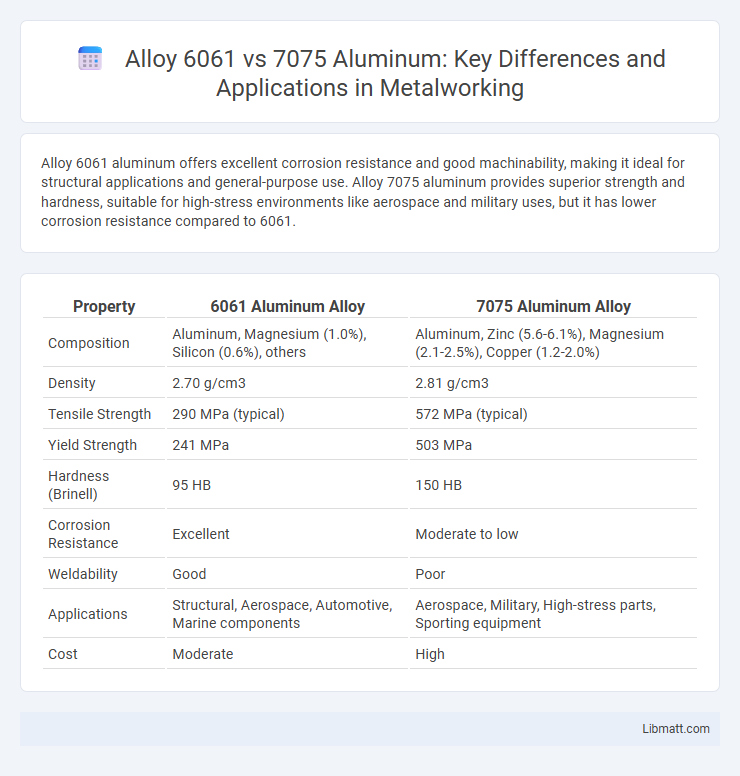
Alloy 6061 aluminum offers excellent corrosion resistance and good machinability, making it ideal for structural applications and general-purpose use. Alloy 7075 aluminum provides superior strength and hardness, suitable for high-stress environments like aerospace and military uses, but it has lower corrosion resistance compared to 6061.
Table of Comparison
| Property | 6061 Aluminum Alloy | 7075 Aluminum Alloy |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Aluminum, Magnesium (1.0%), Silicon (0.6%), others | Aluminum, Zinc (5.6-6.1%), Magnesium (2.1-2.5%), Copper (1.2-2.0%) |
| Density | 2.70 g/cm3 | 2.81 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 290 MPa (typical) | 572 MPa (typical) |
| Yield Strength | 241 MPa | 503 MPa |
| Hardness (Brinell) | 95 HB | 150 HB |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Moderate to low |
| Weldability | Good | Poor |
| Applications | Structural, Aerospace, Automotive, Marine components | Aerospace, Military, High-stress parts, Sporting equipment |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
Overview of Aluminum Alloys 6061 and 7075
Aluminum alloys 6061 and 7075 differ primarily in strength, corrosion resistance, and machining properties, with 7075 offering higher tensile strength ideal for aerospace applications, while 6061 provides excellent corrosion resistance and weldability suited for structural projects. Alloy 6061 contains magnesium and silicon, contributing to its versatility and moderate strength, whereas 7075 is zinc-based, delivering superior strength but lower corrosion resistance. Your choice depends on balancing weight, strength, and exposure conditions to optimize performance in your specific application.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Alloy 6061 aluminum primarily contains magnesium (around 1.0%) and silicon (about 0.6%) which contribute to its good corrosion resistance and weldability, while alloy 7075 boasts a higher zinc content (approximately 5.6%) complemented by magnesium (around 2.5%) that enhances its strength significantly. Your choice depends on the chemical composition requirements, with 6061 offering a balanced mix ideal for general applications and 7075 providing superior strength due to its elevated zinc and magnesium levels. The distinct elemental balance in each alloy directly impacts mechanical properties and suitability for specific industrial uses.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Hardness
Alloy 7075 aluminum offers significantly higher tensile strength, typically around 572 MPa, compared to 6061 aluminum's approximate 310 MPa, making 7075 ideal for high-stress applications. In terms of hardness, 7075 exhibits a Brinell hardness of about 150 HB, while 6061 averages around 95 HB, reflecting its superior resistance to deformation. Both alloys maintain good machinability, but 7075's enhanced strength and hardness make it preferable for aerospace and military-grade components.
Corrosion Resistance Differences
Alloy 6061 aluminum offers superior corrosion resistance compared to 7075, making it ideal for marine and outdoor applications. The presence of magnesium and silicon in 6061 enhances its natural oxide layer, providing better protection against oxidation and environmental factors. If your project requires long-term durability in corrosive environments, choosing alloy 6061 ensures improved performance and longevity.
Machinability and Workability
Alloy 6061 aluminum offers excellent machinability with stable cutting performance and ease in secondary operations due to its balanced composition of magnesium and silicon. In contrast, alloy 7075 aluminum is harder and stronger but presents more challenges in machining, requiring sharper tools and slower feeds to prevent tool wear. Workability favors 6061, which responds well to forming, welding, and bending, whereas 7075 is less malleable and more prone to cracking under stress.
Weldability of 6061 vs 7075 Aluminum
Alloy 6061 aluminum exhibits excellent weldability due to its medium strength and good corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring strong and clean weld joints. In contrast, 7075 aluminum has poor weldability because its high zinc content causes hot cracking and reduced strength in the heat-affected zones during welding. The superior weldability of 6061 makes it more suitable for structural components that require joining, whereas 7075 is often reserved for high-stress applications where welding is not required.
Common Applications and Use Cases
Alloy 6061 aluminum is widely used in structural components, aerospace parts, marine fittings, and automotive frames due to its excellent corrosion resistance and good mechanical strength. Alloy 7075 aluminum is commonly applied in high-stress environments such as aerospace, military equipment, and sports gear because of its superior strength-to-weight ratio and fatigue resistance. Both alloys are favored in manufacturing but differ in application based on strength requirements and environmental exposure.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Alloy 6061 aluminum is more cost-effective and widely available compared to 7075, making it the preferred choice for budget-sensitive projects. 7075 aluminum tends to be more expensive due to its higher strength and limited production volume, impacting overall material costs. Supply chain reliability favors 6061, as it is produced in larger quantities globally, ensuring easier procurement and shorter lead times.
Weight and Density Considerations
Alloy 6061 has a density of approximately 2.70 g/cm3, making it slightly heavier than 7075 aluminum, which has a density of around 2.81 g/cm3. Despite 7075 being denser, it offers higher strength-to-weight ratio, ideal for applications requiring lightweight yet strong materials. Your choice depends on prioritizing weight savings or specific mechanical properties for your project.
Choosing the Right Alloy for Your Project
Alloy 6061 offers excellent corrosion resistance and good mechanical properties, making it ideal for structural applications requiring weldability and moderate strength. Alloy 7075 provides superior strength and fatigue resistance, suited for aerospace and high-stress environments but has lower corrosion resistance compared to 6061. Selecting the right alloy depends on balancing factors like strength requirements, environmental exposure, machinability, and cost constraints for your specific project needs.
alloy 6061 vs 7075 aluminum Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com