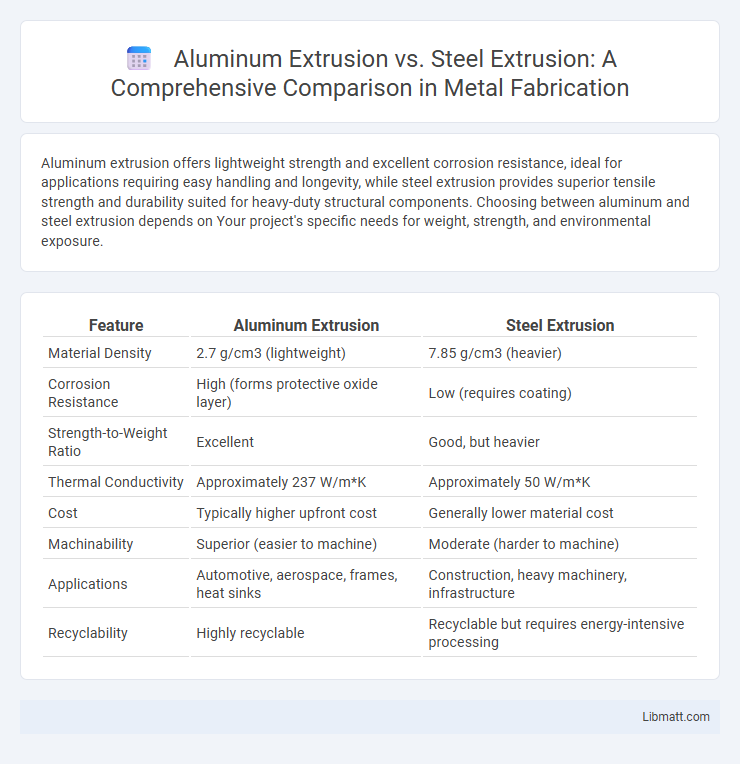
Aluminum extrusion offers lightweight strength and excellent corrosion resistance, ideal for applications requiring easy handling and longevity, while steel extrusion provides superior tensile strength and durability suited for heavy-duty structural components. Choosing between aluminum and steel extrusion depends on Your project's specific needs for weight, strength, and environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Aluminum Extrusion | Steel Extrusion |
|---|---|---|
| Material Density | 2.7 g/cm3 (lightweight) | 7.85 g/cm3 (heavier) |
| Corrosion Resistance | High (forms protective oxide layer) | Low (requires coating) |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Excellent | Good, but heavier |
| Thermal Conductivity | Approximately 237 W/m*K | Approximately 50 W/m*K |
| Cost | Typically higher upfront cost | Generally lower material cost |
| Machinability | Superior (easier to machine) | Moderate (harder to machine) |
| Applications | Automotive, aerospace, frames, heat sinks | Construction, heavy machinery, infrastructure |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable | Recyclable but requires energy-intensive processing |
Overview of Aluminum and Steel Extrusion
Aluminum extrusion offers lightweight, corrosion-resistant properties with excellent thermal conductivity, making it ideal for applications requiring high strength-to-weight ratio and design flexibility. Steel extrusion provides superior strength and durability, suited for heavy-duty structural components and environments demanding high wear resistance. Understanding the distinct benefits of aluminum and steel extrusion helps you select the optimal material based on performance requirements and project specifications.
Material Properties: Aluminum vs Steel
Aluminum extrusion offers lightweight characteristics with excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring high strength-to-weight ratios and natural oxidation protection. Steel extrusion, by contrast, provides superior tensile strength and durability but is heavier and more prone to rust without protective coatings. The thermal conductivity of aluminum outperforms steel, enhancing heat dissipation in industrial components, while steel's rigidity supports higher load-bearing capacities in structural applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Aluminum extrusion offers a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for applications requiring lightweight but durable components, while steel extrusion provides superior tensile strength and impact resistance, suitable for heavy-duty structural uses. Aluminum resists corrosion naturally due to its oxide layer, enhancing durability in outdoor and marine environments, whereas steel often requires protective coatings to prevent rust and degradation. The choice between aluminum and steel extrusion depends on balancing strength requirements, environmental exposure, and weight considerations for optimal performance.
Weight and Density Differences
Aluminum extrusion offers a significant advantage in weight compared to steel extrusion, as aluminum has a density of approximately 2.7 g/cm3, which is roughly one-third that of steel's 7.85 g/cm3. This lower density translates to lighter components, making aluminum extrusions ideal for applications where reducing weight is critical, such as in aerospace and automotive industries. Your choice between aluminum and steel extrusion should consider how these weight and density differences impact overall performance and fuel efficiency.
Corrosion Resistance and Maintenance
Aluminum extrusion offers superior corrosion resistance compared to steel extrusion due to its natural oxide layer that protects against rust and environmental damage. Steel extrusions require protective coatings or galvanization to prevent corrosion and frequent maintenance to address rust issues. Lower maintenance costs and longer lifespan make aluminum extrusion a preferred choice in applications exposed to moisture or harsh environments.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Aluminum extrusion generally offers lower tooling costs and faster production times compared to steel extrusion, making it more cost-effective for complex or custom profiles in medium to large volumes. Steel extrusion involves higher material costs and more energy-intensive processing, which can increase overall expenses but provides greater strength and durability for heavy-duty applications. Your choice depends on balancing upfront costs with long-term performance and lifecycle economic benefits.
Design Flexibility and Complexity
Aluminum extrusion offers superior design flexibility and complexity due to its lightweight properties and ease of machining, allowing for intricate shapes and thinner walls that are difficult to achieve with steel. Steel extrusion, while stronger and more durable, is limited by its higher density and hardness, restricting design complexity and requiring additional processing for detailed features. Your choice between aluminum and steel extrusion depends on the desired balance between intricate design capabilities and structural strength.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aluminum extrusion offers a significant environmental advantage due to its high recyclability and lower carbon footprint compared to steel extrusion, which typically requires more energy-intensive processes and generates greater greenhouse gas emissions. The lightweight nature of extruded aluminum results in reduced transportation emissions and enhanced energy efficiency in end-use applications. Steel extrusion's higher energy consumption and resource intensity make it less sustainable despite its durability, reinforcing aluminum's role as a more eco-friendly material choice in sustainable manufacturing.
Typical Applications in Industry
Aluminum extrusion is widely utilized in aerospace, automotive, and construction industries due to its lightweight, corrosion resistance, and excellent thermal conductivity. Steel extrusion finds common applications in heavy machinery, structural components, and tools, favored for its superior strength, durability, and wear resistance. Both materials serve critical roles in manufacturing, with aluminum preferred for weight-sensitive designs and steel chosen for high-stress, load-bearing applications.
Choosing the Right Material for Extrusion Projects
Aluminum extrusion offers lightweight properties, excellent corrosion resistance, and high thermal conductivity, making it ideal for projects requiring ease of handling and environmental durability. Steel extrusion, known for its superior strength and wear resistance, is suited for heavy-duty applications demanding structural integrity and toughness. Evaluate Your project's specific strength, weight, and corrosion requirements carefully to select the optimal material for extrusion success.
aluminum extrusion vs steel extrusion Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com