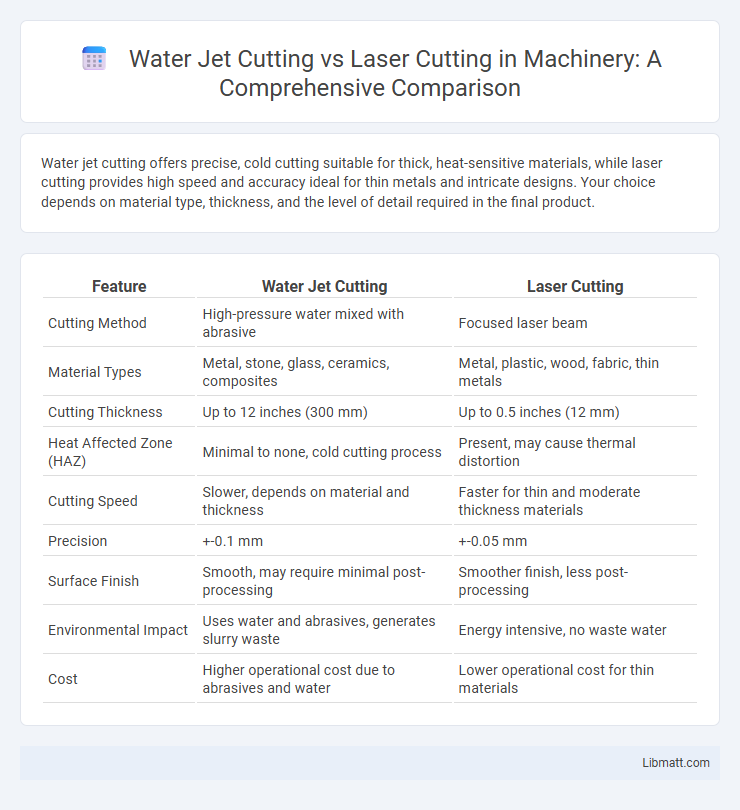
Water jet cutting offers precise, cold cutting suitable for thick, heat-sensitive materials, while laser cutting provides high speed and accuracy ideal for thin metals and intricate designs. Your choice depends on material type, thickness, and the level of detail required in the final product.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Water Jet Cutting | Laser Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Method | High-pressure water mixed with abrasive | Focused laser beam |
| Material Types | Metal, stone, glass, ceramics, composites | Metal, plastic, wood, fabric, thin metals |
| Cutting Thickness | Up to 12 inches (300 mm) | Up to 0.5 inches (12 mm) |
| Heat Affected Zone (HAZ) | Minimal to none, cold cutting process | Present, may cause thermal distortion |
| Cutting Speed | Slower, depends on material and thickness | Faster for thin and moderate thickness materials |
| Precision | +-0.1 mm | +-0.05 mm |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, may require minimal post-processing | Smoother finish, less post-processing |
| Environmental Impact | Uses water and abrasives, generates slurry waste | Energy intensive, no waste water |
| Cost | Higher operational cost due to abrasives and water | Lower operational cost for thin materials |
Introduction to Water Jet and Laser Cutting
Water jet cutting utilizes a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive materials to precisely cut through various metals, stone, and composites without generating heat. Laser cutting employs a focused laser beam to melt, burn, or vaporize materials such as metals, plastics, and wood with high accuracy and smooth edges. Both technologies offer distinct advantages in industrial fabrication, with water jet cutting excelling in thickness versatility and laser cutting providing faster processing speeds.
How Water Jet Cutting Works
Water jet cutting operates by propelling a high-pressure stream of water, often mixed with abrasive materials like garnet, to erode and slice through various materials with precision and minimal heat-affected zones. This cold cutting process can handle metals, stone, ceramics, and composites, making it highly versatile for industrial applications requiring fine tolerances and smooth finishes. Unlike laser cutting, water jet cutting does not generate thermal distortion or hazardous fumes, preserving the integrity of heat-sensitive materials.
How Laser Cutting Works
Laser cutting works by directing a high-powered laser beam through optics to focus on the material's surface, melting, burning, or vaporizing it precisely. The concentrated energy creates a narrow kerf, enabling intricate and clean cuts with minimal heat-affected zones. This process is highly efficient for metals, plastics, and other materials requiring precise and repeatable cutting patterns.
Material Compatibility: Water Jet vs Laser Cutting
Water jet cutting offers superior material compatibility by efficiently cutting metals, ceramics, glass, composites, and heat-sensitive materials without altering their physical properties. Laser cutting, while highly precise and ideal for thin metals, plastics, and wood, may struggle with reflective or heat-sensitive materials due to potential melting or warping. The choice between water jet and laser cutting depends on the specific material's thickness, thermal sensitivity, and reflectivity requirements.
Cutting Speed and Efficiency Comparison
Water jet cutting operates at slower speeds compared to laser cutting but excels in efficiently cutting thicker and heat-sensitive materials without distortion. Laser cutting provides rapid, precise cuts on thinner metals and plastics, maximizing speed and accuracy for high-volume production. Your choice depends on material type and thickness, balancing cutting speed with operational efficiency.
Precision and Edge Quality Analysis
Water jet cutting offers superior edge quality with minimal thermal distortion, maintaining material integrity and producing smooth, burr-free edges ideal for sensitive materials. Laser cutting excels in precision with high-speed, intricate designs and tight tolerances, but may cause slight heat-affected zones leading to potential edge discoloration or micro-cracks. The choice between water jet and laser cutting depends on the specific material type, required edge finish, and tolerance levels needed for the application.
Thickness and Material Limitations
Water jet cutting excels in handling thicker materials, often cutting through metal, stone, and composites up to 12 inches or more, while laser cutting is typically limited to thinner materials, usually under 1 inch for metals and less for other substances. Water jets can precisely cut a wide range of materials, including reflective or heat-sensitive ones, because they do not generate heat, whereas laser cutting struggles with highly reflective metals and materials sensitive to thermal damage. Your choice should consider the material thickness and thermal properties to ensure optimal cutting quality and efficiency.
Cost Factors: Investment and Operation
Water jet cutting typically requires a higher initial investment due to the cost of high-pressure pumps and abrasive materials, whereas laser cutting systems often have lower upfront costs but demand expensive maintenance of laser components. Operational expenses for water jet cutting include abrasive consumption and water usage, which can accumulate significantly, while laser cutting incurs costs mainly from electricity and periodic replacement of laser tubes or optics. Both technologies present varying cost efficiencies depending on material types and thickness, influencing the overall investment and operational budget for manufacturing processes.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Water jet cutting produces minimal harmful fumes and uses water and abrasive materials, making it an environmentally friendly option with reduced air pollution compared to laser cutting, which generates smoke and requires ventilation systems. Safety risks in water jet cutting mainly involve high-pressure water jets that necessitate proper protective gear, while laser cutting poses hazards from intense light exposure and potential fire risks requiring strict safety protocols. You can optimize your manufacturing process by weighing these environmental and safety factors to select the most suitable cutting method.
Choosing the Best Cutting Method for Your Project
Water jet cutting excels at slicing through thick, heat-sensitive, or composite materials without thermal distortion, making it ideal for projects requiring precision and material integrity. Laser cutting offers high-speed precision for thin metals and intricate designs, providing smooth edges and fine detail but may cause heat-affected zones on certain materials. Evaluating your project's material type, thickness, and tolerance for heat will help determine whether water jet or laser cutting best meets your manufacturing needs.
Water jet cutting vs laser cutting Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com