Fast cycling resins enable quicker adsorption and desorption processes, reducing overall cycle times and improving throughput in separation systems. Slow cycling resins offer higher capacity and selectivity, making them ideal for applications requiring extended contact times and precise purification.
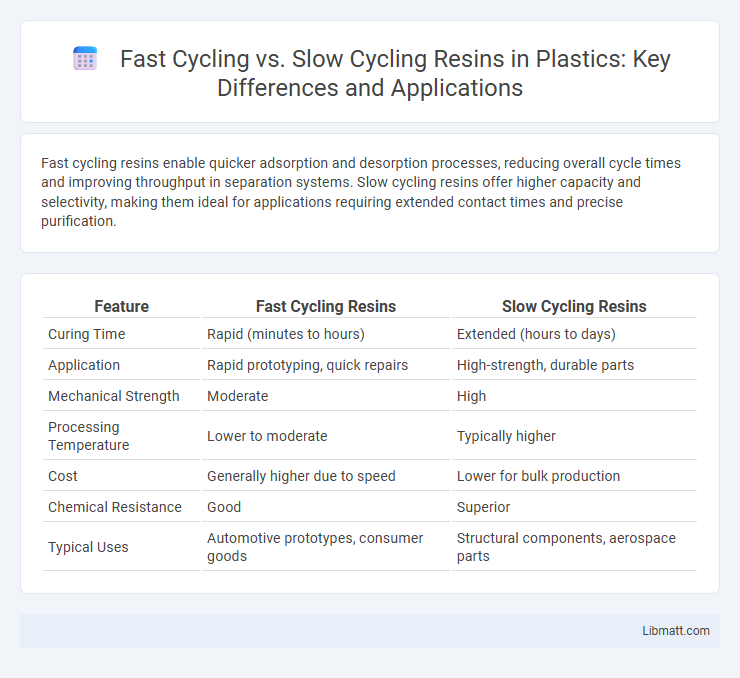
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fast Cycling Resins | Slow Cycling Resins |
|---|---|---|
| Curing Time | Rapid (minutes to hours) | Extended (hours to days) |
| Application | Rapid prototyping, quick repairs | High-strength, durable parts |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | High |
| Processing Temperature | Lower to moderate | Typically higher |
| Cost | Generally higher due to speed | Lower for bulk production |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Superior |
| Typical Uses | Automotive prototypes, consumer goods | Structural components, aerospace parts |
Introduction to Fast and Slow Cycling Resins
Fast cycling resins offer rapid ion exchange capacity regeneration, making them ideal for applications requiring frequent and quick turnaround, such as water softening in industrial processes. Slow cycling resins regenerate more gradually, providing prolonged service life and stable performance in systems with lower demand and extended treatment cycles. Selecting between fast and slow cycling resins depends on operational needs, regeneration frequency, and efficiency targets within water treatment systems.
Defining Fast Cycling Resins
Fast cycling resins are specialized ion exchange materials designed to achieve rapid regeneration and shorter cycle times compared to slow cycling resins. These resins enhance system efficiency by delivering quicker ion exchange capacity restoration, minimizing downtime, and reducing chemical consumption. Your water treatment processes benefit from increased throughput and improved operational performance when using fast cycling resins.
Defining Slow Cycling Resins
Slow cycling resins are ion exchange materials designed to operate efficiently in processes with longer regeneration intervals and lower regeneration frequencies, enhancing resin longevity and reducing operational costs. These resins exhibit high capacity, improved resistance to fouling and chemical degradation, making them ideal for applications requiring consistent water quality over extended periods. Your choice of slow cycling resins can optimize system performance by minimizing downtime and maintenance needs compared to fast cycling resins.
Key Performance Differences
Fast cycling resins demonstrate superior adsorption kinetics, enabling rapid adsorption and desorption cycles, which significantly reduce process time and increase throughput in applications like water treatment and chromatography. Slow cycling resins exhibit higher selectivity and capacity for target molecules due to prolonged contact time, making them ideal for processes requiring deeper purification or separation. The choice between fast and slow cycling resins hinges on balancing operational speed and adsorption efficiency, directly impacting process optimization and overall system performance.
Impact on Production Efficiency
Fast cycling resins significantly enhance production efficiency by reducing cycle times and increasing throughput in manufacturing processes. Slow cycling resins, while offering improved surface finish and mechanical properties, lead to longer production cycles that may reduce overall output. Selecting the appropriate resin depends on balancing the trade-off between speed and product quality to optimize operational efficiency.
Material Properties and Applications
Fast cycling resins exhibit rapid curing times and enhanced thermal stability, making them ideal for high-throughput manufacturing processes such as automotive parts and electronics encapsulation. Slow cycling resins provide superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance, suited for applications requiring long-term durability like aerospace composites and structural adhesives. The choice between fast and slow cycling resins depends on balancing processing speed with end-use performance requirements.
Cost Implications and ROI
Fast cycling resins offer quicker regeneration times, reducing downtime and increasing throughput, which can lead to higher operational efficiency but often come at a higher upfront cost compared to slow cycling resins. Slow cycling resins generally have lower initial costs and longer cycle durations, which may reduce frequent regeneration expenses but can limit overall process speed and capacity. Evaluating the return on investment (ROI) requires balancing faster production rates and increased resin lifespan against initial expenditure, with fast cycling resins typically delivering superior ROI in high-demand industrial applications.
Energy Consumption and Sustainability
Fast cycling resins reduce energy consumption by enabling shorter processing times and lower temperature requirements, leading to decreased overall carbon footprints in industrial applications. Slow cycling resins, while more energy-intensive due to prolonged curing cycles, can offer enhanced durability and lower material waste, promoting long-term sustainability. Selecting the appropriate resin type depends on balancing immediate energy savings with lifecycle environmental impacts to optimize sustainable manufacturing practices.
Common Industries and Use Cases
Fast cycling resins are commonly used in industries requiring rapid production and frequent material changes, such as packaging, automotive, and consumer electronics manufacturing. Slow cycling resins find their place in applications needing high durability and precision, including aerospace, medical devices, and high-performance components. Your choice depends on production speed demands and the durability or detail required for the end product.
Choosing the Right Resin for Your Process
Fast cycling resins offer quicker regeneration times and higher throughput, making them ideal for processes requiring frequent resin turnover and rapid ion exchange. Slow cycling resins provide greater capacity and longer resin life, suitable for applications where process stability and resin durability are priorities. Choosing the right resin for your process depends on balancing throughput needs with resin longevity to optimize efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Fast cycling vs slow cycling resins Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com