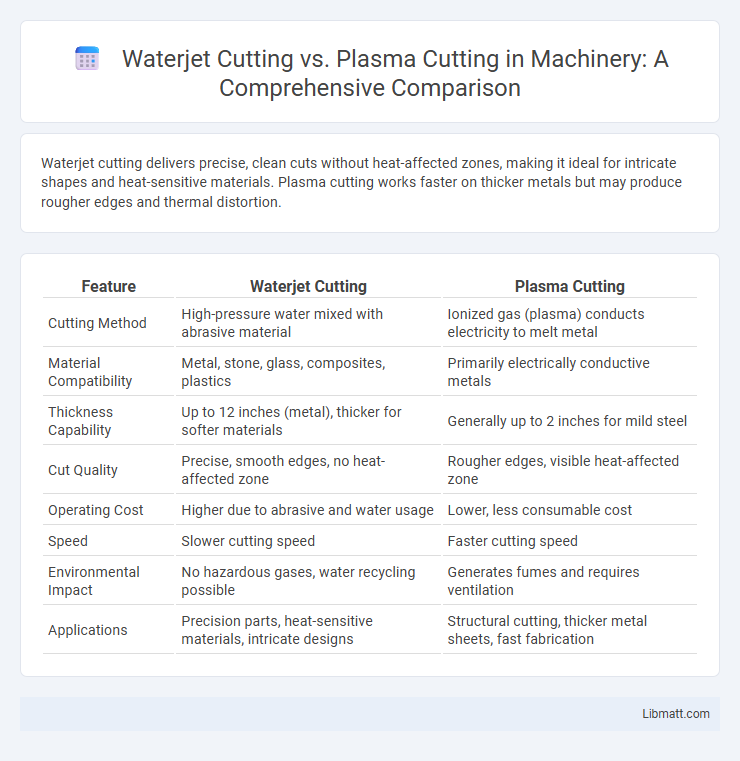
Waterjet cutting delivers precise, clean cuts without heat-affected zones, making it ideal for intricate shapes and heat-sensitive materials. Plasma cutting works faster on thicker metals but may produce rougher edges and thermal distortion.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Waterjet Cutting | Plasma Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Method | High-pressure water mixed with abrasive material | Ionized gas (plasma) conducts electricity to melt metal |
| Material Compatibility | Metal, stone, glass, composites, plastics | Primarily electrically conductive metals |
| Thickness Capability | Up to 12 inches (metal), thicker for softer materials | Generally up to 2 inches for mild steel |
| Cut Quality | Precise, smooth edges, no heat-affected zone | Rougher edges, visible heat-affected zone |
| Operating Cost | Higher due to abrasive and water usage | Lower, less consumable cost |
| Speed | Slower cutting speed | Faster cutting speed |
| Environmental Impact | No hazardous gases, water recycling possible | Generates fumes and requires ventilation |
| Applications | Precision parts, heat-sensitive materials, intricate designs | Structural cutting, thicker metal sheets, fast fabrication |
Introduction to Waterjet and Plasma Cutting
Waterjet cutting uses high-pressure water mixed with abrasive materials to precisely cut a variety of metals, stone, and composites without generating heat, preserving the material's integrity. Plasma cutting employs an electrically conductive gas to produce a high-temperature plasma arc capable of slicing through electrically conductive metals such as steel, aluminum, and copper quickly and efficiently. Your choice between these methods depends on factors like material type, thickness, and the desired edge quality.
How Waterjet Cutting Works
Waterjet cutting uses a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive particles to precisely slice through materials like metal, stone, and glass without generating heat. The process relies on a pump that pressurizes water up to 60,000 psi, forcing it through a tiny nozzle to create a powerful jet capable of clean, intricate cuts. Your choice of waterjet cutting ensures minimal material distortion and a smooth finish, making it ideal for heat-sensitive applications.
How Plasma Cutting Works
Plasma cutting works by generating an electrical arc that ionizes gas, creating a high-temperature plasma jet capable of melting and blowing away metal from the cut area. This process is highly effective for cutting electrically conductive materials like steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. Your choice between waterjet cutting and plasma cutting depends on the material thickness and desired edge quality, with plasma cutting excelling in speed and cost for metals under one inch thick.
Key Differences Between Waterjet and Plasma Cutting
Waterjet cutting uses high-pressure water mixed with abrasive materials to precisely cut various materials without generating heat, making it ideal for heat-sensitive metals and composites. Plasma cutting employs an electrically ionized gas to melt and blow away material, offering faster cutting speeds but producing heat-affected zones that can alter material properties. Waterjet cutting delivers superior edge quality and versatility for intricate shapes, whereas plasma cutting excels in thicker metal cutting with higher productivity for industrial applications.
Material Compatibility: Waterjet vs Plasma
Waterjet cutting excels in versatility, handling a wide range of materials including metals, stone, glass, and composites without altering their intrinsic properties. Plasma cutting efficiently processes electrically conductive metals such as steel, aluminum, and brass but struggles with non-conductive or heat-sensitive materials. Understanding these differences ensures your choice aligns with the specific material requirements of your project for optimal precision and quality.
Precision and Edge Quality Comparison
Waterjet cutting offers superior precision and edge quality compared to plasma cutting, achieving tolerances as tight as +-0.001 inches and producing smooth, burr-free edges. Plasma cutting typically results in wider kerf widths and rougher edges due to higher heat input, making it less suitable for intricate or delicate designs. For applications demanding clean finishes and intricate detail, waterjet cutting remains the preferred method due to its cold-cutting process and minimal thermal distortion.
Speed and Efficiency: Waterjet vs Plasma Cutting
Plasma cutting offers faster cutting speeds on thin and mild steel materials, making it highly efficient for high-volume industrial applications. Waterjet cutting, while generally slower, provides superior precision and eliminates heat-affected zones, preserving material integrity and reducing secondary finishing. Efficiency depends on material type and required cut quality, with plasma favored for speed and waterjet preferred for versatility and accuracy.
Cost Analysis of Waterjet and Plasma Cutting
Waterjet cutting incurs higher initial equipment and operational costs due to the need for abrasive materials and specialized high-pressure pumps, but it offers superior precision and no heat-affected zones, reducing secondary finishing expenses. Plasma cutting provides a more affordable setup and faster cutting speeds, ideal for thick metal sheets, but it often requires additional post-cutting processing due to slag and heat distortion. Overall, waterjet cutting's cost efficiency improves in high-precision applications and diverse material types, whereas plasma cutting is more cost-effective for rapid, straightforward metal fabrication projects.
Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
Waterjet cutting produces no hazardous fumes or gases and uses only water and abrasive materials, making it environmentally friendly and safe for operators. Plasma cutting generates significant amounts of smoke, toxic fumes, and ultraviolet radiation, posing health risks and requiring proper ventilation and protective gear. Waterjet cutting also reduces fire hazards compared to the high temperatures and sparks associated with plasma cutting, enhancing workplace safety.
Choosing the Right Cutting Method for Your Application
Waterjet cutting offers precise, cold cutting ideal for heat-sensitive materials like composites and metals, minimizing distortion. Plasma cutting excels in speed and cost-efficiency when working with thick conductive metals such as steel and aluminum. Your choice depends on material type, thickness, desired edge quality, and budget to ensure optimal results.
Waterjet cutting vs plasma cutting Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com