Hot dip galvanizing provides a thick, durable zinc coating by immersing steel in molten zinc, offering superior corrosion resistance for outdoor applications. Electroplating applies a thinner, more precise metal layer through electrical deposition, ideal for decorative finishes and intricate parts requiring uniform coverage.
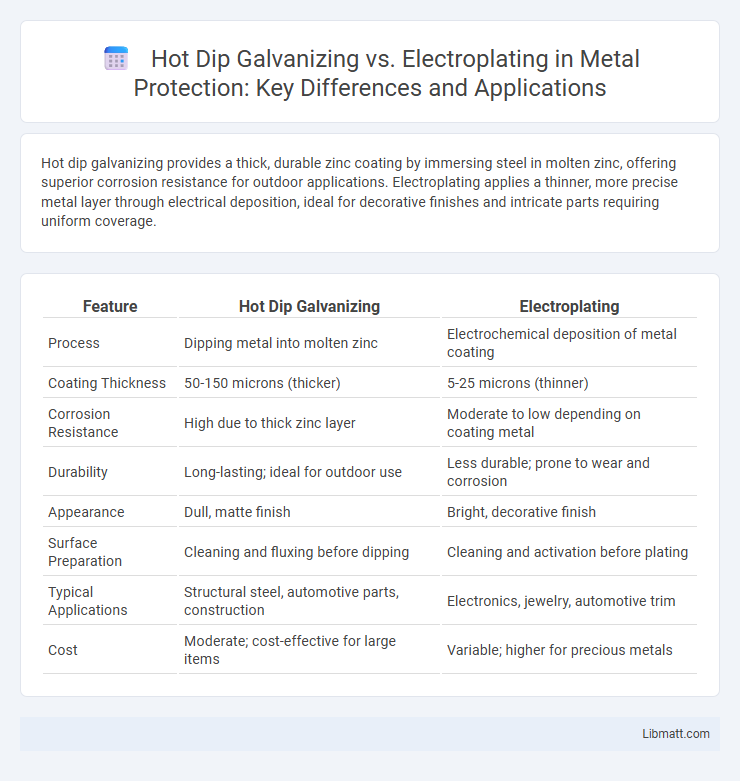
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hot Dip Galvanizing | Electroplating |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Dipping metal into molten zinc | Electrochemical deposition of metal coating |
| Coating Thickness | 50-150 microns (thicker) | 5-25 microns (thinner) |
| Corrosion Resistance | High due to thick zinc layer | Moderate to low depending on coating metal |
| Durability | Long-lasting; ideal for outdoor use | Less durable; prone to wear and corrosion |
| Appearance | Dull, matte finish | Bright, decorative finish |
| Surface Preparation | Cleaning and fluxing before dipping | Cleaning and activation before plating |
| Typical Applications | Structural steel, automotive parts, construction | Electronics, jewelry, automotive trim |
| Cost | Moderate; cost-effective for large items | Variable; higher for precious metals |
Introduction to Metal Coating Techniques
Hot dip galvanizing involves immersing steel in molten zinc, creating a thick, durable, and corrosion-resistant coating that bonds metallurgically to the base metal. Electroplating uses an electric current to deposit a thin, uniform layer of metal, such as nickel or chromium, onto the surface, providing enhanced aesthetic appeal and precise thickness control. Both techniques serve as essential metal coating methods to improve corrosion resistance and extend the lifespan of metal components in various industrial applications.
Overview of Hot Dip Galvanizing
Hot dip galvanizing involves immersing steel or iron into molten zinc, creating a robust, corrosion-resistant coating that bonds metallurgically to the base metal. This process forms a thicker, more durable layer compared to electroplating, making it ideal for outdoor or industrial applications demanding long-term protection. Your metal assets benefit from enhanced corrosion resistance and reduced maintenance when treated with hot dip galvanizing.
Understanding Electroplating
Electroplating is a precise metal coating process that uses electrical current to deposit a thin layer of metal onto a surface, enhancing corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Unlike hot dip galvanizing, which involves immersing the material in molten zinc for thick, durable protection, electroplating offers fine control over coating thickness and surface finish. Understanding electroplating can help you choose the right metal treatment based on your product's specific durability and appearance requirements.
Key Differences Between Hot Dip and Electroplating
Hot dip galvanizing involves immersing steel or iron into molten zinc, creating a thick, durable coating that offers superior corrosion resistance compared to electroplating. Electroplating deposits a thin layer of metal, such as chromium or nickel, onto a substrate using an electrical current, resulting in a smoother and more decorative finish but less robust protection. Your choice depends on the desired balance between corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, with hot dip favored for heavy-duty protection and electroplating ideal for precision and surface smoothness.
Materials Suitable for Each Method
Hot dip galvanizing is ideal for steel and iron components that require thick, corrosion-resistant zinc coatings, especially for outdoor or heavy-duty applications. Electroplating suits a wide range of metals, including copper, nickel, and silver, and excels at providing precise, decorative, or thin protective layers on delicate or small parts. Each method's suitability depends on the base material's compatibility with the coating process and the desired properties of the finished surface.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance Compared
Hot dip galvanizing provides superior durability and corrosion resistance by coating steel with a thick layer of zinc that forms a robust metallurgical bond, protecting the base metal even in harsh environments. Electroplating deposits a thinner zinc layer primarily through an electrical process, which offers less protection and wears away faster under abrasive conditions or prolonged exposure to moisture. You should choose hot dip galvanizing for long-lasting, heavy-duty applications requiring maximum corrosion resistance.
Cost Analysis: Hot Dip vs Electroplating
Hot dip galvanizing typically incurs higher upfront costs due to the thick zinc coating and industrial equipment involved, but it offers long-term cost savings through superior corrosion resistance and reduced maintenance. Electroplating generally features lower initial expenses and precise, thin metal layers ideal for decorative or lightweight applications but may require more frequent re-coating or touch-ups, increasing lifecycle costs. Your choice depends on balancing initial investment with durability requirements and maintenance budgets for optimal cost-efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
Hot dip galvanizing typically has a lower environmental impact due to its longer-lasting corrosion resistance, reducing the frequency of reapplications and associated waste. The process involves molten zinc, which can be hazardous if not properly managed, requiring strict safety protocols to protect workers from high temperatures and fumes. Electroplating uses hazardous chemicals like cyanide or heavy metals, posing risks of water contamination and toxic exposure, making waste treatment and stringent safety measures essential.
Common Applications in Industry
Hot dip galvanizing is commonly applied in industries requiring robust corrosion resistance for structural steel, such as construction, automotive, and outdoor equipment manufacturing. Electroplating is widely used in electronics, jewelry, and precision engineering to provide thin, decorative, or functional metal coatings. Your choice depends on whether durability or aesthetic finish is the priority in your industrial application.
Choosing the Right Process for Your Needs
Hot dip galvanizing provides a thicker, more durable zinc coating ideal for outdoor structures exposed to harsh weather and corrosion. Electroplating offers precise, uniform coatings suitable for delicate components requiring aesthetic finishes and controlled thickness. Selecting the right process depends on factors like environmental exposure, required coating thickness, durability, and cost efficiency for your specific application.
hot dip vs electroplating Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com