Laser engraving offers precise, customizable designs with minimal material waste, ideal for intricate patterns and durable markings on various surfaces. Chemical etching provides a cost-effective method for producing fine details on metals but involves hazardous chemicals and longer processing times compared to the clean, fast results of laser engraving.
Table of Comparison
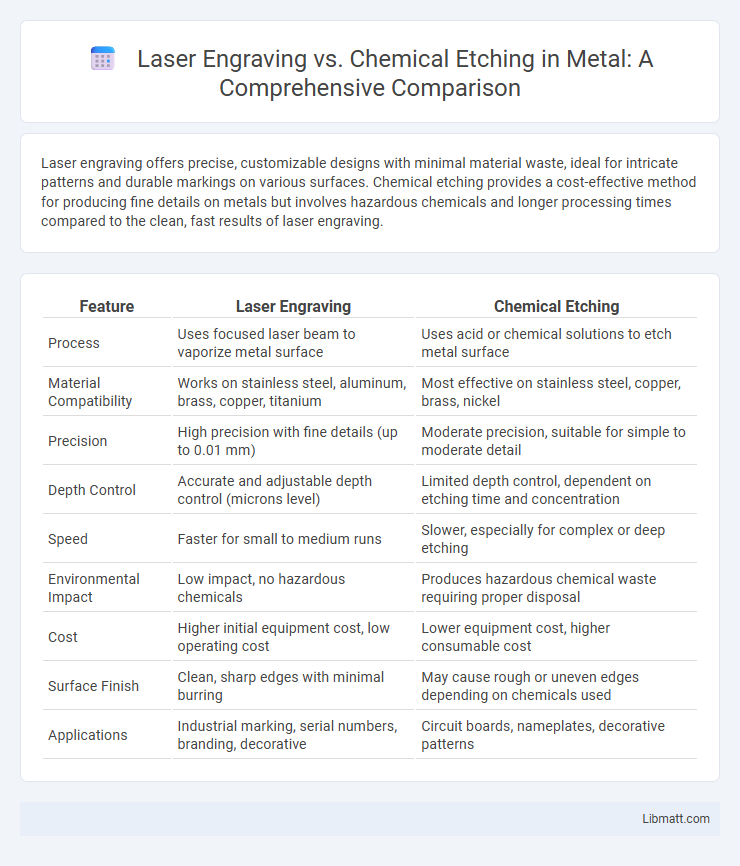
| Feature | Laser Engraving | Chemical Etching |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Uses focused laser beam to vaporize metal surface | Uses acid or chemical solutions to etch metal surface |
| Material Compatibility | Works on stainless steel, aluminum, brass, copper, titanium | Most effective on stainless steel, copper, brass, nickel |
| Precision | High precision with fine details (up to 0.01 mm) | Moderate precision, suitable for simple to moderate detail |
| Depth Control | Accurate and adjustable depth control (microns level) | Limited depth control, dependent on etching time and concentration |
| Speed | Faster for small to medium runs | Slower, especially for complex or deep etching |
| Environmental Impact | Low impact, no hazardous chemicals | Produces hazardous chemical waste requiring proper disposal |
| Cost | Higher initial equipment cost, low operating cost | Lower equipment cost, higher consumable cost |
| Surface Finish | Clean, sharp edges with minimal burring | May cause rough or uneven edges depending on chemicals used |
| Applications | Industrial marking, serial numbers, branding, decorative | Circuit boards, nameplates, decorative patterns |
Introduction to Laser Engraving and Chemical Etching
Laser engraving employs focused laser beams to precisely remove material, creating detailed and permanent designs on various surfaces such as metals, plastics, and wood. Chemical etching uses corrosive acids or alkalis to selectively dissolve material, producing intricate patterns mainly on metal substrates through controlled masking techniques. Understanding these methods helps you choose the optimal process for durability, detail, and application requirements in manufacturing or personalization projects.
How Laser Engraving Works
Laser engraving works by directing a focused beam of light onto a material's surface, causing it to vaporize or melt and create precise, permanent marks. This technique offers high accuracy and detail by controlling laser intensity, speed, and movement to customize designs on metals, plastics, wood, or glass. You benefit from a clean, eco-friendly process with minimal waste, unlike chemical etching that involves hazardous acids and longer processing times.
The Chemical Etching Process Explained
Chemical etching involves applying a resist material to a metal surface, then exposing it to an acid or etchant that dissolves unprotected areas, creating precise designs. This process allows for high-detail engraving on thin metals with uniform depth and minimal mechanical stress. It is particularly effective for producing intricate patterns, fine text, and delicate components in industries such as electronics and aerospace.
Material Compatibility: Laser Engraving vs Chemical Etching
Laser engraving offers broad material compatibility, effectively marking metals, plastics, wood, glass, and ceramics with high precision and depth control. Chemical etching primarily targets metals like stainless steel, aluminum, and copper, relying on acid or alkaline solutions to create shallow, detailed designs without thermal impact. Understanding your material type and desired finish helps determine whether laser engraving's versatility or chemical etching's precision is best suited for your application.
Precision and Detail Comparison
Laser engraving offers superior precision and intricate detail capabilities, achieving resolutions as fine as 1000 DPI, making it ideal for complex designs and delicate patterns. Chemical etching typically provides less detailed results due to the etching process's inherent limitations, with resolutions around 250-500 DPI, often resulting in softer edges and less accuracy. Materials compatibility and customization flexibility further enhance laser engraving's advantages in producing high-definition, consistent detailed markings.
Speed and Efficiency: Which Is Faster?
Laser engraving offers significantly faster processing speeds compared to chemical etching, making it highly efficient for high-volume production. Its digital precision eliminates setup time required for chemical masks and etchants, accelerating turnaround times. While chemical etching involves longer exposure and rinsing stages, laser engraving achieves detailed results in a fraction of the time, optimizing workflow speed.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-Term Expenses
Laser engraving requires a higher initial investment due to the cost of the laser equipment, typically ranging from $5,000 to $50,000, but offers lower long-term expenses with minimal consumables and maintenance. Chemical etching has a lower upfront cost, around $1,000 to $10,000 for basic setups, yet incurs ongoing costs from chemicals, disposal, and safety measures. Your decision should consider the trade-off between initial capital and recurring operational costs to optimize budget efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
Laser engraving generates fewer hazardous chemicals and waste compared to chemical etching, reducing environmental pollution and disposal concerns. It operates without corrosive acids or toxic etchants, minimizing risks to worker health and safety. Laser systems also produce less air and water contamination, supporting more sustainable manufacturing practices.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Laser engraving offers precise, high-resolution marking ideal for electronics, automotive parts, and medical devices where detailed customization and durability are critical. Chemical etching excels in producing complex metal components for aerospace, signage, and jewelry industries due to its ability to create fine, intricate patterns on thin metal sheets. Both technologies serve manufacturing sectors requiring permanent surface modifications but differ in material compatibility and process intricacy.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Project
Laser engraving offers high precision and versatility, making it ideal for intricate designs on various materials like wood, metal, and plastic. Chemical etching provides a cost-effective solution for large-scale production with consistent, fine details, especially suited for metal surfaces. Evaluating factors such as project scale, material type, budget, and desired detail level helps determine the most efficient and effective method.
laser engraving vs chemical etching Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com