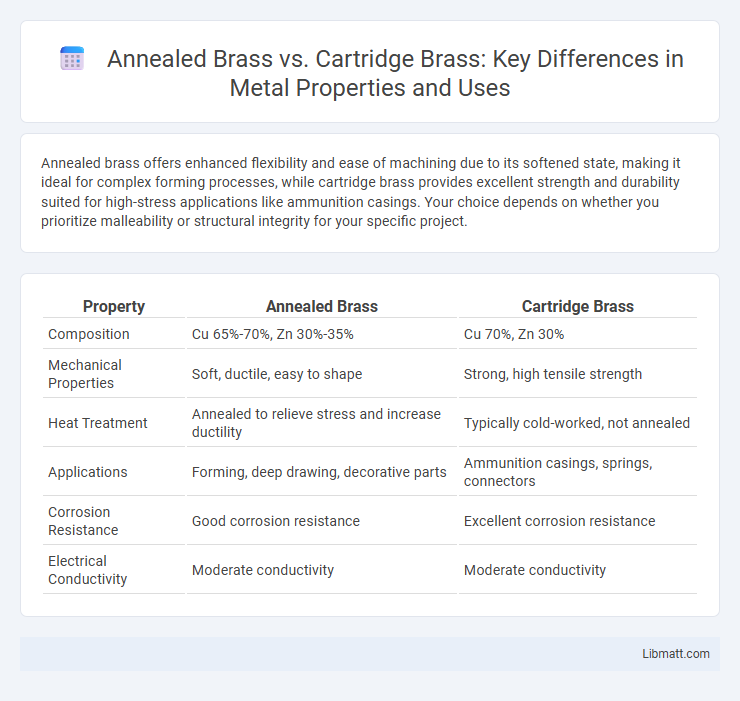
Annealed brass offers enhanced flexibility and ease of machining due to its softened state, making it ideal for complex forming processes, while cartridge brass provides excellent strength and durability suited for high-stress applications like ammunition casings. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize malleability or structural integrity for your specific project.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Annealed Brass | Cartridge Brass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Cu 65%-70%, Zn 30%-35% | Cu 70%, Zn 30% |
| Mechanical Properties | Soft, ductile, easy to shape | Strong, high tensile strength |
| Heat Treatment | Annealed to relieve stress and increase ductility | Typically cold-worked, not annealed |
| Applications | Forming, deep drawing, decorative parts | Ammunition casings, springs, connectors |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good corrosion resistance | Excellent corrosion resistance |
| Electrical Conductivity | Moderate conductivity | Moderate conductivity |
Introduction to Brass Alloys
Brass alloys, primarily composed of copper and zinc, vary significantly in properties depending on their treatment and composition. Annealed brass undergoes a heat treatment process that softens the metal, enhancing its ductility and making it easier to work with for complex shapes, while cartridge brass, typically 70% copper and 30% zinc, is prized for its strength and corrosion resistance in ammunition casings. Understanding these distinctions in brass alloys can help you choose the right material for applications requiring specific mechanical and chemical properties.
What is Annealed Brass?
Annealed brass is a heat-treated form of brass that becomes softer and more malleable through controlled heating and cooling processes, enhancing its ductility for easier shaping and forming. This treatment alters the metal's crystal structure, reducing hardness without compromising strength, making it ideal for applications requiring intricate bending or stamping. Your projects benefit from annealed brass when flexibility and workability are essential, such as in manufacturing high-quality cartridges and precision components.
What is Cartridge Brass?
Cartridge brass is a type of brass alloy composed primarily of 70% copper and 30% zinc, known for its excellent ductility and corrosion resistance. It is widely used in ammunition casings due to its ability to withstand high pressure and its ease of forming during the manufacturing process. Unlike annealed brass, cartridge brass is typically used in its hardened state to maintain structural integrity under stress.
Key Chemical Compositions
Annealed brass typically contains around 60-70% copper and 30-40% zinc, with trace amounts of lead to improve machinability during the annealing process. Cartridge brass, known as 70/30 brass, consists of approximately 70% copper and 30% zinc, providing enhanced strength and corrosion resistance ideal for ammunition casings. The main chemical difference lies in the controlled zinc content and minimal impurities in cartridge brass, optimizing its mechanical properties for industrial applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Annealed brass exhibits improved ductility and reduced hardness compared to cartridge brass, making it more suitable for forming and bending applications. Cartridge brass, typically with higher tensile strength and hardness, offers superior resistance to wear and is commonly used in ammunition casings. Your choice between annealed and cartridge brass should depend on whether flexibility or strength is the priority in your mechanical application.
Applications of Annealed Brass
Annealed brass is widely used in applications requiring enhanced ductility and machinability, such as intricate electrical connectors, plumbing fittings, and decorative hardware. Its softened state allows for easier shaping and forming, making it ideal for precision components in automotive and aerospace industries. The improved malleability of annealed brass also supports complex manufacturing processes like deep drawing and extrusion.
Applications of Cartridge Brass
Cartridge brass, primarily composed of 70% copper and 30% zinc, is widely used in manufacturing ammunition casings due to its excellent ductility and corrosion resistance. Its superior strength and formability also make it suitable for producing decorative items, plumbing fixtures, and musical instruments. The alloy's ability to maintain structural integrity under repeated stress significantly enhances its application in high-performance engineering components.
Performance in Ammunition Manufacturing
Annealed brass offers superior malleability and ductility compared to cartridge brass, enhancing formability during cartridge case manufacturing without cracking. Cartridge brass, typically composed of 70% copper and 30% zinc, provides higher strength and elasticity, which improves the durability and pressure resistance of ammunition cases. In ammunition production, annealed brass reduces tooling wear and defects, while cartridge brass maintains dimensional stability under high firing stresses.
Durability and Longevity
Annealed brass offers enhanced durability due to its softened structure, making it more resistant to cracking and easier to form without losing strength. Cartridge brass, typically composed of 70% copper and 30% zinc, provides excellent longevity with its superior corrosion resistance and high tensile strength, ideal for enduring repeated stress. Understanding these differences helps you select the best brass type for applications requiring both durability and long-term performance.
Choosing the Right Brass for Your Needs
Annealed brass offers enhanced flexibility and improved machinability due to its softened state, making it ideal for applications requiring intricate shaping or forming. Cartridge brass, known for its high strength and excellent corrosion resistance, is commonly used in ammunition casings and structural components where durability is essential. Evaluating your project's specific demands for strength, malleability, and corrosion resistance will help you choose the right brass alloy for your needs.
Annealed Brass vs Cartridge Brass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com