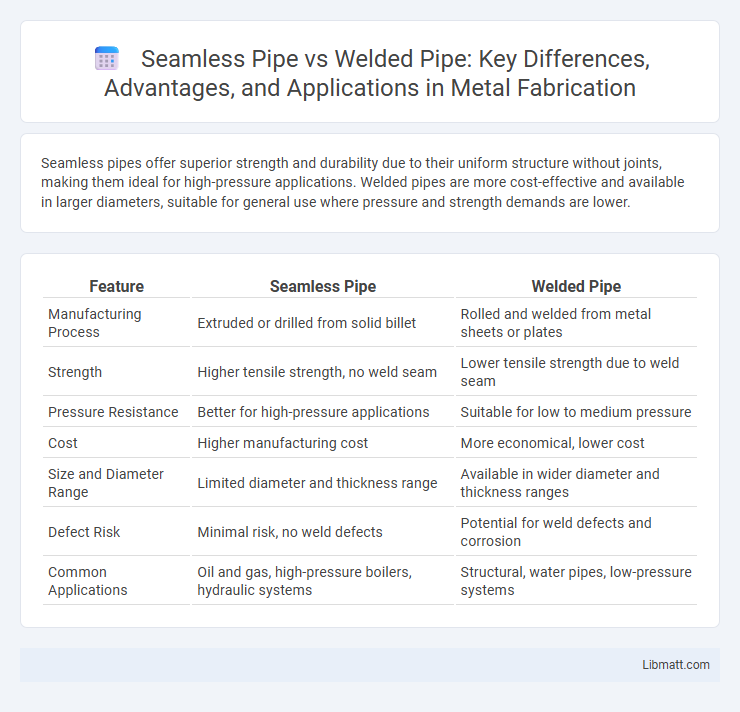
Seamless pipes offer superior strength and durability due to their uniform structure without joints, making them ideal for high-pressure applications. Welded pipes are more cost-effective and available in larger diameters, suitable for general use where pressure and strength demands are lower.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Seamless Pipe | Welded Pipe |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Extruded or drilled from solid billet | Rolled and welded from metal sheets or plates |
| Strength | Higher tensile strength, no weld seam | Lower tensile strength due to weld seam |
| Pressure Resistance | Better for high-pressure applications | Suitable for low to medium pressure |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | More economical, lower cost |
| Size and Diameter Range | Limited diameter and thickness range | Available in wider diameter and thickness ranges |
| Defect Risk | Minimal risk, no weld defects | Potential for weld defects and corrosion |
| Common Applications | Oil and gas, high-pressure boilers, hydraulic systems | Structural, water pipes, low-pressure systems |
Introduction to Seamless and Welded Pipes
Seamless pipes are manufactured from a solid billet, creating a uniform structure with no joints, which enhances strength and pressure resistance, making them ideal for high-stress applications such as oil and gas pipelines. Welded pipes, produced by rolling metal sheets and welding the edges, offer cost-effectiveness and greater dimensional versatility, commonly used in water supply and structural applications. Material selection between seamless and welded pipes depends on factors like application pressure, corrosion resistance, and budget constraints.
Manufacturing Process Overview
Seamless pipes are manufactured through extrusion or rotary piercing, where a solid billet is heated and formed into a hollow tube without any joints, ensuring uniform strength and corrosion resistance. Welded pipes are produced by rolling metal plates or strips into a cylindrical shape, then joining the edges using electric resistance welding, which introduces a seam that may affect structural integrity under high pressure. Understanding the differences in manufacturing processes helps you select the right pipe type for applications requiring durability and reliability.
Key Differences Between Seamless and Welded Pipes
Seamless pipes are manufactured without any joints by extruding metal to form a single, solid tube, offering superior strength and resistance to pressure compared to welded pipes, which are made by rolling metal plates and welding the edges together. Welded pipes are typically more cost-effective and available in larger diameters but may have weaker points along the weld seam, affecting their performance in high-pressure environments. Your choice between seamless and welded pipes should consider factors like application pressure, budget, and the required durability for optimal results.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Seamless pipes offer superior strength and durability due to their uniform structure, which eliminates weak points caused by welding seams. Welded pipes may have varying mechanical properties and potential weaknesses along the weld, making them less reliable under high pressure or extreme conditions. Your choice between seamless and welded pipes should consider the specific requirements for strength and longevity in your application.
Cost Analysis: Seamless vs Welded Pipes
Seamless pipes generally incur higher manufacturing costs due to their complex production process involving extrusion or rotary piercing, whereas welded pipes are typically more cost-effective because they are made by rolling and welding steel sheets or strips. The cost difference is influenced by factors such as raw material prices, production volume, and equipment expenses, with welded pipes offering better scalability and lower upfront investment. For projects prioritizing budget constraints, welded pipes often provide a more economical solution without compromising basic performance requirements.
Common Applications for Each Pipe Type
Seamless pipes are commonly used in high-pressure applications such as oil and gas pipelines, power plants, and chemical processing due to their superior strength and resistance to corrosion. Welded pipes are preferred for water transportation, structural purposes, and low to medium pressure applications because they are more cost-effective and easier to manufacture in large diameters. Understanding your project's requirements helps determine whether seamless or welded pipes offer the best performance and longevity.
Dimensional Accuracy and Size Range
Seamless pipes offer superior dimensional accuracy due to their uniform structure formed by extrusion, making them ideal for precision applications demanding tight tolerances. Welded pipes provide a broader size range and are available in larger diameters and varied wall thicknesses, catering to diverse industrial needs where flexibility in size is critical. Your selection depends on whether you prioritize exact dimensional consistency or a wider range of size options for your project.
Corrosion Resistance and Maintenance
Seamless pipes offer superior corrosion resistance due to the absence of weld joints, which eliminates potential weak points where corrosion can initiate, making them ideal for high-pressure and corrosive environments. Welded pipes may require more frequent maintenance to monitor and repair weld seams that are susceptible to corrosion and stress cracks over time. Choosing seamless pipes can significantly reduce your maintenance costs and enhance the longevity of piping systems exposed to aggressive substances.
Industry Standards and Certifications
Seamless pipes are manufactured according to ASTM A106 and ASME B36.10 standards, ensuring uniformity and strength in high-pressure applications without welding seams. Welded pipes comply with ASTM A53 and API 5L standards, requiring thorough inspections such as radiographic testing to verify weld integrity for safety and performance. Both pipe types must meet certifications like ISO 9001 and PED (Pressure Equipment Directive) to guarantee quality control and regulatory compliance in oil, gas, and construction industries.
Choosing the Right Pipe for Your Project
Seamless pipes offer superior strength and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for high-pressure applications, while welded pipes are more cost-effective and suitable for low to moderate pressure projects. Your choice depends on factors like pressure requirements, budget constraints, and the environmental conditions of the installation site. Carefully assessing these parameters ensures the right pipe selection for project durability and efficiency.
Seamless Pipe vs Welded Pipe Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com