Impact modifiers enhance the toughness and durability of plastics by absorbing and dissipating energy during impact, preventing cracks and fractures. Plasticizers increase the flexibility and workability of polymers by reducing intermolecular forces, making your materials softer and easier to shape.
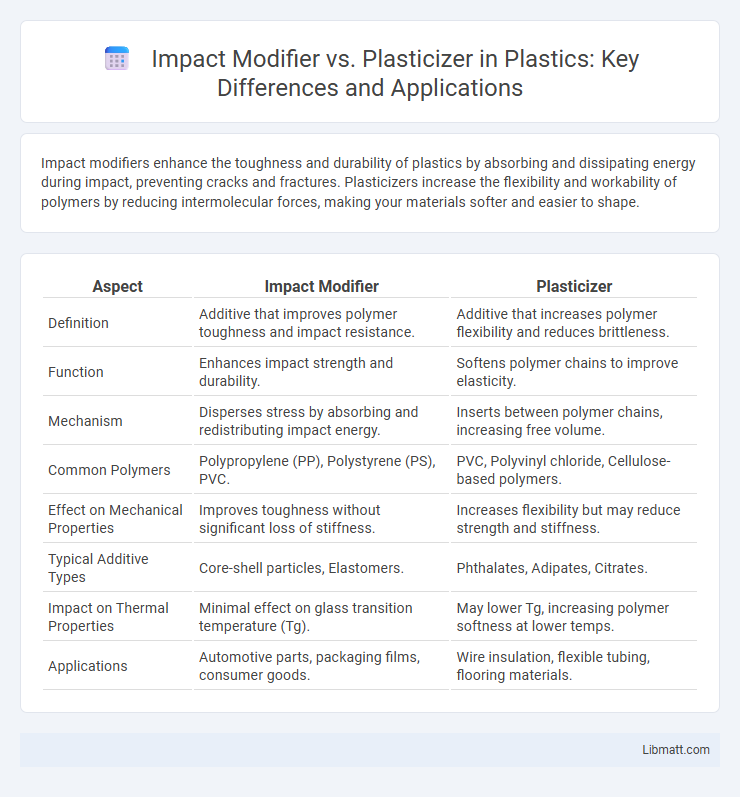
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Impact Modifier | Plasticizer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Additive that improves polymer toughness and impact resistance. | Additive that increases polymer flexibility and reduces brittleness. |
| Function | Enhances impact strength and durability. | Softens polymer chains to improve elasticity. |
| Mechanism | Disperses stress by absorbing and redistributing impact energy. | Inserts between polymer chains, increasing free volume. |
| Common Polymers | Polypropylene (PP), Polystyrene (PS), PVC. | PVC, Polyvinyl chloride, Cellulose-based polymers. |
| Effect on Mechanical Properties | Improves toughness without significant loss of stiffness. | Increases flexibility but may reduce strength and stiffness. |
| Typical Additive Types | Core-shell particles, Elastomers. | Phthalates, Adipates, Citrates. |
| Impact on Thermal Properties | Minimal effect on glass transition temperature (Tg). | May lower Tg, increasing polymer softness at lower temps. |
| Applications | Automotive parts, packaging films, consumer goods. | Wire insulation, flexible tubing, flooring materials. |
Introduction to Polymer Additives
Impact modifiers enhance the toughness and durability of polymers by improving resistance to impact and reducing brittleness, while plasticizers increase polymer flexibility and workability by decreasing the glass transition temperature. Both additives play crucial roles in tailoring polymer properties without altering the base polymer's chemical structure. Understanding the distinct functions of impact modifiers and plasticizers is essential for optimizing performance in applications such as automotive parts, packaging, and flexible films.
Defining Impact Modifiers
Impact modifiers are specialized additives designed to enhance the toughness and flexibility of polymers, reducing brittleness and improving resistance to impact stress. Unlike plasticizers, which primarily increase polymer flexibility by lowering the glass transition temperature, impact modifiers work by absorbing and dissipating energy during sudden shocks. Understanding the role of impact modifiers helps you optimize materials for applications requiring enhanced durability and resistance to mechanical failure.
Understanding Plasticizers
Plasticizers enhance the flexibility and workability of polymers by reducing intermolecular forces within the material, making them softer and easier to process. Impact modifiers improve the toughness of plastics by absorbing and dissipating energy during impact, preventing fractures without significantly altering the polymer's flexibility. Understanding plasticizers helps you select the right additive to increase your product's pliability and durability in various applications.
Key Differences Between Impact Modifiers and Plasticizers
Impact modifiers enhance a polymer's toughness by improving resistance to crack propagation and increasing impact strength without significantly altering its flexibility. Plasticizers primarily increase polymer flexibility and reduce the glass transition temperature (Tg), making materials softer and easier to process. Unlike plasticizers, which act by embedding between polymer chains to increase free volume, impact modifiers function by dispersing elastomeric particles within the polymer matrix to absorb and dissipate impact energy.
Mechanisms of Action: Impact Modifiers vs Plasticizers
Impact modifiers enhance polymer toughness by absorbing and dissipating energy through mechanisms like crazing and shear yielding, which improve resistance to cracking and impact forces. Plasticizers function by embedding themselves between polymer chains, reducing intermolecular forces and increasing chain mobility, resulting in greater flexibility and softness. Understanding these distinct mechanisms helps optimize your material formulation for desired mechanical properties and performance.
Typical Applications in Polymer Industries
Impact modifiers are primarily used in polymer industries to enhance toughness and resistance to impact in applications such as automotive parts, packaging films, and consumer goods. Plasticizers improve flexibility and processability of polymers, making them essential in producing PVC products like cables, flooring, and medical devices. Your choice between impact modifiers and plasticizers depends on whether you need increased durability or enhanced flexibility in the final product.
Effects on Mechanical Properties
Impact modifiers enhance the toughness and impact resistance of plastics by improving energy absorption during deformation without significantly reducing stiffness. Plasticizers increase polymer flexibility and elongation at break by reducing intermolecular forces, often lowering tensile strength and stiffness. Their differing mechanisms result in impact modifiers being preferred for applications requiring improved durability, while plasticizers suit needs for increased flexibility and softness.
Influence on Polymer Processing
Impact modifiers enhance the toughness of polymers by improving resistance to cracking and impact, often requiring adjustments in processing temperatures to ensure proper dispersion. Plasticizers increase polymer flexibility and reduce glass transition temperature, allowing easier flow and lower processing energy demands during extrusion or molding. Your choice between impact modifiers and plasticizers significantly influences polymer viscosity, melt flow rate, and overall processability for optimized manufacturing outcomes.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Impact modifiers and plasticizers differ significantly in environmental and health considerations; impact modifiers are typically more stable and less prone to leaching, reducing potential toxic exposure. Plasticizers, especially phthalate-based types, can migrate into the environment and human bodies, raising concerns about endocrine disruption and long-term health effects. Selecting the right additive for Your applications involves weighing durability against potential ecological and physiological impacts.
Future Trends in Polymer Additive Technology
Impact modifiers and plasticizers play crucial roles in enhancing polymer properties, with future trends aimed at developing bio-based and sustainable additives to reduce environmental impact. Advanced nanotechnology integration is expected to create multifunctional modifiers that improve mechanical strength and flexibility simultaneously. Your polymer formulations will benefit from smarter additives that enable tailored performance and easier recyclability in next-generation materials.
Impact modifier vs plasticizer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com