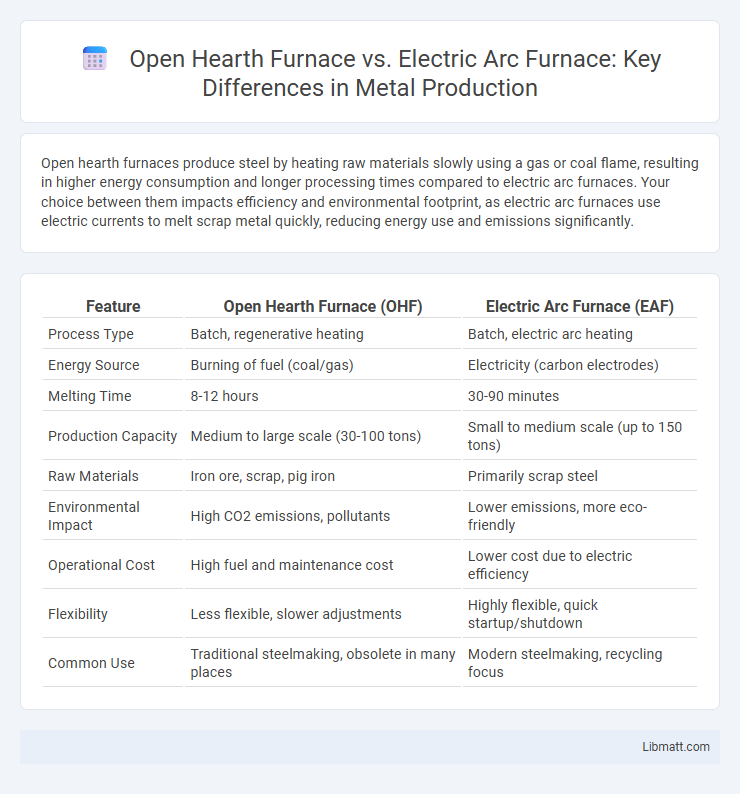
Open hearth furnaces produce steel by heating raw materials slowly using a gas or coal flame, resulting in higher energy consumption and longer processing times compared to electric arc furnaces. Your choice between them impacts efficiency and environmental footprint, as electric arc furnaces use electric currents to melt scrap metal quickly, reducing energy use and emissions significantly.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Open Hearth Furnace (OHF) | Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Batch, regenerative heating | Batch, electric arc heating |
| Energy Source | Burning of fuel (coal/gas) | Electricity (carbon electrodes) |
| Melting Time | 8-12 hours | 30-90 minutes |
| Production Capacity | Medium to large scale (30-100 tons) | Small to medium scale (up to 150 tons) |
| Raw Materials | Iron ore, scrap, pig iron | Primarily scrap steel |
| Environmental Impact | High CO2 emissions, pollutants | Lower emissions, more eco-friendly |
| Operational Cost | High fuel and maintenance cost | Lower cost due to electric efficiency |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, slower adjustments | Highly flexible, quick startup/shutdown |
| Common Use | Traditional steelmaking, obsolete in many places | Modern steelmaking, recycling focus |
Introduction to Steelmaking Furnaces
Open Hearth Furnaces and Electric Arc Furnaces represent two pivotal technologies in steelmaking, each differing significantly in energy source and operational efficiency. Open Hearth Furnaces utilize a regenerative heat system burning coke and gas, enabling large-scale steel production but with longer processing times and higher emissions. Electric Arc Furnaces leverage electric arcs to melt scrap steel rapidly, offering flexibility, reduced environmental impact, and suitability for recycling in modern steel manufacturing.
Overview of Open Hearth Furnace
The Open Hearth Furnace is a traditional steelmaking method that heats raw materials using a regenerative furnace design, allowing for large batch processing with consistent temperature control. This furnace operates at high temperatures for extended periods, making it suitable for producing high-quality steel with precise chemical compositions. Your choice of furnace impacts production efficiency and environmental emissions, with Open Hearth Furnaces typically having higher energy consumption compared to modern alternatives like Electric Arc Furnaces.
Overview of Electric Arc Furnace
The Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) uses electrical energy to melt scrap steel or direct reduced iron, providing a more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly alternative compared to traditional methods. EAFs offer greater flexibility in production, lower emissions, and faster startup times, making them ideal for recycling steel and producing specialty alloys. Your choice of EAF can significantly reduce operating costs while supporting sustainable steel manufacturing practices.
Historical Evolution and Adoption
Open Hearth Furnaces dominated steel production from the late 19th century until the mid-20th century due to their ability to produce large quantities of steel with relatively uniform quality. Electric Arc Furnaces (EAFs) gained prominence in the latter half of the 20th century, driven by advancements in electric power and a need for more flexible, energy-efficient steelmaking processes. Your choice between these technologies often depends on historical context and modern demands for sustainability and production agility.
Raw Materials and Energy Consumption
Open Hearth Furnaces primarily utilize iron ore, scrap steel, and limestone as raw materials, consuming substantial amounts of coal or coke to generate the necessary heat. Electric Arc Furnaces rely heavily on scrap steel as their main raw material and use electric energy to melt the metal, significantly reducing fossil fuel consumption. Your choice between these methods affects both the raw material sourcing and the overall energy efficiency of steel production.
Process Efficiency and Production Time
Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF) offer higher process efficiency by rapidly melting scrap metal using intense electric arcs, resulting in shorter production cycles compared to Open Hearth Furnaces (OHF), which rely on slower combustion heating. EAFs can complete steel production in a few hours, significantly reducing production time, whereas OHFs require up to 12 hours or more due to prolonged heating and refining stages. The superior energy utilization in EAFs also leads to lower operational costs and faster turnaround, making them the preferred choice for modern steelmaking.
Environmental Impact and Emissions
Open Hearth Furnaces generate significantly higher greenhouse gas emissions, including CO2 and sulfur oxides, compared to Electric Arc Furnaces (EAFs), which rely on electricity and produce fewer pollutants. EAFs support the recycling of scrap steel, reducing raw material demand and minimizing energy consumption, thereby lowering overall environmental impact. The cleaner, more energy-efficient operation of EAFs aligns with stricter environmental regulations and sustainability goals in modern steel production.
Cost Comparison and Economic Viability
Open Hearth Furnaces generally incur higher operating costs due to longer production times and greater fuel consumption, making them less economically viable compared to Electric Arc Furnaces. Electric Arc Furnaces offer lower energy expenses and faster melting cycles, enhancing cost efficiency, especially for recycling scrap steel. Your choice will impact overall budget efficiency, with Electric Arc Furnaces providing a more cost-effective solution for modern steel production.
Quality of Steel Produced
Open Hearth Furnaces produce steel with relatively lower purity and higher levels of impurities due to longer processing times and less precise temperature control. Electric Arc Furnaces enable the production of higher quality steel by melting scrap steel with greater temperature accuracy and faster processing, resulting in improved chemical composition and fewer contaminants. Consequently, Electric Arc Furnaces are favored in industries requiring superior steel quality such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
Future Trends in Steelmaking Technology
Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) technology is rapidly advancing with innovations such as automation, improved energy efficiency, and enhanced recycling capabilities, positioning it as the future standard in sustainable steel production. Open Hearth Furnaces are largely being phased out due to higher energy consumption and environmental concerns, while EAFs support greener steelmaking through flexible raw material use and lower carbon emissions. For your steel operations, adopting EAF technology aligns with industry trends emphasizing decarbonization and digital integration for optimized performance.
Open Hearth Furnace vs Electric Arc Furnace Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com