Drop forging uses a hammer to shape heated metal by repeatedly striking it, producing strong, durable parts with refined grain structure. Press forging applies continuous pressure to deform the metal slowly, offering better control over dimensions and reducing internal stresses for higher precision in your final component.
Table of Comparison
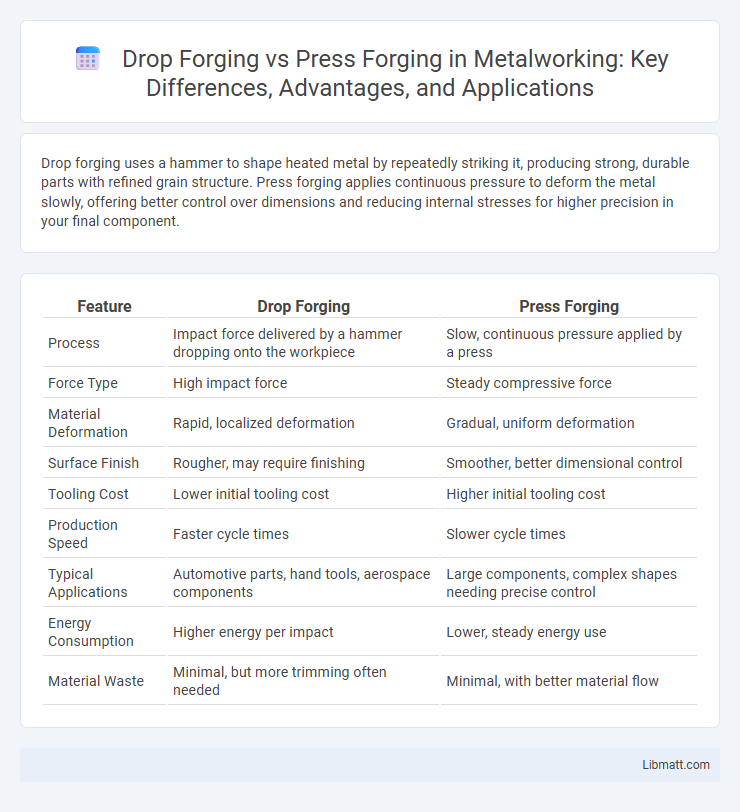
| Feature | Drop Forging | Press Forging |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Impact force delivered by a hammer dropping onto the workpiece | Slow, continuous pressure applied by a press |
| Force Type | High impact force | Steady compressive force |
| Material Deformation | Rapid, localized deformation | Gradual, uniform deformation |
| Surface Finish | Rougher, may require finishing | Smoother, better dimensional control |
| Tooling Cost | Lower initial tooling cost | Higher initial tooling cost |
| Production Speed | Faster cycle times | Slower cycle times |
| Typical Applications | Automotive parts, hand tools, aerospace components | Large components, complex shapes needing precise control |
| Energy Consumption | Higher energy per impact | Lower, steady energy use |
| Material Waste | Minimal, but more trimming often needed | Minimal, with better material flow |
Introduction to Drop Forging and Press Forging
Drop forging involves shaping metal using a heavy, swinging hammer that delivers high-impact blows to a heated workpiece, enhancing grain structure and mechanical properties. Press forging uses slow, steady pressure applied by a press to deform the metal, offering precise control over shape and thickness with less impact-induced stress. Both processes are essential in manufacturing durable components, with drop forging preferred for high-strength parts and press forging valued for dimensional accuracy.
Understanding the Forging Process
Drop forging utilizes a hammer dropped onto the heated metal workpiece to shape it quickly with high impact force, ideal for producing strong, dense parts. Press forging applies slow, continuous pressure using a hydraulic or mechanical press, resulting in precise deformation and reduced internal stresses. Both processes involve shaping heated metal but differ in force application, speed, and control, affecting final mechanical properties and surface finish.
Key Differences Between Drop Forging and Press Forging
Drop forging involves shaping metal by gravity-driven impact using a hammer, producing high strength and grain refinement with rapid deformation. Press forging applies slow, continuous pressure with a press machine, offering precise dimensional control and reduced internal stresses. Drop forging is preferred for high-volume, robust parts, while press forging suits intricate shapes and materials sensitive to strain rate.
Material Suitability for Each Method
Drop forging is ideal for high-strength materials such as carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel, where precise grain structure control and enhanced mechanical properties are critical. Press forging suits materials with high ductility like aluminum, copper, and brass, enabling gradual deformation to minimize internal stresses and produce smooth, uniform parts. Selecting the right forging process depends on the metal's hardness, ductility, and final product requirements to optimize strength and durability.
Strength and Mechanical Properties Comparison
Drop forging produces parts with superior mechanical properties due to the higher impact forces that refine grain structure and enhance strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance. Press forging applies gradual pressure, resulting in more uniform deformation and improved dimensional accuracy but generally lower strength compared to drop forging. The slower deformation in press forging reduces internal defects, making it suitable for components requiring precision and moderate mechanical properties.
Production Efficiency and Cost Analysis
Drop forging offers faster cycle times and higher production efficiency due to its impact-based shaping process, making it suitable for large volume manufacturing. Press forging, characterized by gradual deformation under sustained pressure, provides superior dimensional accuracy but generally involves slower production rates and higher energy consumption. In terms of cost analysis, drop forging typically results in lower per-unit costs for mass production, while press forging incurs greater initial investment and operating expenses, offset by reduced material wastage and improved product consistency.
Typical Applications for Drop Forging
Drop forging is commonly used in manufacturing heavy-duty components such as automotive crankshafts, connecting rods, and industrial gears due to its ability to produce high-strength, durable parts with excellent structural integrity. This method is favored in aerospace and military industries for critical components that require superior fatigue resistance and toughness. Drop forging is also essential in producing hand tools, agricultural machinery parts, and hardware fittings where reliability and strength are paramount.
Typical Applications for Press Forging
Press forging excels in manufacturing complex shapes with precise dimensions, commonly used in automotive components such as crankshafts and connecting rods. It is preferred for aerospace parts where uniform grain structure and high strength are critical, including turbine blades and landing gear components. Press forging also suits the production of large industrial machinery parts, offering enhanced metal flow control for improved mechanical properties.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Forging Type
Drop forging offers advantages such as producing high-strength components with superior grain structure and excellent dimensional accuracy, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. However, it involves higher equipment costs, noise levels, and slower production speed compared to press forging. Press forging provides consistent deformation control and reduced flash with faster cycle times, but it may result in less uniform grain flow and is generally better suited for thinner, simpler parts.
Choosing the Right Forging Process for Your Needs
Drop forging offers superior strength and durability due to its high-impact hammering process, making it ideal for applications requiring maximum structural integrity, such as automotive and aerospace components. Press forging provides greater dimensional accuracy and surface finish with a slower, continuous pressing action, suitable for complex shapes or thin-walled parts in industries like electronics and precision engineering. Selecting between drop forging and press forging depends on factors like production volume, material properties, complexity, and desired mechanical characteristics.
Drop forging vs press forging Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com