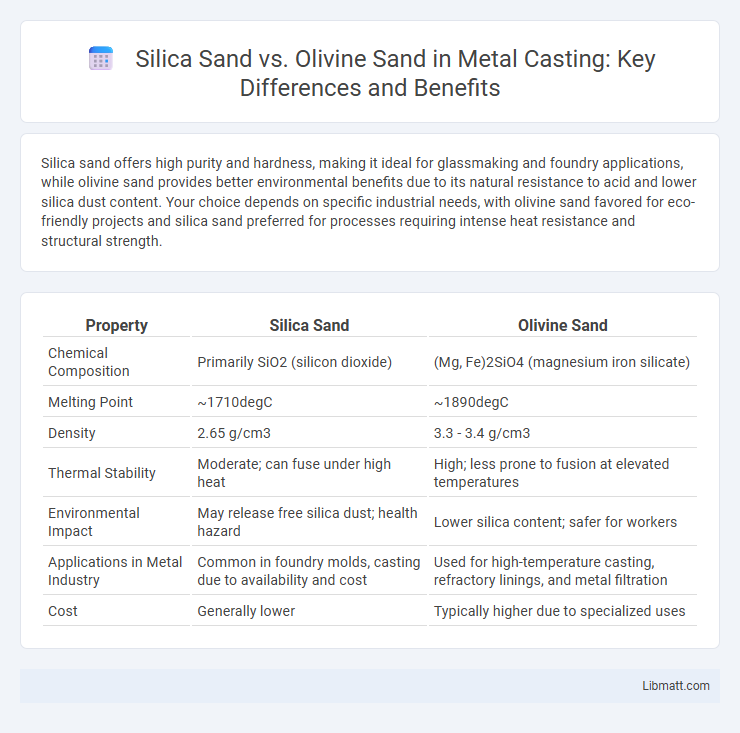
Silica sand offers high purity and hardness, making it ideal for glassmaking and foundry applications, while olivine sand provides better environmental benefits due to its natural resistance to acid and lower silica dust content. Your choice depends on specific industrial needs, with olivine sand favored for eco-friendly projects and silica sand preferred for processes requiring intense heat resistance and structural strength.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Silica Sand | Olivine Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Primarily SiO2 (silicon dioxide) | (Mg, Fe)2SiO4 (magnesium iron silicate) |
| Melting Point | ~1710degC | ~1890degC |
| Density | 2.65 g/cm3 | 3.3 - 3.4 g/cm3 |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate; can fuse under high heat | High; less prone to fusion at elevated temperatures |
| Environmental Impact | May release free silica dust; health hazard | Lower silica content; safer for workers |
| Applications in Metal Industry | Common in foundry molds, casting due to availability and cost | Used for high-temperature casting, refractory linings, and metal filtration |
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher due to specialized uses |
Introduction to Silica Sand and Olivine Sand
Silica sand primarily consists of quartz and is widely used in glassmaking, construction, and foundry applications due to its high purity and durability. Olivine sand, composed mainly of magnesium iron silicate, offers superior environmental benefits by reducing CO2 emissions during industrial processes and is valued for its high melting point. Understanding the unique chemical properties and applications of both silica and olivine sand can help you make informed decisions for manufacturing or environmental projects.
Geological Origins of Silica and Olivine Sands
Silica sand primarily originates from the weathering and erosion of quartz-rich rocks such as granite and sandstone, accumulating in sedimentary environments over millions of years. Olivine sand forms from the rapid cooling and fragmentation of ultramafic igneous rocks, especially peridotite and basalt, commonly found in volcanic regions and tectonic plate boundaries. These distinct geological processes result in varying mineral compositions and physical properties critical for their industrial applications.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Silica sand primarily consists of silicon dioxide (SiO2), making it highly resistant to chemical weathering and ideal for applications requiring high purity and durability. Olivine sand contains significant amounts of magnesium iron silicate ((Mg, Fe)2SiO4), which provides superior thermal stability and lower thermal expansion compared to silica sand. Your choice between silica and olivine sand depends on the chemical needs of your process, as olivine's unique composition offers enhanced corrosion resistance and environmental benefits in specific industrial uses.
Physical Properties and Characteristics
Silica sand primarily consists of quartz with a high hardness of 7 on the Mohs scale, offering excellent durability and chemical stability, whereas olivine sand is composed mainly of the mineral olivine, which has a slightly lower hardness around 6.5, providing effective wear resistance but with greater susceptibility to weathering. Silica sand typically exhibits a uniform grain size and angular shape, contributing to superior packing and filtration properties, while olivine sand features a more irregular grain shape and higher specific gravity, impacting its abrasive performance. Both sands differ in color, with silica sand ranging from white to light brown and olivine sand showing greenish hues due to iron and magnesium content, influencing their suitability for various industrial applications.
Industrial Applications: Silica vs. Olivine
Silica sand is widely used in industrial applications such as glass manufacturing, foundry casting, and hydraulic fracturing due to its high purity and hardness. Olivine sand, with its lower silica content and higher magnesium iron content, is preferred in steel manufacturing for refractory linings and as a sandblasting abrasive because of its thermal stability and eco-friendly slag formation. Both sands serve crucial roles, but silica excels in filtration and glass production, while olivine is favored for environmentally sustainable industrial processes.
Thermal Performance and Refractoriness
Silica sand offers high refractoriness with a melting point around 1710degC, making it suitable for applications requiring excellent thermal stability, though its thermal conductivity is relatively low. Olivine sand, with a melting point near 1890degC, provides superior thermal performance and resistance to slag corrosion, enhancing durability in high-temperature environments. Your choice between silica and olivine sand depends on the specific thermal demands and refractory requirements of your project.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Silica sand mining often results in habitat disruption and significant dust emissions, raising concerns about respiratory health and environmental degradation. Olivine sand, sourced primarily from volcanic regions, offers lower silica dust hazards and has potential for carbon sequestration by reacting with CO2 to form stable minerals. Sustainable extraction of olivine sand requires careful management to minimize ecological disturbance and promote long-term environmental benefits.
Health and Safety Considerations
Silica sand poses significant health risks due to its crystalline silica content, which can cause silicosis, lung cancer, and other respiratory diseases when inhaled as fine dust. Olivine sand is considered a safer alternative, as it contains minimal crystalline silica, reducing the risk of respiratory issues during handling and processing. Proper protective equipment and dust control measures are essential when working with either material to ensure workplace safety.
Cost and Economic Factors
Silica sand generally costs less than olivine sand due to its widespread availability and extensive mining infrastructure, making it a more economical choice for industrial applications. Olivine sand, with higher purity and specific geological sources, commands a premium price reflecting its niche applications in foundries and abrasives. The economic viability of each depends on the required material properties, with silica sand favored for cost-sensitive bulk use and olivine sand preferred where enhanced performance justifies higher investment.
Choosing the Right Sand for Your Application
Silica sand and olivine sand differ significantly in composition and performance, influencing their suitability for various applications such as foundry casting, abrasive blasting, and water filtration. Silica sand, rich in silicon dioxide, offers high hardness and chemical stability, making it ideal for precision molding and filtration systems, whereas olivine sand, composed primarily of magnesium iron silicate, provides superior heat resistance and lower thermal expansion, beneficial in high-temperature environments like metallurgical processes. Understanding the specific requirements of your application, including chemical reactivity, thermal properties, and environmental impact, ensures the selection of the optimal sand type for enhanced efficiency and durability.
silica sand vs olivine sand Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com