Polycarbonate resin offers superior impact resistance and clarity, making it ideal for applications requiring high durability and transparency, while PC-ABS combines the toughness of polycarbonate with the flexibility of ABS, providing enhanced mechanical strength and ease of processing. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize optical properties and toughness or a balanced blend of strength and flexibility for your projects.
Table of Comparison
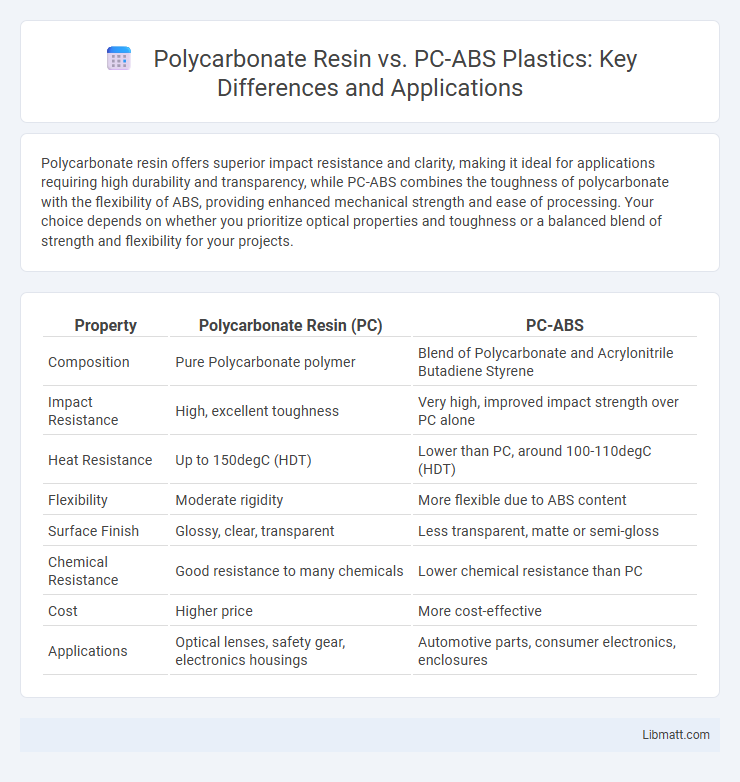
| Property | Polycarbonate Resin (PC) | PC-ABS |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure Polycarbonate polymer | Blend of Polycarbonate and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene |
| Impact Resistance | High, excellent toughness | Very high, improved impact strength over PC alone |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 150degC (HDT) | Lower than PC, around 100-110degC (HDT) |
| Flexibility | Moderate rigidity | More flexible due to ABS content |
| Surface Finish | Glossy, clear, transparent | Less transparent, matte or semi-gloss |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to many chemicals | Lower chemical resistance than PC |
| Cost | Higher price | More cost-effective |
| Applications | Optical lenses, safety gear, electronics housings | Automotive parts, consumer electronics, enclosures |
Introduction to Polycarbonate Resin and PC-ABS
Polycarbonate resin is a highly durable thermoplastic polymer known for its exceptional impact resistance, optical clarity, and thermal stability, making it ideal for applications in automotive, electronics, and protective gear. PC-ABS is a blend of polycarbonate and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, combining the strength and heat resistance of polycarbonate with the flexibility and processability of ABS, widely used in consumer electronics, automotive parts, and enclosures. Both materials offer distinct advantages in mechanical properties and thermal performance, influencing their selection based on specific application requirements.
Composition and Material Structure
Polycarbonate resin is a thermoplastic polymer composed mainly of bisphenol A and carbonate groups, offering high impact resistance and transparency. PC-ABS is a blend of polycarbonate and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, combining the toughness and heat resistance of polycarbonate with the flexibility and processability of ABS. The material structure of polycarbonate is amorphous with a rigid backbone, whereas PC-ABS features a heterogeneous microstructure that balances rigidity and ductility for enhanced mechanical performance.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polycarbonate resin exhibits superior impact resistance, high tensile strength, and excellent dimensional stability compared to PC-ABS, which combines polycarbonate with acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene to enhance processability and reduce cost. PC-ABS offers improved flexibility and better resistance to chemical stress but generally falls short in heat resistance and stiffness when compared to pure polycarbonate. Mechanical properties such as tensile strength typically range from 60 to 70 MPa for polycarbonate resin, whereas PC-ABS ranges between 50 to 60 MPa, highlighting polycarbonate's dominance in structural applications requiring durability.
Thermal Resistance and Performance
Polycarbonate resin offers superior thermal resistance, withstanding continuous use temperatures up to 130degC, which enhances its performance in high-heat environments. PC-ABS blends combine the toughness of polycarbonate with the flexibility and chemical resistance of ABS, providing moderate thermal resistance typically around 105degC. Understanding these differences ensures your selection meets specific application requirements for durability and heat endurance.
Chemical Resistance Differences
Polycarbonate resin exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to PC-ABS, particularly against oils, greases, and dilute acids, making it ideal for applications involving exposure to harsh chemicals. PC-ABS blends tend to absorb more moisture and are less resistant to solvents, which can lead to degradation in aggressive chemical environments. Understanding these differences helps you select the appropriate material for durability and longevity in chemically demanding conditions.
Impact Strength and Durability
Polycarbonate resin exhibits superior impact strength compared to PC-ABS, making it highly resistant to sudden shocks and fractures in demanding applications. PC-ABS combines the toughness of PC with the flexibility of ABS, offering balanced durability with enhanced chemical resistance and improved surface finish. For applications requiring maximum impact resistance and long-term durability, pure polycarbonate resin is preferred, while PC-ABS is ideal for environments needing a blend of strength and aesthetic quality.
Ease of Manufacturing and Processing
Polycarbonate Resin offers excellent ease of manufacturing with high melt flow, allowing for precise injection molding and rapid cycle times. PC-ABS blends enhance processing flexibility by combining the toughness of polycarbonate with the chemical resistance and cost-effectiveness of ABS, though they may require stricter temperature control. Both materials support complex geometries, but Polycarbonate Resin generally provides superior clarity and toughness, making it preferred for applications requiring high-quality surface finishes.
Typical Applications and Industries
Polycarbonate resin is widely used in automotive parts, electronic housings, and optical lenses, valued for its high impact resistance and transparency; key industries include automotive, electronics, and consumer goods. PC-ABS blends combine the strength and heat resistance of polycarbonate with the flexibility of ABS, making them ideal for durable enclosures, connectors, and consumer appliances within electronics, telecommunications, and automotive sectors. Both materials serve critical roles in manufacturing, with polycarbonate favored for clarity and toughness, while PC-ABS excels in applications requiring balanced mechanical performance and processability.
Cost Considerations
Polycarbonate resin generally offers high impact resistance and clarity but comes at a higher cost compared to PC-ABS blends, which combine polycarbonate with acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene to reduce expenses while maintaining durability. PC-ABS is often chosen for applications requiring a balance between cost-efficiency and mechanical strength, making it ideal for consumer electronics and automotive parts. When budgeting for your project, selecting PC-ABS can lower material costs without significantly compromising performance.
Choosing the Right Material: Polycarbonate Resin or PC-ABS
Polycarbonate resin offers superior impact resistance, clarity, and heat resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and transparency. PC-ABS blends polycarbonate with acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, enhancing chemical resistance and improving processability while maintaining good mechanical properties. Your choice depends on balancing performance needs: opt for polycarbonate resin when clarity and toughness are critical, or PC-ABS for cost-effectiveness and versatile molding requirements.
Polycarbonate Resin vs PC-ABS Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com