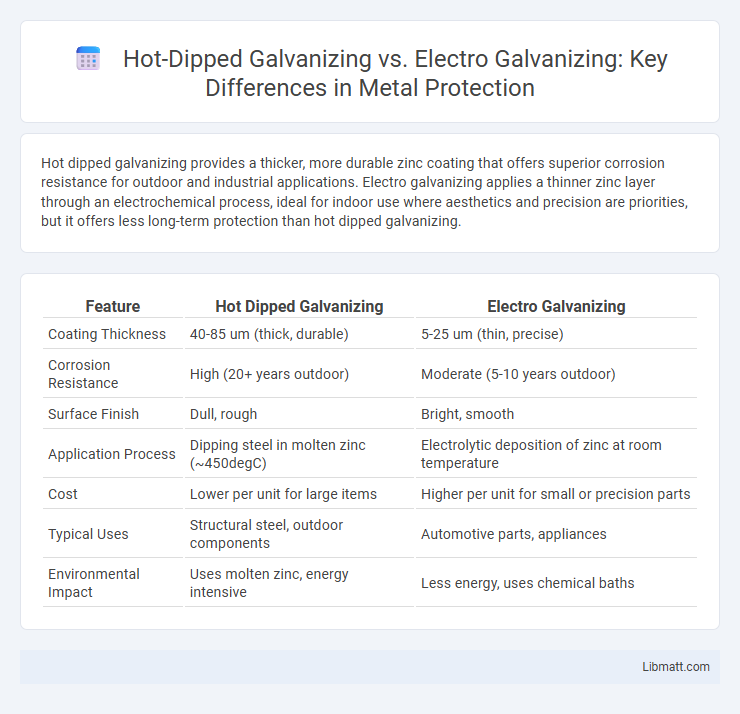
Hot dipped galvanizing provides a thicker, more durable zinc coating that offers superior corrosion resistance for outdoor and industrial applications. Electro galvanizing applies a thinner zinc layer through an electrochemical process, ideal for indoor use where aesthetics and precision are priorities, but it offers less long-term protection than hot dipped galvanizing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hot Dipped Galvanizing | Electro Galvanizing |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Thickness | 40-85 um (thick, durable) | 5-25 um (thin, precise) |
| Corrosion Resistance | High (20+ years outdoor) | Moderate (5-10 years outdoor) |
| Surface Finish | Dull, rough | Bright, smooth |
| Application Process | Dipping steel in molten zinc (~450degC) | Electrolytic deposition of zinc at room temperature |
| Cost | Lower per unit for large items | Higher per unit for small or precision parts |
| Typical Uses | Structural steel, outdoor components | Automotive parts, appliances |
| Environmental Impact | Uses molten zinc, energy intensive | Less energy, uses chemical baths |
Introduction to Galvanizing: Purpose and Process
Hot dipped galvanizing provides a durable protective zinc coating by immersing steel in molten zinc, creating a thick, corrosion-resistant layer ideal for outdoor or industrial use. Electro galvanizing applies a thinner zinc layer through electroplating, offering a smoother finish suited for indoor applications where appearance matters. Your choice depends on the balance between corrosion resistance needed and the desired surface quality.
What is Hot Dipped Galvanizing?
Hot dipped galvanizing is a corrosion protection process where steel or iron is submerged in molten zinc at approximately 450degC, forming a metallurgical bond between the zinc and the base metal. This coating provides a thick, robust layer highly resistant to abrasion, corrosion, and weathering, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial applications. The zinc layer's durability surpasses that of electro galvanizing, which typically applies a thinner zinc coating via an electrical current.
What is Electro Galvanizing?
Electro galvanizing is a process that uses an electrical current to deposit a thin layer of zinc onto steel or iron surfaces, providing corrosion resistance. This method creates a smooth, uniform coating with precise thickness control, ideal for applications requiring enhanced surface appearance and moderate protection. Your choice between electro galvanizing and hot dipped galvanizing depends on the required durability, environmental exposure, and finish quality.
Key Differences Between Hot Dipped and Electro Galvanizing
Hot dipped galvanizing involves immersing steel in molten zinc, creating a thick, durable coating that offers superior corrosion resistance and longevity compared to electro galvanizing, which uses an electrical current to deposit a thinner zinc layer. The hot dipped process results in a rougher, more ductile finish ideal for heavy-duty outdoor applications, while electro galvanizing provides a smoother, more uniform appearance suited for indoor or light exposure environments. Your choice depends on the required durability, aesthetic preference, and intended environmental conditions for the galvanized steel.
Corrosion Resistance: Which Method Lasts Longer?
Hot dipped galvanizing provides superior corrosion resistance due to its thicker zinc coating, which forms a robust barrier that withstands harsh environmental conditions for decades. Electro galvanizing applies a thinner, more uniform zinc layer that offers moderate protection but tends to wear off faster, making it less durable in outdoor or industrial settings. Consequently, hot dipped galvanizing lasts significantly longer, especially in corrosive environments such as marine or industrial atmospheres.
Surface Finish and Appearance Comparison
Hot dipped galvanizing produces a thicker, more rugged coating with a matte, spangled surface, which offers robust corrosion protection but may appear less smooth. Electro galvanizing creates a thinner, more uniform zinc layer that results in a brighter, shinier, and smoother surface finish ideal for indoor applications or decorative purposes. The choice depends on the required durability and aesthetic preference, with hot dipped galvanizing favored for heavy-duty exposure and electro galvanizing for enhanced visual appeal.
Application Areas: Where Each Method Excels
Hot dipped galvanizing excels in heavy-duty applications such as structural steel, outdoor bridges, and industrial equipment due to its thick, durable zinc coating that provides superior corrosion resistance. Electro galvanizing is ideal for precision components, automotive parts, and household appliances where a smooth finish and thinner protective layer meet aesthetic and light-duty protection needs. Your choice depends on the required durability and surface finish for specific environmental conditions and usage.
Cost Analysis: Hot Dipped vs Electro Galvanizing
Hot dipped galvanizing typically incurs higher initial costs due to the extensive surface preparation and thicker zinc coating application, but offers superior long-term corrosion resistance, reducing maintenance expenses. Electro galvanizing presents a lower upfront price with a thinner zinc layer, making it cost-effective for indoor or less corrosive environments but may require more frequent re-coating. Evaluating lifecycle costs and environmental exposure is essential for accurate cost-benefit analysis between hot dipped and electro galvanizing methods.
Environmental Impact of Both Galvanizing Methods
Hot dipped galvanizing involves immersing steel in molten zinc, creating a thick, durable coating that offers long-lasting corrosion resistance, but the process consumes significant energy and produces more zinc waste. Electro galvanizing, using an electric current to deposit zinc layers, generates less waste and lower energy emissions but results in a thinner coating that may reduce product lifespan. Your choice between these methods affects not only environmental sustainability but also the overall durability and maintenance needs of galvanized steel products.
Choosing the Right Galvanizing Process for Your Project
Hot dipped galvanizing offers superior corrosion resistance by coating steel in molten zinc, creating a thick, durable layer ideal for outdoor and industrial applications. Electro galvanizing deposits a thin, uniform zinc layer through an electrical process, providing a smoother finish best suited for indoor or decorative uses with less exposure to harsh environments. Selecting the right galvanizing method depends on factors like required durability, environmental exposure, and budget constraints to ensure optimal protection and cost-effectiveness.
hot dipped galvanizing vs electro galvanizing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com