Pneumatic systems use compressed air to generate motion and are ideal for lightweight, fast, and clean applications, while hydraulic systems rely on pressurized fluid to deliver higher force and precise control in heavy-duty tasks. Your choice between pneumatic and hydraulic systems depends on factors like required power, speed, and the operating environment.
Table of Comparison
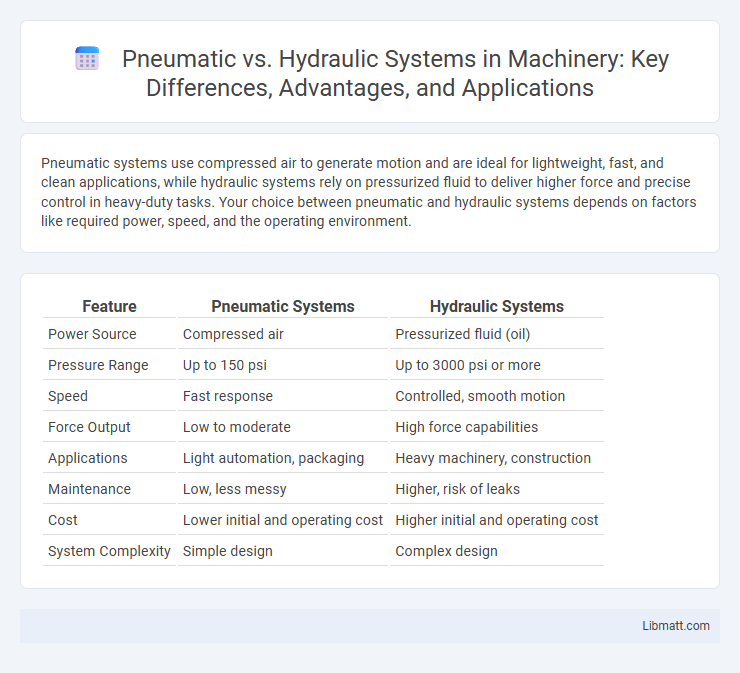
| Feature | Pneumatic Systems | Hydraulic Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Compressed air | Pressurized fluid (oil) |
| Pressure Range | Up to 150 psi | Up to 3000 psi or more |
| Speed | Fast response | Controlled, smooth motion |
| Force Output | Low to moderate | High force capabilities |
| Applications | Light automation, packaging | Heavy machinery, construction |
| Maintenance | Low, less messy | Higher, risk of leaks |
| Cost | Lower initial and operating cost | Higher initial and operating cost |
| System Complexity | Simple design | Complex design |
Introduction to Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems
Pneumatic systems utilize compressed air to transmit and control energy, offering advantages such as fast response times and clean operation ideal for automation in manufacturing. Hydraulic systems rely on pressurized liquids, typically oil, providing high force and precise control suitable for heavy machinery and industrial applications. Both systems convert energy into mechanical motion but differ in fluid medium, pressure levels, and typical use cases.
Core Principles of Operation
Pneumatic systems operate using compressed air to transmit and control energy, relying on the compressibility and low viscosity of air to create motion and force. Hydraulic systems use pressurized liquid, typically oil, to generate power, leveraging the incompressibility of fluids for precise and high-force applications. The core principle distinction lies in pneumatic systems favoring speed and cleanliness, while hydraulic systems emphasize strength and control accuracy.
Key Components and Materials
Pneumatic systems use compressed air as the working fluid, with key components including air compressors, air tanks, valves, and actuators typically made from lightweight metals and plastics to withstand pressure and corrosion. Hydraulic systems rely on incompressible fluids like oil, featuring pumps, hydraulic cylinders, valves, and reservoirs constructed from high-strength steel and alloys to handle higher pressure and provide durability. Choosing between these systems depends on your application's load requirements, precision, and material compatibility for optimal performance.
Energy Sources and Efficiency
Pneumatic systems use compressed air as their energy source, offering rapid response times and cleanliness but lower energy efficiency due to air leakage and compressibility. Hydraulic systems rely on pressurized fluids, providing higher power density and better energy efficiency for heavy-duty applications despite potential fluid leakage and maintenance requirements. Energy losses in pneumatic systems often occur through air expansion and exhaust, while hydraulic systems minimize losses with sealed circuits and fluid incompressibility.
Force, Speed, and Power Comparison
Pneumatic systems typically generate lower force but offer faster speed due to the compressibility and quick flow of air, making them ideal for applications requiring rapid movement. Hydraulic systems provide significantly higher force and power output because of the incompressibility of liquid, allowing precise control in heavy-duty tasks. Your choice depends on whether speed or force is the priority, with hydraulics excelling in power-demanding environments and pneumatics favored for speed and lighter force requirements.
Typical Applications in Industry
Pneumatic systems are widely used in industries requiring fast, repetitive motion such as packaging, automation, and assembly lines due to their lightweight and clean operation. Hydraulic systems excel in heavy-duty applications like construction equipment, manufacturing presses, and material handling where high force and precise control are essential. Both systems play crucial roles in industrial automation, with choice driven by factors like load capacity, speed, and environmental conditions.
Maintenance and Durability
Hydraulic systems generally require more intensive maintenance due to fluid leaks, contamination, and component wear, but they offer superior durability and power density for heavy-duty applications. Pneumatic systems, using compressed air, tend to have lower maintenance costs and cleaner operation but experience faster wear on seals and compressors under continuous use. Understanding your system's operational demands helps optimize maintenance schedules and ensures long-term reliability.
Safety Considerations
Pneumatic systems use compressed air, which is non-flammable and reduces fire risk, making them safer in explosive environments than hydraulic systems that rely on flammable fluids. Hydraulic systems can pose hazards such as fluid leaks causing slips or high-pressure injection injuries, requiring stricter maintenance and safety protocols. Understanding these differences helps you implement appropriate safety measures and choose the best system for your operational needs.
Cost Analysis and Investment
Pneumatic systems typically have lower initial investment costs due to simpler components and easier maintenance compared to hydraulic systems. Hydraulic systems require more expensive equipment such as pumps, valves, and fluid reservoirs, resulting in higher upfront expenses but often offer greater power density and precision. Long-term cost analysis must consider energy consumption, fluid management, and potential downtime, where pneumatic systems benefit from cleaner operation but hydraulic systems may reduce operating costs through higher efficiency in heavy-duty applications.
Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
Pneumatic systems excel in applications requiring fast, lightweight, and clean operation with moderate force, commonly used in automation and packaging industries. Hydraulic systems provide superior power and precise control for heavy-duty tasks such as construction equipment and manufacturing presses. Selecting the right system depends on factors like required force, speed, environmental conditions, and maintenance preferences to optimize performance and cost-effectiveness.
Pneumatic vs hydraulic systems Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com