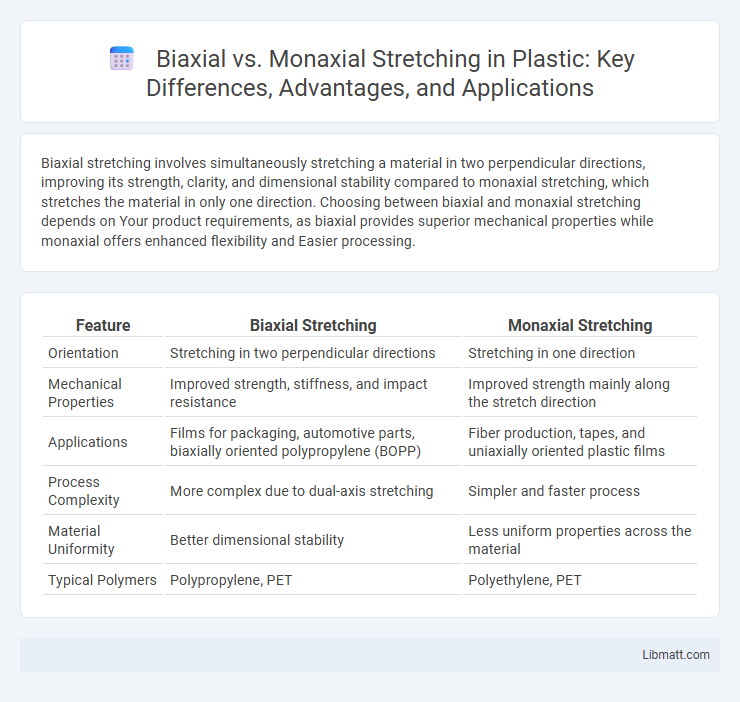
Biaxial stretching involves simultaneously stretching a material in two perpendicular directions, improving its strength, clarity, and dimensional stability compared to monaxial stretching, which stretches the material in only one direction. Choosing between biaxial and monaxial stretching depends on Your product requirements, as biaxial provides superior mechanical properties while monaxial offers enhanced flexibility and Easier processing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biaxial Stretching | Monaxial Stretching |
|---|---|---|
| Orientation | Stretching in two perpendicular directions | Stretching in one direction |
| Mechanical Properties | Improved strength, stiffness, and impact resistance | Improved strength mainly along the stretch direction |
| Applications | Films for packaging, automotive parts, biaxially oriented polypropylene (BOPP) | Fiber production, tapes, and uniaxially oriented plastic films |
| Process Complexity | More complex due to dual-axis stretching | Simpler and faster process |
| Material Uniformity | Better dimensional stability | Less uniform properties across the material |
| Typical Polymers | Polypropylene, PET | Polyethylene, PET |
Introduction to Polymer Film Stretching Techniques
Polymer film stretching techniques, including biaxial and monaxial stretching, play a crucial role in enhancing the mechanical, optical, and barrier properties of films used in packaging, electronics, and industrial applications. Monaxial stretching involves elongating the polymer film in a single direction to improve tensile strength and clarity, while biaxial stretching stretches the film in two perpendicular directions, significantly increasing dimensional stability and isotropic strength. These techniques optimize polymer orientation at the molecular level, resulting in films with superior performance characteristics tailored for specific industrial requirements.
Understanding Monaxial Stretching: Process and Applications
Monaxial stretching involves elongating a material in a single direction, typically used to enhance strength and flexibility along that axis. This process is common in manufacturing polymer films, where controlled stretching improves tensile properties and dimensional stability. Applications include packaging films, textile fibers, and plastic components requiring directional durability and reduced thickness.
Biaxial Stretching Explained: Mechanisms and Benefits
Biaxial stretching involves simultaneously stretching a material in two perpendicular directions, enhancing its mechanical properties such as tensile strength, flexibility, and clarity. This process aligns polymer chains more uniformly compared to monaxial stretching, resulting in improved dimensional stability and resistance to tearing or puncturing. Understanding biaxial stretching mechanisms can help you optimize material performance for applications like packaging films and flexible electronics.
Key Differences Between Biaxial and Monaxial Stretching
Biaxial stretching involves simultaneous stretching in two perpendicular directions, enhancing material strength, uniformity, and clarity, especially in polymers like PET films, whereas monaxial stretching stretches material in only one direction, improving tensile strength and stiffness primarily along that axis. This key distinction affects your choice of processing methods depending on the desired mechanical and optical properties in applications such as packaging, electronics, or textiles. Understanding how biaxial stretching provides multi-directional reinforcement compared to the unidirectional impact of monaxial stretching is crucial for optimizing product performance.
Mechanical Properties Comparison: Strength, Clarity, and Flexibility
Biaxial stretching enhances mechanical properties by improving strength, clarity, and flexibility compared to monaxial stretching due to the uniform orientation of polymer chains in two perpendicular directions. Monaxial stretching typically provides strength and clarity along a single axis but results in lower flexibility and less isotropic mechanical performance. Understanding these differences allows you to select the optimal stretching process for applications requiring balanced strength, optical clarity, and flexible material behavior.
Performance in Packaging Applications
Biaxial stretching enhances the mechanical strength and clarity of packaging films by stretching the material in two perpendicular directions, resulting in improved barrier properties and durability. Monaxial stretching, involving stretching in only one direction, offers increased tensile strength primarily along that axis but may lack the multidirectional resistance needed for high-performance packaging. Your choice between biaxial and monaxial stretching depends on the specific packaging requirements for flexibility, strength, and moisture or gas barrier efficiency.
Cost Implications: Biaxial vs Monaxial Stretching
Biaxial stretching generally incurs higher costs due to more complex machinery and increased energy consumption compared to monaxial stretching, which uses simpler equipment and lower operational expenses. Your budget may benefit from monaxial stretching for applications requiring unidirectional strength, while biaxial stretching delivers superior mechanical properties at a premium price. These cost implications are crucial when selecting the optimal process for manufacturing films or plastic products.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Factors
Biaxial stretching in polymer films improves mechanical strength and barrier properties, enabling thinner materials that reduce raw material use and waste, contributing to lower environmental footprints. Monaxial stretching offers easier recyclability due to uniform molecular orientation but often results in thicker films that increase resource consumption and energy demands. Choosing biaxial stretching processes can optimize sustainability by reducing plastic volume and enhancing durability, supporting circular economy goals in packaging and industrial applications.
Industry Use Cases and Examples
Biaxial stretching enhances material strength and clarity by simultaneously stretching film in two perpendicular directions, making it ideal for packaging industries such as food wrapping and photographic films. Monaxial stretching, which elongates material in a single direction, is commonly used in applications like plastic strapping and labels where directional strength is critical. Your choice between biaxial and monaxial stretching depends on the specific mechanical and optical properties required for the product's industry use case.
Choosing the Right Stretching Process for Your Needs
Selecting between biaxial and monaxial stretching hinges on the desired material properties and application demands. Biaxial stretching enhances dimensional stability and uniform strength by stretching film or sheet in two perpendicular directions, making it ideal for packaging requiring high tensile strength and barrier properties. Monaxial stretching, applied in a single direction, suits applications needing directional strength or flexibility, such as certain plastic films or fibers where controlled elongation and anisotropic mechanical properties are essential.
Biaxial vs Monaxial Stretching Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com