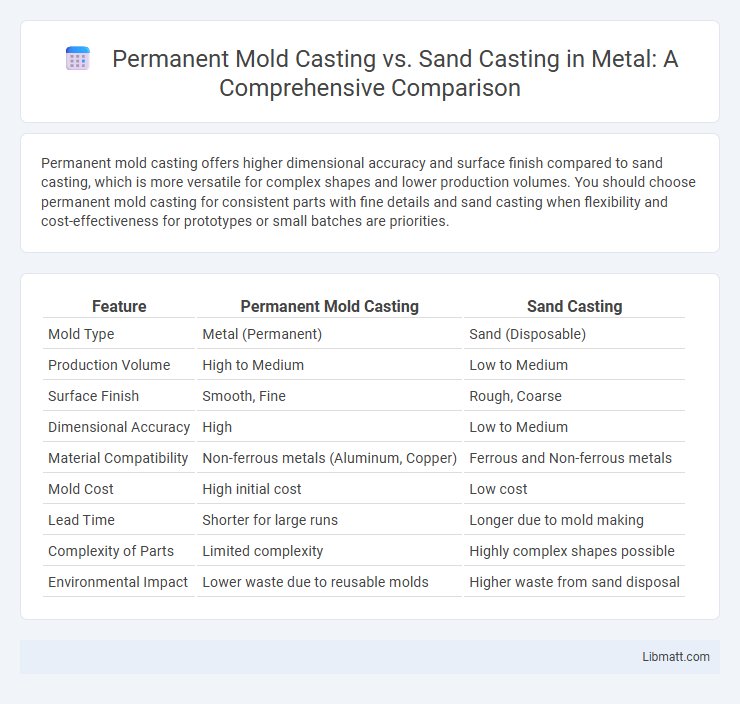
Permanent mold casting offers higher dimensional accuracy and surface finish compared to sand casting, which is more versatile for complex shapes and lower production volumes. You should choose permanent mold casting for consistent parts with fine details and sand casting when flexibility and cost-effectiveness for prototypes or small batches are priorities.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Permanent Mold Casting | Sand Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Mold Type | Metal (Permanent) | Sand (Disposable) |
| Production Volume | High to Medium | Low to Medium |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, Fine | Rough, Coarse |
| Dimensional Accuracy | High | Low to Medium |
| Material Compatibility | Non-ferrous metals (Aluminum, Copper) | Ferrous and Non-ferrous metals |
| Mold Cost | High initial cost | Low cost |
| Lead Time | Shorter for large runs | Longer due to mold making |
| Complexity of Parts | Limited complexity | Highly complex shapes possible |
| Environmental Impact | Lower waste due to reusable molds | Higher waste from sand disposal |
Introduction to Permanent Mold Casting and Sand Casting
Permanent mold casting involves pouring molten metal into a reusable metal mold, offering precise dimensional control and smoother surface finishes, making it ideal for high-volume production of non-ferrous metals like aluminum and copper alloys. Sand casting uses a disposable sand mold, allowing for greater design flexibility and suitability for complex geometries or larger parts, though it often results in a rougher surface and lower dimensional accuracy. Understanding these differences helps you choose the most efficient casting process tailored to your manufacturing needs.
Key Differences Between Permanent Mold and Sand Casting
Permanent mold casting uses reusable metal molds made from cast iron or steel, ensuring higher dimensional accuracy and surface finish compared to sand casting's expendable sand molds. Sand casting is more versatile for complex shapes and larger parts but often results in rougher surfaces and lower precision. Your choice depends on production volume, cost, and required detail, with permanent molds suited for high-volume, consistent parts and sand casting ideal for prototyping or low-volume runs.
Material Compatibility in Permanent Mold vs Sand Casting
Permanent mold casting offers superior material compatibility with non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, magnesium, and copper alloys due to its precise temperature control and reusable molds, resulting in finer grain structures and enhanced mechanical properties. Sand casting accommodates a wider range of metals, including ferrous and non-ferrous alloys, making it versatile for complex shapes and large components but typically yields coarser microstructures and lower surface finish quality. The choice between permanent mold and sand casting depends on the alloy requirements, production volume, and desired material properties for the final product.
Surface Finish and Dimensional Accuracy Comparison
Permanent mold casting delivers a superior surface finish with smoother textures and fewer imperfections compared to sand casting, which often produces rougher surfaces due to the granular nature of sand molds. Dimensional accuracy in permanent mold casting is higher, providing tighter tolerances and consistent part dimensions, while sand casting tends to have greater variability and often requires additional machining. Your choice between these methods impacts the need for post-processing and the precision of the final component.
Production Efficiency: Cycle Time and Automation
Permanent mold casting offers superior production efficiency with significantly shorter cycle times, often ranging from 30 seconds to a few minutes per part, due to rapid solidification and mold reuse. In contrast, sand casting requires longer cycle times, typically 20 to 60 minutes, because of mold preparation and cooling processes. Automation is more feasible in permanent mold casting, enabling consistent quality and high-volume production, while sand casting remains more labor-intensive and less suited for automation.
Cost Analysis: Tooling, Labor, and Maintenance
Permanent mold casting involves higher initial tooling costs due to durable metal molds, but it offers lower labor expenses and reduced maintenance over time thanks to mold reusability. Sand casting presents lower upfront tooling costs with expendable sand molds, yet incurs higher labor and maintenance costs stemming from mold preparation and disposal for each casting. Your cost efficiency depends on production volume, as permanent mold casting becomes economical for large runs, while sand casting suits smaller batches with flexible tooling needs.
Suitable Applications for Permanent Mold Casting
Permanent mold casting is ideal for producing medium to high-volume metal parts with excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy, commonly used in automotive components, aerospace parts, and household appliances. Your production benefits from this method when manufacturing aluminum, magnesium, or copper alloys requiring consistent quality and structural integrity. The process supports applications requiring tight tolerances and smooth surfaces that reduce the need for additional machining or finishing.
Sand Casting: Advantages and Limitations
Sand casting offers flexibility with complex geometries and large component sizes, making it ideal for low-volume production and prototypes. Its primary limitations include lower surface finish quality, less dimensional accuracy, and longer lead times compared to permanent mold casting. The process is cost-effective due to inexpensive sand molds but can result in higher porosity and rough surfaces requiring additional machining.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Permanent mold casting significantly reduces environmental impact compared to sand casting by allowing repeated use of molds, minimizing waste generation and resource consumption. Sand casting produces large volumes of spent sand and associated waste, requiring energy-intensive recycling or disposal processes. Sustainable manufacturing benefits from permanent mold casting's lower energy requirements and reduced raw material usage, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint and enhanced lifecycle sustainability.
Choosing the Right Casting Method for Your Project
Permanent mold casting delivers superior surface finish and dimensional accuracy, ideal for high-volume production with metals like aluminum and magnesium. Sand casting offers greater design flexibility and cost-effectiveness for low-volume or large, complex parts, accommodating a wide range of metals including cast iron and steel. Selecting the optimal method depends on factors such as production volume, material properties, complexity, and budget constraints to ensure efficiency and quality.
Permanent mold casting vs sand casting Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com