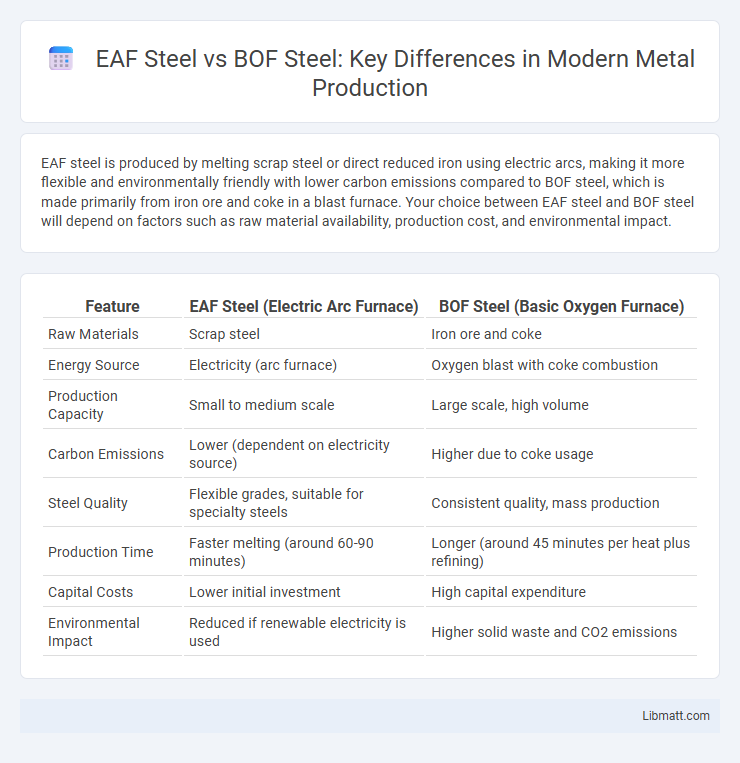
EAF steel is produced by melting scrap steel or direct reduced iron using electric arcs, making it more flexible and environmentally friendly with lower carbon emissions compared to BOF steel, which is made primarily from iron ore and coke in a blast furnace. Your choice between EAF steel and BOF steel will depend on factors such as raw material availability, production cost, and environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | EAF Steel (Electric Arc Furnace) | BOF Steel (Basic Oxygen Furnace) |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | Scrap steel | Iron ore and coke |
| Energy Source | Electricity (arc furnace) | Oxygen blast with coke combustion |
| Production Capacity | Small to medium scale | Large scale, high volume |
| Carbon Emissions | Lower (dependent on electricity source) | Higher due to coke usage |
| Steel Quality | Flexible grades, suitable for specialty steels | Consistent quality, mass production |
| Production Time | Faster melting (around 60-90 minutes) | Longer (around 45 minutes per heat plus refining) |
| Capital Costs | Lower initial investment | High capital expenditure |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced if renewable electricity is used | Higher solid waste and CO2 emissions |
Introduction to EAF and BOF Steelmaking
Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) steelmaking uses recycled scrap metal melted by electric arcs, offering flexibility and energy efficiency for producing various steel grades. Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) steelmaking relies on blowing oxygen through molten iron to reduce carbon content and produce large volumes of steel from iron ore and scrap. Your choice between EAF and BOF depends on factors like raw material availability, production scale, and environmental impact.
Process Overview: How EAF and BOF Work
Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) steelmaking involves melting scrap steel using high-powered electric arcs, offering flexibility and energy efficiency by recycling metallic waste. Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) steelmaking converts molten pig iron and scrap steel into steel through oxygen blowing, which reduces carbon content and removes impurities at high temperatures. Your choice between EAF and BOF depends on factors like raw material availability, production scale, and environmental considerations.
Raw Materials Used in EAF vs BOF Steel Production
Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) steel production primarily relies on scrap steel as its raw material, offering greater flexibility and recycling benefits, while Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) steel production depends mainly on iron ore and coking coal to produce molten iron. The use of scrap steel in EAF reduces the need for extraction of raw minerals and lowers energy consumption, making it a more sustainable option. Understanding these raw material differences can help you choose the most environmentally and economically suitable steel manufacturing process.
Energy Consumption and Efficiency Comparison
Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) steel production typically consumes 60-70% less energy per ton compared to Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) steel due to its reliance on electricity to melt scrap steel. EAFs achieve higher operational efficiency, with energy usage ranging from 350 to 550 kWh per ton, while BOFs require approximately 20-40 GJ of energy primarily from coke and coal combustion. The energy efficiency of EAF processes translates into lower greenhouse gas emissions and reduced reliance on fossil fuels compared to BOF steelmaking.
Environmental Impact: EAF Steel vs BOF Steel
Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) steel production significantly reduces environmental impact compared to Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) steel by emitting up to 70% less CO2 due to the recycling of scrap metal and lower reliance on raw materials. BOF steel manufacturing depends heavily on iron ore and coal, resulting in higher greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption. Your choice of EAF steel supports sustainable practices through energy efficiency and a smaller carbon footprint in the steel industry.
Cost Differences Between EAF and BOF Methods
Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) steel production generally incurs lower costs compared to Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) methods due to its reliance on scrap metal, which is less expensive than raw iron ore and coke used in BOF processes. EAF steelmaking also requires less energy and shorter processing times, reducing operational expenses. However, BOF steel typically benefits from economies of scale in large integrated mills, which can offset some cost differences in high-production scenarios.
Steel Quality and Product Applications
EAF steel typically offers superior cleanliness with lower sulfur and nitrogen content, making it ideal for high-quality steel products requiring precise chemical properties. BOF steel often contains higher levels of impurities but excels in large-scale production of structural and construction-grade steel. Your choice between EAF and BOF steel should consider the end-use application, balancing quality requirements with production scale.
Flexibility and Scalability in Production
Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) steel production offers superior flexibility and scalability, enabling rapid adjustments in batch sizes and easier integration of recycled scrap metal compared to Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) steelmaking. EAF technology supports smaller, modular production units that can be scaled up or down efficiently, meeting fluctuating market demands without significant downtime. In contrast, BOF processes require large, continuous operations with less adaptability to production shifts, limiting responsiveness and scalability in dynamic steel markets.
Global Trends in EAF and BOF Adoption
Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) steel production has surged globally due to its lower carbon emissions and flexibility in using recycled scrap metal, making it the preferred choice in regions with stringent environmental regulations and abundant scrap supply. Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) steel remains dominant in countries with ample access to iron ore and coal, such as China and India, where economies of scale and existing infrastructure support this traditional method. Your steel sourcing decisions can benefit from understanding these global trends, as the shift towards EAF reflects increasing demand for sustainable and cost-efficient steelmaking solutions.
Future Outlook for Steelmaking Technologies
EAF steel production is rapidly gaining traction due to its lower carbon footprint and adaptability to recycling scrap steel, making it a sustainable choice aligning with global decarbonization goals. BOF steel remains essential for primary iron ore processing but faces increasing pressure to reduce emissions through technological innovations like carbon capture and alternative fuels. Your decision between EAF and BOF methods will significantly impact environmental compliance and operational efficiency in the evolving steel industry landscape.
EAF steel vs BOF steel Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com