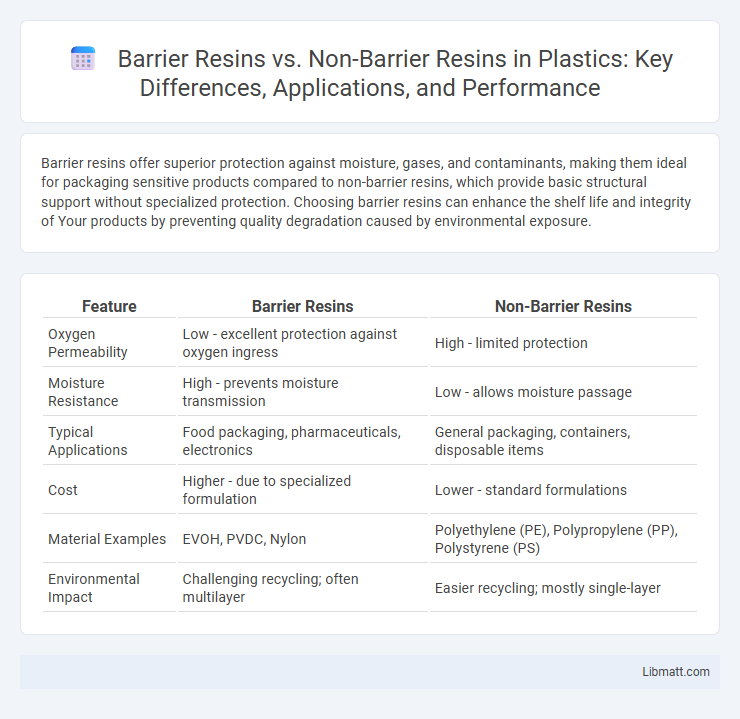
Barrier resins offer superior protection against moisture, gases, and contaminants, making them ideal for packaging sensitive products compared to non-barrier resins, which provide basic structural support without specialized protection. Choosing barrier resins can enhance the shelf life and integrity of Your products by preventing quality degradation caused by environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Barrier Resins | Non-Barrier Resins |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Permeability | Low - excellent protection against oxygen ingress | High - limited protection |
| Moisture Resistance | High - prevents moisture transmission | Low - allows moisture passage |
| Typical Applications | Food packaging, pharmaceuticals, electronics | General packaging, containers, disposable items |
| Cost | Higher - due to specialized formulation | Lower - standard formulations |
| Material Examples | EVOH, PVDC, Nylon | Polyethylene (PE), Polypropylene (PP), Polystyrene (PS) |
| Environmental Impact | Challenging recycling; often multilayer | Easier recycling; mostly single-layer |
Introduction to Barrier and Non-barrier Resins
Barrier resins are engineered polymers designed to prevent the passage of gases, moisture, and odors, making them essential in food packaging and pharmaceutical applications where product preservation is critical. Non-barrier resins lack these protective properties and are typically used for products where barrier protection is less important, such as in general packaging or everyday consumer goods. Understanding the difference between barrier and non-barrier resins helps you select materials that optimize product shelf life and integrity based on specific application requirements.
Key Differences Between Barrier and Non-barrier Resins
Barrier resins provide enhanced protection against moisture, gases, and odors, making them ideal for packaging sensitive products like food and pharmaceuticals. Non-barrier resins lack this protective layer, resulting in higher permeability and reduced shelf life for packaged goods. Your choice between barrier and non-barrier resins directly impacts product preservation and quality during storage and transportation.
Common Types of Barrier Resins
Common types of barrier resins include ethylene vinyl alcohol (EVOH), polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC), and nylon, each offering superior protection against oxygen, moisture, and contaminants in packaging applications. Non-barrier resins such as polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) provide excellent sealing and flexibility but lack the ability to prevent gas or vapor transmission effectively. Your choice between barrier and non-barrier resins depends on the specific preservation needs of the product inside the packaging.
Typical Applications of Non-barrier Resins
Non-barrier resins are commonly used in applications requiring basic containment and structural support, such as packaging for dry foods, containers for non-perishable goods, and general-purpose films. These resins provide cost-effective solutions where moisture, oxygen, or aroma protection is not critical, making them ideal for products with shorter shelf lives or less sensitive contents. Your choice of non-barrier resins ensures flexibility and affordability in manufacturing processes without compromising basic functional requirements.
Advantages of Barrier Resins
Barrier resins provide superior protection against moisture, oxygen, and odor transmission, significantly extending product shelf life compared to non-barrier resins. They enhance packaging durability and preserve product quality, making them ideal for sensitive food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic applications. Their ability to maintain the integrity of contents reduces waste and supports sustainability efforts.
Limitations of Non-barrier Resins
Non-barrier resins lack the protective properties needed to prevent gas, moisture, and chemical permeation, which can compromise product integrity and shelf life. These resins offer limited resistance against external contamination, making them unsuitable for packaging sensitive or perishable goods. Your choice of packaging material should consider these limitations to ensure optimal preservation and durability.
Performance Comparison: Barrier vs Non-barrier Resins
Barrier resins provide superior protection against moisture, oxygen, and chemical permeation, enhancing shelf life and product integrity compared to non-barrier resins. Non-barrier resins typically offer cost-effective solutions with adequate mechanical strength but lack the advanced barrier properties necessary for extended preservation. Your choice between barrier and non-barrier resins depends on the specific performance requirements of your packaging or manufacturing application.
Cost Considerations in Resin Selection
Barrier resins typically incur higher costs due to their specialized formulations designed to prevent gas, moisture, and odor transmission, making them ideal for packaging sensitive products. Non-barrier resins, being less complex, offer a more economical option but may compromise product shelf life or quality in demanding applications. Your choice between barrier and non-barrier resins should weigh upfront material costs against potential savings from reduced spoilage or product degradation.
Environmental Impact of Barrier and Non-barrier Resins
Barrier resins significantly reduce product spoilage and waste by extending shelf life, contributing to lower environmental impact through decreased resource consumption. Non-barrier resins, often made from single-polymer compositions, tend to be more recyclable but may lead to higher food wastage due to shorter shelf life. Balancing recyclability and product preservation is crucial for minimizing overall environmental footprint in packaging.
Future Trends in Resin Technology
Future trends in resin technology highlight a shift towards sustainable barrier resins designed to enhance product protection while reducing environmental impact through biodegradable and recyclable materials. Non-barrier resins continue evolving with improvements in cost-efficiency and performance for applications where moisture and gas protection are less critical. For your packaging needs, selecting advanced barrier resins ensures extended shelf life and optimal preservation in response to increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly solutions.
Barrier Resins vs Non-barrier Resins Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com