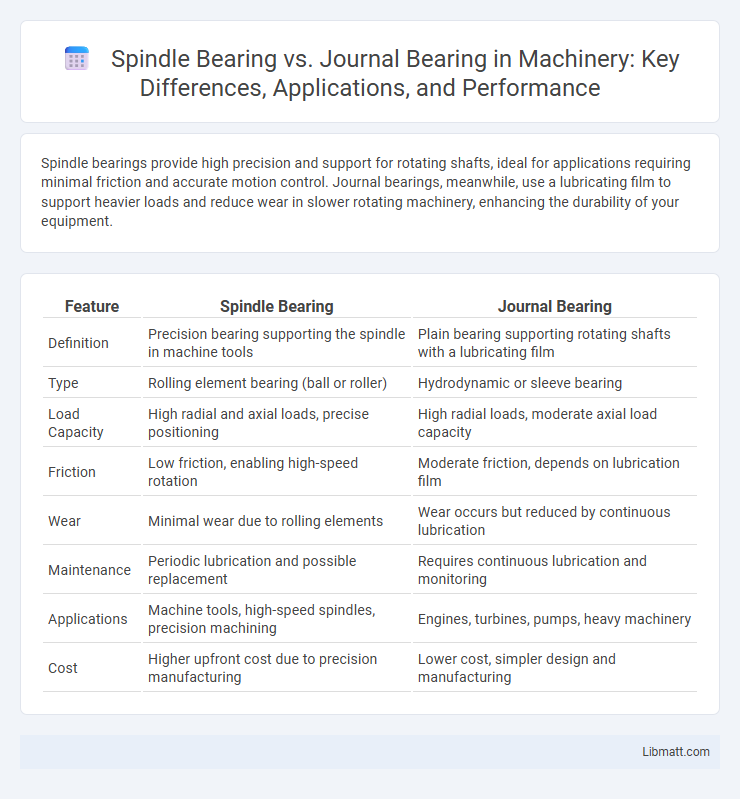
Spindle bearings provide high precision and support for rotating shafts, ideal for applications requiring minimal friction and accurate motion control. Journal bearings, meanwhile, use a lubricating film to support heavier loads and reduce wear in slower rotating machinery, enhancing the durability of your equipment.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Spindle Bearing | Journal Bearing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Precision bearing supporting the spindle in machine tools | Plain bearing supporting rotating shafts with a lubricating film |
| Type | Rolling element bearing (ball or roller) | Hydrodynamic or sleeve bearing |
| Load Capacity | High radial and axial loads, precise positioning | High radial loads, moderate axial load capacity |
| Friction | Low friction, enabling high-speed rotation | Moderate friction, depends on lubrication film |
| Wear | Minimal wear due to rolling elements | Wear occurs but reduced by continuous lubrication |
| Maintenance | Periodic lubrication and possible replacement | Requires continuous lubrication and monitoring |
| Applications | Machine tools, high-speed spindles, precision machining | Engines, turbines, pumps, heavy machinery |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost due to precision manufacturing | Lower cost, simpler design and manufacturing |
Introduction to Spindle Bearings and Journal Bearings
Spindle bearings and journal bearings are crucial components in rotating machinery, each designed to support radial and axial loads while minimizing friction. Spindle bearings are typically rolling-element bearings, offering high precision and rigidity for high-speed applications such as machine tools and spindles. In contrast, journal bearings are fluid-film bearings that rely on a thin film of lubricant to support the shaft and provide smooth, low-friction rotation under heavy loads and moderate speeds.
Fundamental Design Differences
Spindle bearings are typically designed as precision rolling element bearings, offering low friction and high rotational accuracy for high-speed applications. Journal bearings rely on a lubricating film between a stationary bearing surface and a rotating shaft, accommodating heavier loads with smoother operation but potentially higher friction. Your choice between spindle bearing and journal bearing depends on speed requirements, load capacity, and the need for precise shaft positioning.
Materials and Construction
Spindle bearings are typically made from high-grade steel alloys with precision-machined balls or rollers enclosed within hardened steel races, optimized for high-speed rotation and reduced friction. Journal bearings utilize softer materials such as babbitt metals, bronze, or composite polymers lined within a rigid housing, designed to support radial loads through a thin film of lubricating oil. The construction of spindle bearings emphasizes rigidity and accuracy for dynamic performance, while journal bearings prioritize conformability and load distribution to accommodate shaft misalignment and wear.
Performance and Load Handling
Spindle bearings offer superior precision and higher rotational speeds, making them ideal for applications demanding exceptional performance and rigidity. Journal bearings excel in handling heavier radial loads and provide smoother operation under continuous heavy-duty conditions due to their hydrodynamic lubrication. Your choice between these bearings should consider the balance between speed, load capacity, and operational stability required by your machinery.
Applications in Various Industries
Spindle bearings are essential in high-speed precision machinery such as CNC machines, robotics, and aerospace components, where accurate rotational support and minimal vibration are critical. Journal bearings are widely used in heavy-duty industrial applications like turbines, compressors, and automotive engines, providing robust load support and efficient lubrication under high pressure. Understanding these differences helps you select the optimal bearing type to improve equipment performance and longevity in your specific industry.
Lubrication Requirements
Spindle bearings require precise lubrication with low-viscosity oils or grease to minimize heat generation and ensure high-speed performance, whereas journal bearings typically demand a continuous supply of oil under pressure to maintain a hydrodynamic film that prevents metal-to-metal contact. The lubrication system for spindle bearings must control friction and wear at high rotational speeds, while journal bearings rely on stable oil film thickness to support heavy radial loads and avoid shaft damage. Proper lubrication in both bearing types is crucial for extending service life and optimizing machine efficiency.
Maintenance and Lifespan
Spindle bearings require regular lubrication and periodic inspection to prevent wear and extend their lifespan, often lasting between 5 to 10 years under proper maintenance. Journal bearings depend heavily on a continuous oil film to operate effectively, making oil quality and flow essential for preventing metal-to-metal contact and prolonging service life, which can range from 10 to 20 years. Understanding these maintenance demands helps you optimize bearing performance and avoid unexpected downtime.
Cost Comparison
Spindle bearings generally have a higher initial cost due to precision manufacturing and materials, but they offer longer service life and reduced maintenance expenses. Journal bearings are more affordable upfront and simpler in design, making them suitable for budget-sensitive applications, though they may incur higher operational costs from lubrication and wear. Your choice depends on balancing upfront investment with long-term performance and maintenance considerations.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Spindle bearings offer high precision and rigidity, making them ideal for applications requiring accurate rotational positioning, but they often come with higher costs and limited speed capabilities. Journal bearings excel in handling heavy loads and high-speed operations due to their fluid film lubrication, though they may suffer from higher friction and maintenance demands. Your choice between spindle and journal bearings depends on the balance of precision, load capacity, maintenance, and operational speed needed for your machinery.
Choosing the Right Bearing for Your Needs
Choosing the right bearing for your needs involves evaluating the specific operational requirements and load conditions of your machinery. Spindle bearings provide high precision and rotational accuracy, ideal for applications demanding minimal vibration and stiffness, such as machine tools, while journal bearings excel in supporting heavy radial loads and can accommodate larger shafts in engines or turbines. Understanding the differences in load capacity, lubrication needs, and maintenance demands ensures optimal performance and longevity in your equipment.
Spindle bearing vs journal bearing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com