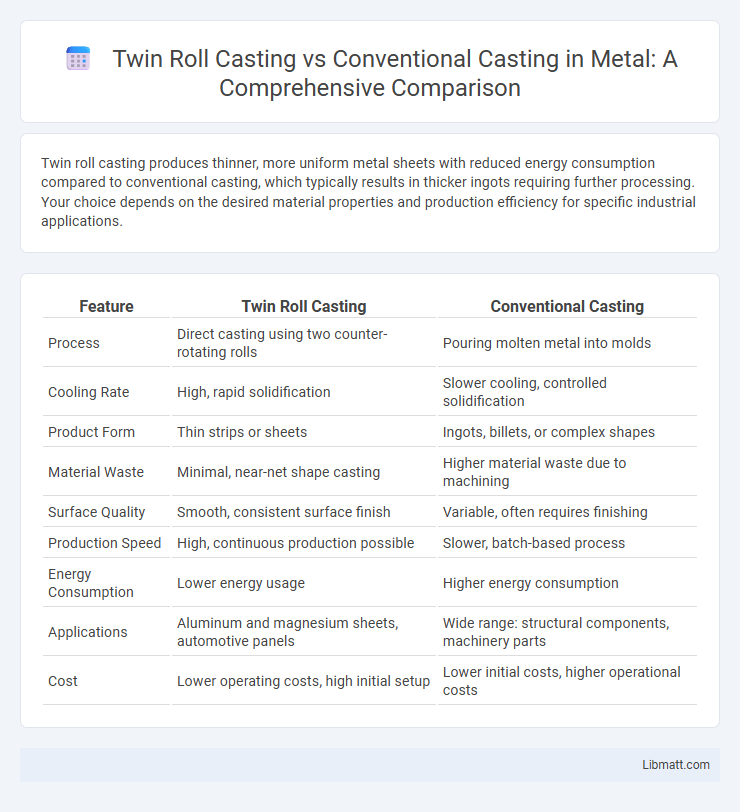
Twin roll casting produces thinner, more uniform metal sheets with reduced energy consumption compared to conventional casting, which typically results in thicker ingots requiring further processing. Your choice depends on the desired material properties and production efficiency for specific industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Twin Roll Casting | Conventional Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Direct casting using two counter-rotating rolls | Pouring molten metal into molds |
| Cooling Rate | High, rapid solidification | Slower cooling, controlled solidification |
| Product Form | Thin strips or sheets | Ingots, billets, or complex shapes |
| Material Waste | Minimal, near-net shape casting | Higher material waste due to machining |
| Surface Quality | Smooth, consistent surface finish | Variable, often requires finishing |
| Production Speed | High, continuous production possible | Slower, batch-based process |
| Energy Consumption | Lower energy usage | Higher energy consumption |
| Applications | Aluminum and magnesium sheets, automotive panels | Wide range: structural components, machinery parts |
| Cost | Lower operating costs, high initial setup | Lower initial costs, higher operational costs |
Introduction to Twin Roll Casting and Conventional Casting
Twin roll casting employs two counter-rotating rolls to solidify molten metal into thin strips, enabling rapid cooling and minimizing defects compared to conventional casting methods. Conventional casting typically involves pouring molten metal into molds, resulting in slower solidification and higher chances of grain segregation and porosity. The twin roll process enhances microstructure uniformity and material properties, offering significant advantages for aluminum and magnesium alloy production.
Historical Overview of Metal Casting Methods
Twin roll casting emerged in the late 20th century, revolutionizing metal casting by combining solidification and rolling into a single continuous process, contrasting with conventional casting methods that date back thousands of years and rely on pouring molten metal into molds. Conventional casting, including sand casting and die casting, traditionally involved slower, batch-based processes with higher energy consumption and material waste. The innovation of twin roll casting significantly improved production speed, material efficiency, and surface quality in metals like aluminum and magnesium compared to historic casting techniques.
Process Principles: Twin Roll Casting vs Conventional Casting
Twin roll casting employs a continuous casting process where molten metal solidifies directly between two rotating rolls, enabling rapid cooling and thin slab production. Conventional casting typically involves pouring molten metal into molds for slower solidification, resulting in thicker ingots or blooms with higher chances of segregation. The twin roll method enhances microstructure control and reduces downstream processing compared to the conventional batch-based casting techniques.
Material Compatibility and Range
Twin roll casting supports a wide range of alloys, including aluminum, magnesium, and copper-based materials, providing enhanced flexibility for various industrial applications. Conventional casting methods are compatible with a broader spectrum of metals, such as steel, iron, and complex alloys, allowing for the production of diverse component shapes and sizes. Your choice between these methods depends on the specific material properties required and the desired product characteristics.
Equipment and Technology Requirements
Twin roll casting requires specialized equipment including dual counter-rotating rolls with precise cooling and casting control systems to solidify metal strips directly, offering higher production efficiency. Conventional casting relies on molds or continuous casting machines that demand extensive infrastructure and often additional processing steps, such as hot rolling. Your choice of technology impacts operational costs and production speed significantly, with twin roll casting favoring compact, high-speed manufacturing setups.
Production Speed and Efficiency Comparison
Twin roll casting significantly increases production speed by directly solidifying molten metal into thin strips, eliminating multiple processing steps typical in conventional casting. This method achieves higher efficiency through reduced energy consumption and material waste, enhancing throughput with minimal finishing requirements. Conventional casting involves slower cooling rates and multiple secondary processes like hot rolling, leading to longer production cycles and increased operational costs.
Surface Quality and Product Properties
Twin roll casting produces superior surface quality with smoother finishes and fewer defects due to rapid solidification and controlled cooling rates. This method enhances product properties by refining microstructure, increasing strength, and improving uniformity compared to conventional casting. Conventional casting often results in coarser grain structures and surface irregularities due to slower cooling and less precise control during solidification.
Energy Consumption and Environmental Impact
Twin roll casting significantly reduces energy consumption by directly solidifying molten metal into thin strips, bypassing multiple reheating and rolling stages typical of conventional casting. This process lowers greenhouse gas emissions and minimizes waste generation, making it a more environmentally friendly option. Your choice of twin roll casting supports sustainable manufacturing by enhancing energy efficiency and reducing the overall carbon footprint.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Operating Costs
Twin roll casting demands a higher initial investment due to specialized machinery and technology compared to conventional casting methods, which typically use more established and less expensive equipment. Operating costs for twin roll casting are generally lower because of reduced energy consumption, faster production rates, and minimized material waste. Conventional casting often incurs higher ongoing expenses related to longer cooling times, increased labor, and additional secondary processing steps.
Future Trends and Innovations in Metal Casting
Twin roll casting is driving future trends in metal casting by enabling higher production speeds and reduced energy consumption compared to conventional casting methods. Innovations such as advanced cooling systems and real-time monitoring are enhancing the precision and quality of twin roll cast products, particularly for aluminum alloys. Emerging developments in additive manufacturing integration and AI-driven process optimization are expected to further elevate the efficiency and sustainability of metal casting in industrial applications.
Twin roll casting vs conventional casting Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com