Boron steel offers exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for automotive and structural applications where durability is crucial. Manganese steel provides superior impact resistance and toughness, perfect for high-stress environments like mining and heavy machinery, ensuring your equipment withstands extreme conditions.
Table of Comparison
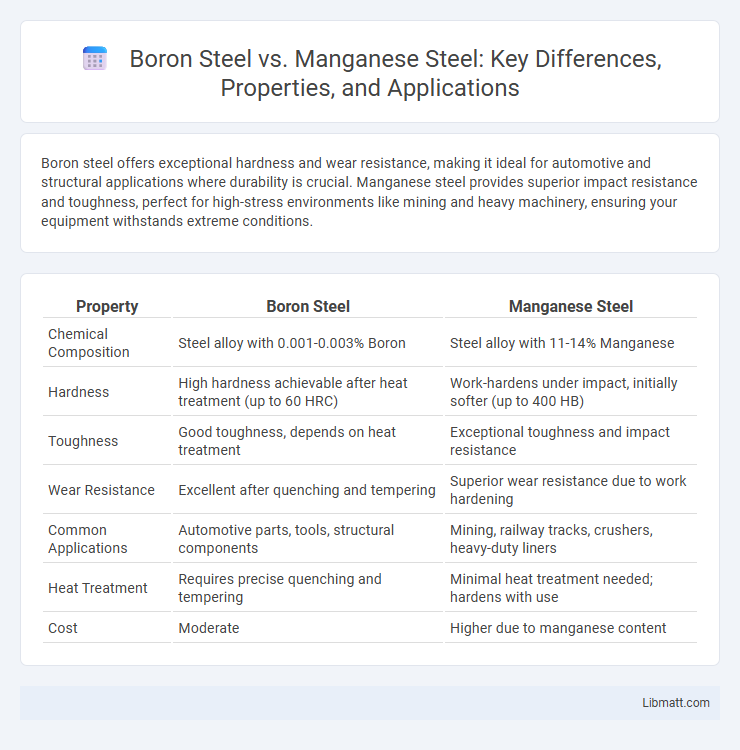
| Property | Boron Steel | Manganese Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Steel alloy with 0.001-0.003% Boron | Steel alloy with 11-14% Manganese |
| Hardness | High hardness achievable after heat treatment (up to 60 HRC) | Work-hardens under impact, initially softer (up to 400 HB) |
| Toughness | Good toughness, depends on heat treatment | Exceptional toughness and impact resistance |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent after quenching and tempering | Superior wear resistance due to work hardening |
| Common Applications | Automotive parts, tools, structural components | Mining, railway tracks, crushers, heavy-duty liners |
| Heat Treatment | Requires precise quenching and tempering | Minimal heat treatment needed; hardens with use |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher due to manganese content |
Introduction to Boron Steel vs Manganese Steel
Boron steel offers exceptional hardness and tensile strength, making it ideal for automotive and protective applications where durability is crucial. Manganese steel excels in impact resistance and wear toughness, commonly used in heavy equipment and mining industries. Understanding your specific needs can help determine whether boron steel's hardness or manganese steel's toughness better suits your project.
Chemical Composition: Boron Steel and Manganese Steel
Boron steel contains a small percentage of boron (typically 0.0005% to 0.003%) added to carbon steel, enhancing hardenability and tensile strength, with common elements including carbon (0.2%-0.5%), manganese (0.3%-1.2%), and traces of silicon. Manganese steel, also known as Hadfield steel, features high manganese content (usually 12%-14%) combined with about 1.0%-1.4% carbon, which provides exceptional toughness and resistance to abrasion. The primary distinction in chemical composition lies in boron's role as a microalloying element that improves hardening, whereas manganese in large amounts primarily enhances impact strength and wear resistance.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Boron steel exhibits higher tensile strength and hardness due to the addition of boron, making it ideal for wear-resistant applications and structural components requiring superior toughness. Manganese steel, known for its exceptional impact resistance and work-hardening properties, offers superior durability in high-impact environments but typically has lower tensile strength compared to boron steel. The choice between the two depends on the balance between hardness and toughness required, with boron steel excelling in hardness and manganese steel in impact and abrasion resistance.
Strength and Hardness Differences
Boron steel offers higher tensile strength and superior hardness compared to manganese steel, making it ideal for applications requiring exceptional wear resistance and structural integrity. While manganese steel provides excellent toughness and impact resistance due to its high work-hardening capabilities, its hardness is generally lower than boron steel's, affecting long-term durability under abrasive conditions. Your choice between the two should consider whether hardness or impact resistance is more critical for the specific use case.
Wear and Abrasion Resistance
Boron steel offers exceptional wear and abrasion resistance due to its high hardness achieved through heat treatment, making it ideal for automotive and structural applications. Manganese steel, renowned for its work-hardening properties, enhances abrasion resistance by becoming harder under impact and deformation, suitable for mining and heavy-duty machinery. Wear resistance in boron steel relies on its alloying with boron and controlled heat treatment, whereas manganese steel's resistance improves dynamically with operational stress.
Applications in Automotive and Construction
Boron steel is widely used in automotive manufacturing for its exceptional hardness and tensile strength, making it ideal for safety components like door beams and chassis reinforcements. Manganese steel, known for its high impact resistance and durability, is favored in construction applications such as heavy-duty earthmoving equipment and wear-resistant structural parts. Your choice between these materials depends on whether you need superior strength and lightweight properties for vehicle performance or toughness and abrasion resistance for rugged construction environments.
Weldability and Fabrication Challenges
Boron steel presents challenges in weldability due to its high hardenability, requiring preheating and controlled cooling to avoid cracking, while manganese steel offers excellent weldability but demands skilled welders to manage its transformation-hardening properties. Fabrication of boron steel involves precise thermal management to maintain strength without brittleness; manganese steel requires specialized techniques to prevent distortion and preserve its toughness. Both materials necessitate tailored welding procedures and experienced fabricators to ensure structural integrity and performance in demanding applications.
Corrosion Resistance: Boron vs. Manganese Alloys
Boron steel exhibits moderate corrosion resistance due to its alloying elements, but it typically requires protective coatings or treatments to prevent rust in harsh environments. Manganese steel, known for its high impact strength, has lower corrosion resistance and is more prone to oxidation without protective measures. Comparing both, boron alloys offer better resistance to corrosion, making them more suitable for applications exposed to moisture or chemicals.
Cost and Availability Factors
Boron steel generally offers a more cost-effective option due to its widespread availability and simpler manufacturing process compared to manganese steel. Manganese steel, known for its exceptional impact resistance, tends to be more expensive because of higher alloying content and specialized heat treatment requirements. Availability of boron steel is greater globally, making it more accessible for large-scale production and lowering overall procurement costs.
Choosing the Right Steel: Key Considerations
Choosing between boron steel and manganese steel hinges on the specific application requirements such as hardness, wear resistance, and toughness. Boron steel offers superior strength and hardenability, making it ideal for automotive components and structural parts, while manganese steel excels in impact resistance and abrasion, suitable for heavy-duty mining and industrial machinery. Understanding these material properties helps in selecting the optimal steel type that balances performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness for the intended use.
Boron Steel vs Manganese Steel Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com