Worm gears provide high torque transmission and smooth, quiet operation in compact spaces, making them ideal for applications requiring significant speed reduction. Bevel gears offer efficient power transfer between intersecting shafts with varying angles, delivering greater mechanical efficiency and versatility in your machinery design.
Table of Comparison
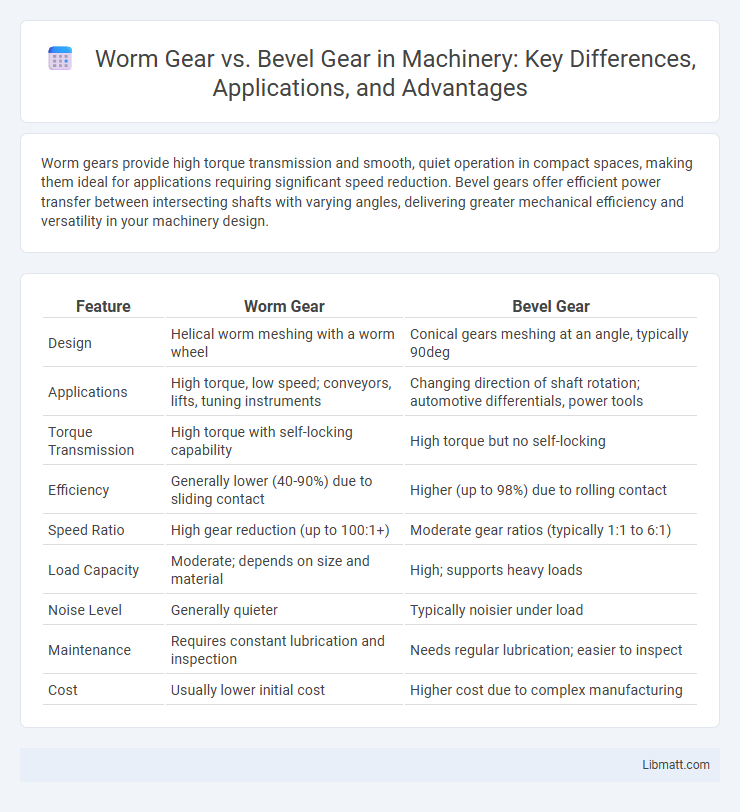
| Feature | Worm Gear | Bevel Gear |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Helical worm meshing with a worm wheel | Conical gears meshing at an angle, typically 90deg |
| Applications | High torque, low speed; conveyors, lifts, tuning instruments | Changing direction of shaft rotation; automotive differentials, power tools |
| Torque Transmission | High torque with self-locking capability | High torque but no self-locking |
| Efficiency | Generally lower (40-90%) due to sliding contact | Higher (up to 98%) due to rolling contact |
| Speed Ratio | High gear reduction (up to 100:1+) | Moderate gear ratios (typically 1:1 to 6:1) |
| Load Capacity | Moderate; depends on size and material | High; supports heavy loads |
| Noise Level | Generally quieter | Typically noisier under load |
| Maintenance | Requires constant lubrication and inspection | Needs regular lubrication; easier to inspect |
| Cost | Usually lower initial cost | Higher cost due to complex manufacturing |
Introduction to Worm Gears and Bevel Gears
Worm gears consist of a screw-like worm meshing with a worm wheel, providing high torque reduction and compact design ideal for heavy load applications. Bevel gears feature intersecting shafts with conical tooth profiles, enabling efficient angular power transmission, typically at 90 degrees. Understanding the distinct geometries and torque capabilities of worm gears versus bevel gears helps optimize your mechanical system's performance and durability.
Core Differences Between Worm and Bevel Gears
Worm gears feature a screw-like worm engaging with a worm wheel, enabling high torque transmission and significant speed reduction in compact spaces, while bevel gears have conically shaped teeth allowing torque transfer between intersecting shafts, typically at a 90-degree angle. Worm gears provide smoother, quieter operation and self-locking capabilities, unlike bevel gears which offer higher efficiency and the ability to handle more radial load. The core differences lie in their geometry, direction of power transmission, load capacity, and application suitability, with worm gears favored for precision and high reduction ratios and bevel gears chosen for intersecting shaft drives with higher torque requirements.
Design and Construction Comparison
Worm gears feature a screw-like worm engaging with a gear wheel, allowing for high reduction ratios in a compact design ideal for applications requiring large speed reductions and torque multiplication. Bevel gears consist of two intersecting shafts with conical-shaped gears, enabling efficient angular power transmission and versatility in changing the axis of rotation, typically at 90 degrees. Your choice between worm and bevel gears depends on the need for space-saving designs and self-locking capability in worm gears versus the high efficiency and angular flexibility provided by bevel gears.
Efficiency and Performance Analysis
Worm gears typically exhibit lower efficiency, ranging from 40% to 90%, due to high friction and sliding contact, making them better suited for applications requiring high reduction ratios and torque rather than speed. Bevel gears offer higher efficiency, often between 90% and 98%, thanks to rolling contact and precise tooth engagement, resulting in smoother performance and less power loss. Your choice between worm and bevel gears should consider the balance between efficiency needs and specific operational demands such as space constraints and load capacity.
Load Capacity and Torque Transmission
Worm gears excel in load capacity and torque transmission due to their high gear reduction ratios and self-locking ability, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring precise speed control. Bevel gears offer superior torque transmission efficiency and load capacity in intersecting shaft configurations, providing smooth operation with minimal backlash. Your choice depends on the need for high torque at low speeds with compact space (worm gears) or efficient torque transfer at varying angles (bevel gears).
Space and Alignment Considerations
Worm gears require less space due to their compact, perpendicular shaft arrangement, making them ideal for applications with limited room. Bevel gears demand precise alignment as their shafts intersect at specific angles, typically 90 degrees, which can increase installation complexity. Your choice between worm and bevel gears should factor in the available space and the tolerance for alignment precision in your mechanical system.
Noise and Vibration Characteristics
Worm gears generate less noise and vibration due to their sliding contact and gradual engagement of teeth, making them ideal for applications requiring quiet operation. In contrast, bevel gears tend to produce higher noise and vibration levels because of their rolling contact and more abrupt teeth engagement. Your choice between worm gear and bevel gear should consider the importance of minimizing noise and vibration for optimal performance and comfort.
Applications in Modern Machinery
Worm gears excel in applications requiring high torque and compact design, such as conveyors, lifts, and tuning instruments, where smooth, quiet operation and self-locking capabilities are essential. Bevel gears are preferred in automotive differentials, marine applications, and industrial equipment due to their efficiency in transferring power between intersecting shafts at various angles. Your choice depends on specific mechanical requirements like speed ratio, load capacity, and spatial constraints in modern machinery design.
Maintenance and Longevity Factors
Worm gears require regular lubrication and monitoring for wear due to their sliding contact, which generates more heat and friction, potentially reducing longevity if neglected. Bevel gears, with their rolling contact, generally experience less friction and wear, resulting in lower maintenance needs and longer service life under proper operating conditions. Your choice should consider the maintenance frequency you can support and the operational environment to maximize gear longevity.
Choosing Between Worm Gear and Bevel Gear
When choosing between worm gear and bevel gear, consider that worm gears provide high torque reduction and smooth, quiet operation ideal for heavy load applications, while bevel gears excel in transmitting motion between intersecting shafts with greater efficiency and speed. Your selection depends on factors such as load capacity, speed requirements, shaft orientation, and space constraints. Worm gears typically offer self-locking capability, whereas bevel gears deliver better power transmission efficiency in systems needing precise angular direction changes.
Worm gear vs bevel gear Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com