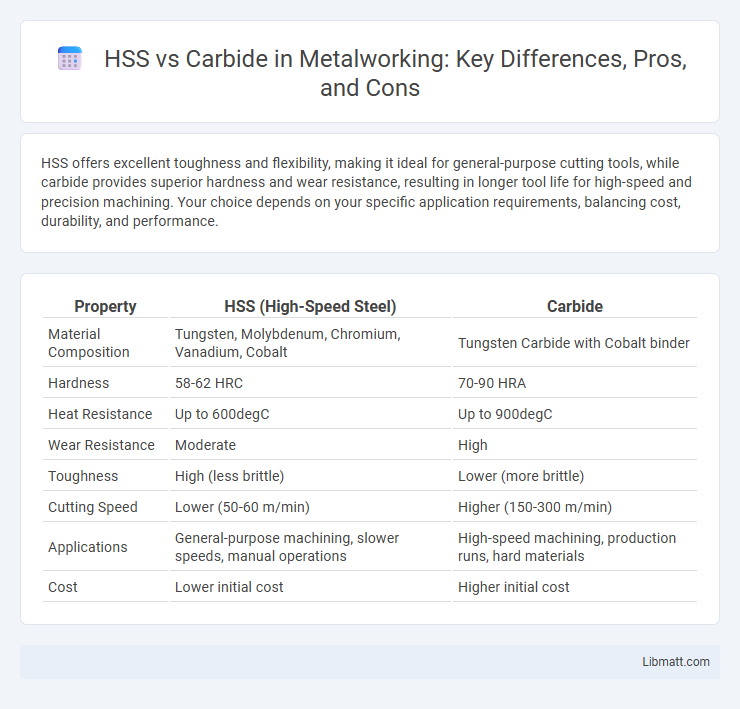
HSS offers excellent toughness and flexibility, making it ideal for general-purpose cutting tools, while carbide provides superior hardness and wear resistance, resulting in longer tool life for high-speed and precision machining. Your choice depends on your specific application requirements, balancing cost, durability, and performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | HSS (High-Speed Steel) | Carbide |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Tungsten, Molybdenum, Chromium, Vanadium, Cobalt | Tungsten Carbide with Cobalt binder |
| Hardness | 58-62 HRC | 70-90 HRA |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 600degC | Up to 900degC |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Toughness | High (less brittle) | Lower (more brittle) |
| Cutting Speed | Lower (50-60 m/min) | Higher (150-300 m/min) |
| Applications | General-purpose machining, slower speeds, manual operations | High-speed machining, production runs, hard materials |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
Introduction to HSS and Carbide
High-Speed Steel (HSS) is a versatile tool material known for its toughness and ability to withstand high temperatures without losing hardness, making it suitable for general-purpose machining. Carbide, composed of tungsten carbide particles bonded with cobalt, offers superior hardness and wear resistance, ideal for high-speed cutting and abrasive conditions. Your choice between HSS and carbide depends on factors like machining speed, material hardness, and tool life requirements.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
High-Speed Steel (HSS) is primarily composed of iron alloyed with tungsten, molybdenum, chromium, vanadium, and cobalt, manufactured through a hot-working or powder metallurgy process that enhances toughness and wear resistance. Carbide tools consist mainly of tungsten carbide particles bonded with cobalt, produced via powder metallurgy sintering, resulting in superior hardness and heat resistance compared to HSS. Your choice between HSS and carbide depends on the specific application, where HSS offers better toughness and carbides excel in hardness and high-temperature cutting.
Key Properties Comparison
High-speed steel (HSS) offers excellent toughness and resistance to shock, making it suitable for cutting tools that require durability under intermittent cutting conditions. Carbide, composed primarily of tungsten carbide particles, provides superior hardness and wear resistance, enabling higher cutting speeds and longer tool life in continuous machining operations. Your choice between HSS and carbide depends on the balance needed between toughness and cutting speed for your specific application.
Performance in Cutting Applications
High-Speed Steel (HSS) offers excellent toughness and resistance to chipping, making it suitable for interrupted cuts and general-purpose machining, while carbide provides superior hardness and wear resistance, enabling higher cutting speeds and longer tool life in abrasive materials. Carbide tools maintain sharpness and dimensional stability at elevated temperatures, enhancing performance in high-speed and high-feed applications. HSS excels in low-speed cutting scenarios where flexibility and impact resistance are critical, whereas carbide is preferred for precision machining requiring high productivity and surface finish quality.
Tool Life and Durability
High-Speed Steel (HSS) offers moderate tool life with good toughness, making it suitable for applications involving intermittent cuts and vibration. Carbide tools exhibit superior durability and significantly longer tool life due to their hardness and wear resistance, especially in high-speed cutting and abrasive materials. The choice between HSS and carbide directly impacts production efficiency, with carbide providing extended tool replacement intervals and enhanced cutting performance.
Cost Analysis: HSS vs Carbide
High-Speed Steel (HSS) tools typically have a lower initial cost compared to carbide tools, making them more budget-friendly for small-scale or less demanding machining operations. Carbide tools, while more expensive upfront, offer superior wear resistance and longer tool life, which can lead to reduced downtime and lower overall tooling costs in high-volume production environments. Factoring in tool replacement frequency and machining efficiency is essential for a comprehensive cost analysis between HSS and carbide tooling.
Suitability for Various Materials
High-Speed Steel (HSS) is suitable for machining softer materials such as aluminum, brass, and mild steel due to its toughness and ability to withstand impact. Carbide excels in processing harder materials including stainless steel, cast iron, and hardened alloys because of its superior hardness and heat resistance. Choosing between HSS and carbide depends on the material hardness and machining conditions to optimize tool life and performance.
Maintenance and Re-sharpening
High-Speed Steel (HSS) tools allow for easier maintenance and more frequent re-sharpening due to their softer composition, enabling precise edge restoration without specialized equipment. Carbide tools require professional-grade machinery for re-sharpening because of their hardness and brittleness, making maintenance more complex and costly. Regular sharpening of HSS extends tool life efficiently, whereas carbide's durability reduces sharpening frequency but increases maintenance expenses when re-sharpening is necessary.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbide tooling often involves energy-intensive mining and complex chemical processing, contributing to higher carbon emissions and resource depletion compared to High-Speed Steel (HSS), which uses more abundant materials and simpler manufacturing processes. HSS can be more sustainable due to its longer tool life and easier recyclability, reducing waste and environmental footprint in machining operations. Choosing HSS over carbide aligns with efforts to minimize ecological impact while maintaining efficient metal cutting performance.
Choosing the Right Tool: HSS or Carbide?
Choosing between HSS and carbide tools depends on your specific machining needs, as HSS offers excellent toughness and is ideal for cutting softer materials at slower speeds, while carbide excels in high-speed applications and hard material cutting due to its superior hardness and wear resistance. Your choice should consider factors like machining speed, material hardness, tool life, and cost-effectiveness; carbide tools generally provide longer life and better performance in demanding conditions but come at a higher price. Selecting the right tool ensures optimal cutting efficiency, surface finish, and overall productivity in your manufacturing process.
HSS vs carbide Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com