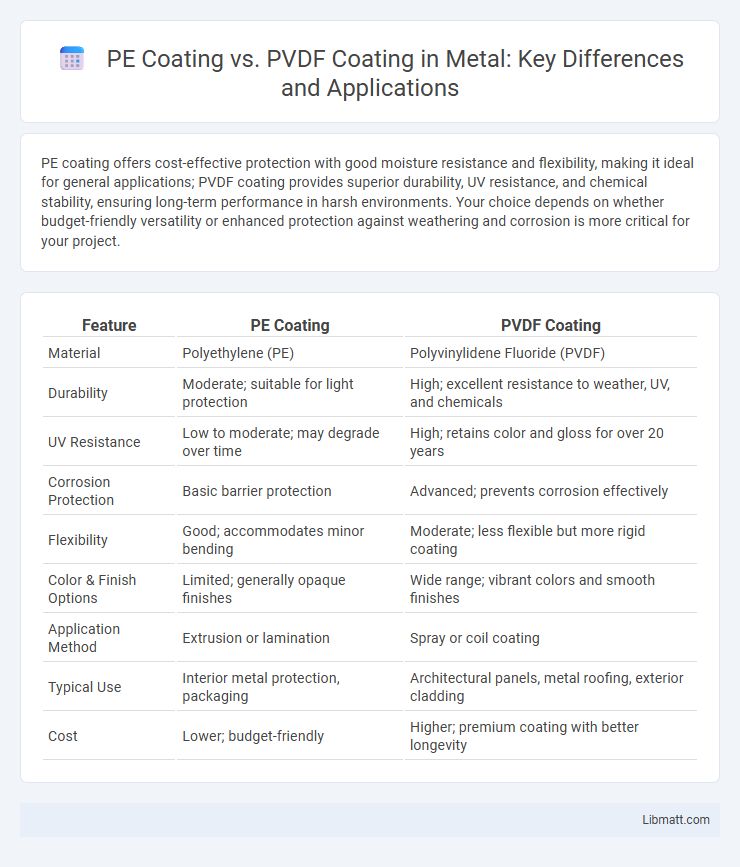
PE coating offers cost-effective protection with good moisture resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for general applications; PVDF coating provides superior durability, UV resistance, and chemical stability, ensuring long-term performance in harsh environments. Your choice depends on whether budget-friendly versatility or enhanced protection against weathering and corrosion is more critical for your project.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | PE Coating | PVDF Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polyethylene (PE) | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) |
| Durability | Moderate; suitable for light protection | High; excellent resistance to weather, UV, and chemicals |
| UV Resistance | Low to moderate; may degrade over time | High; retains color and gloss for over 20 years |
| Corrosion Protection | Basic barrier protection | Advanced; prevents corrosion effectively |
| Flexibility | Good; accommodates minor bending | Moderate; less flexible but more rigid coating |
| Color & Finish Options | Limited; generally opaque finishes | Wide range; vibrant colors and smooth finishes |
| Application Method | Extrusion or lamination | Spray or coil coating |
| Typical Use | Interior metal protection, packaging | Architectural panels, metal roofing, exterior cladding |
| Cost | Lower; budget-friendly | Higher; premium coating with better longevity |
Introduction to PE and PVDF Coatings
PE (Polyethylene) coating offers robust resistance to moisture, chemicals, and abrasion, making it ideal for industrial and agricultural applications where durability and cost-effectiveness are priorities. PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride) coating exhibits superior UV resistance, weatherability, and color retention, commonly used in architectural, automotive, and aerospace industries requiring long-lasting aesthetic and protective properties. Both PE and PVDF coatings enhance substrate longevity, but PVDF's advanced chemical structure provides enhanced performance in harsh environmental conditions.
Chemical Composition and Structure
PE coating consists primarily of polyethylene, a thermoplastic polymer made of long chains of ethylene monomers, providing a non-polar, hydrophobic surface with excellent chemical resistance and flexibility. PVDF coating is based on polyvinylidene fluoride, a fluoropolymer characterized by strong carbon-fluorine bonds that create a highly durable, UV-resistant, and chemically inert barrier. Your choice between PE and PVDF coatings depends on the specific chemical exposure and environmental durability requirements, as PVDF offers superior resistance to harsh chemicals and weathering compared to the more economical and flexible PE coating.
Key Properties Comparison
PE coating offers excellent flexibility and chemical resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability against harsh environmental conditions. PVDF coating provides superior UV resistance and color retention, ensuring long-lasting aesthetic appeal and protection against weathering. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize mechanical toughness with PE or enhanced environmental resilience and longevity with PVDF coatings.
Durability and Weather Resistance
PVDF coating offers superior durability and weather resistance compared to PE coating, maintaining color stability and gloss under prolonged UV exposure and harsh environmental conditions. PE coating demonstrates moderate weather resistance but tends to degrade faster with fading, chalking, and loss of adhesion when exposed to extreme temperatures and moisture over time. PVDF's fluoropolymer composition ensures enhanced protection against corrosion, chemical exposure, and abrasion, making it ideal for long-term outdoor applications.
Application Areas and Suitability
PE coating excels in applications requiring cost-effective protection and flexibility, commonly used in agricultural films, packaging, and corrosion-resistant pipes. PVDF coating suits environments demanding superior chemical resistance and durability, ideal for architectural cladding, industrial equipment, and harsh outdoor conditions. Your choice depends on balancing budget considerations with the need for longevity and chemical exposure resistance.
Ease of Application and Maintenance
PE coating offers straightforward application due to its flexibility and quick cure time, allowing for efficient coverage on various surfaces with minimal preparation. PVDF coating requires more precise application conditions, including controlled temperature and multiple thin layers, but provides a durable finish that resists dirt and fading, reducing long-term maintenance. Your choice depends on whether ease of initial application or long-lasting, low-maintenance performance is the priority for your project.
Environmental Impact and Safety
PE coating (Polyethylene) involves lower energy consumption during manufacturing and is generally recyclable, contributing to reduced environmental impact compared to PVDF coating (Polyvinylidene Fluoride). PVDF coatings contain fluorinated compounds that can release toxic substances during production and disposal, posing greater environmental and health risks. PE coatings are often preferred for applications where minimizing ecological footprint and ensuring safer handling are priorities.
Cost Differences: PE vs. PVDF
PE coating offers a more cost-effective solution compared to PVDF coating, with prices typically 30-50% lower due to simpler manufacturing processes and less expensive raw materials. PVDF coatings provide superior durability, chemical resistance, and UV stability, which justifies their higher initial cost in long-term applications. Budget-sensitive projects commonly prefer PE coatings for short to medium lifespan products, whereas PVDF coatings are favored in environments demanding extended performance and low maintenance.
Industry Standards and Certifications
PE coating meets basic industry standards for corrosion resistance and durability, commonly certified under ASTM and ISO specifications. PVDF coating adheres to more stringent certifications such as AAMA 2605, ensuring superior UV resistance, color retention, and long-term performance in architectural applications. Your choice depends on the certification requirements of your project, with PVDF preferred for high-end, certified coatings.
Choosing the Right Coating for Your Project
PE coating offers excellent flexibility and impact resistance, making it ideal for projects requiring durability in harsh environments. PVDF coating provides superior UV resistance and color retention, ensuring long-lasting aesthetics for architectural applications. Selecting the right coating depends on balancing budget constraints with performance needs like weather resistance and longevity.
PE coating vs PVDF coating Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com